3. FOOD ChEMISTRy & bIOTEChNOLOGy 3.1. Lectures
3. FOOD ChEMISTRy & bIOTEChNOLOGy 3.1. Lectures
3. FOOD ChEMISTRy & bIOTEChNOLOGy 3.1. Lectures
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chem. Listy, 102, s265–s1311 (2008) Food Chemistry & Biotechnology<br />
Experimental<br />
M a t e r i a l s a n d M e t h o d s<br />
Standards of mycotoxins nivalenol (nIV), deoxynivalenol<br />
(DOn), deoxynivalenole-3-glucoside (DOn-3-Glc),<br />
3-acetyldeoxynivalenol (3-ADOn), 15-acetyldeoxynivalenol<br />
(15-ADOn), fusarenone-X (fus-X), T-2 toxin (T-2),<br />
HT-2 toxin (HT-2) and zearalenone (ZEA) were purchased<br />
from Biopure (Tulln, Austria). A Synergi Hydro RP column<br />
(Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA), a liquid chromatograph<br />
HP1100 Binary Series LC system (Agilent Technologies,<br />
Palo Alto, CA, USA) coupled to an ion trap mass analyser<br />
LCQ Deca (Finnigan, San Jose, CA, USA) were employed<br />
for LC separation and MS/MS detection. For GC–ECD<br />
method, a gas chromatograf HP 5890 Series II with an<br />
electron capture detector ( 63 ni) and a capillary column HP-<br />
35 (30 m × 0,25 mm I.D. × 0,25 μm phase) with (35%-fenyl)methylpolysiloxan<br />
stationary phase (Agilent Technologies,<br />
Palo Alto, CA, USA) were used. For ELISA analysis, two<br />
commercial available DOn kits, i.e. Ridascreen ® DOn (R-<br />
Biopharm, Darmstadt, Germany) and AgraQuant ® DOn<br />
Assay 0.25/5.0 Test Kit (Romer Labs, Tulln, Austria), were<br />
purchased.<br />
gC-eCD method: An amount of 10 g of homogenised<br />
ground sample was extracted by shaking with 100 mL of an<br />
acetonitrile–water mixture (84 : 16, v/v) for one hour and<br />
extract was filtered (Filtrak no. 390, VEB Freiberger, Berlin,<br />
Germany). The crude extract was passed through MycoSep<br />
#225 and four millilitres of cleaned extract was evaporated.<br />
Residue after evaporation was redissolved in methanol,<br />
transferred into the derivatisation vial, and after methanol<br />
evaporation using a gentle stream of nitrogen, derivatisation<br />
for 20 min at 60 °C using 100 μl trifluoracetanhydride with<br />
addition of 10 mg naHCO 3 was performed. Further, 500 μl<br />
of isooctane, 1 ml of deionised water and 0.5 g of anhydrous<br />
sodium sulphate was added followed by removing of 300 µl<br />
of the organic layer and addition of 200 μl of isooctane to the<br />
vial for GC–ECD analysis.<br />
lC-Ms/Ms method: An amount of 12.5 g of homogenised<br />
ground sample was extracted by shaking with 50 mL<br />
of an acetonitrile–water mixture (84 : 16, v/v) for one hour<br />
and the crude extract was filtered (Filtrak no. 390, VEB Freiberger,<br />
Berlin, Germany). Eight millilitres of filtered extract<br />
were passed through the MycoSep #226 column and four<br />
millilitres of filtered extract were evaporated to dryness and<br />
dissolved in 1 mL of a water–methanol mixture (50 : 50, v/v).<br />
Finally, the sample was passed through a 0.2 µm microfilter<br />
(Alltech, Deerfield, IL, USA) prior to analysis.<br />
elisA: In case of immunochemical assays, both sample<br />
preparation and the ELISA analysis itself were carried<br />
out strictly according to manufacturer recommendations. An<br />
amount of 20 g of ground sample was extracted with 100 ml<br />
of deionised water and vigorously shaken for 3 minutes. Further,<br />
the extract was filtered and an appropriate aliquot was<br />
placed into the microwell.<br />
s572<br />
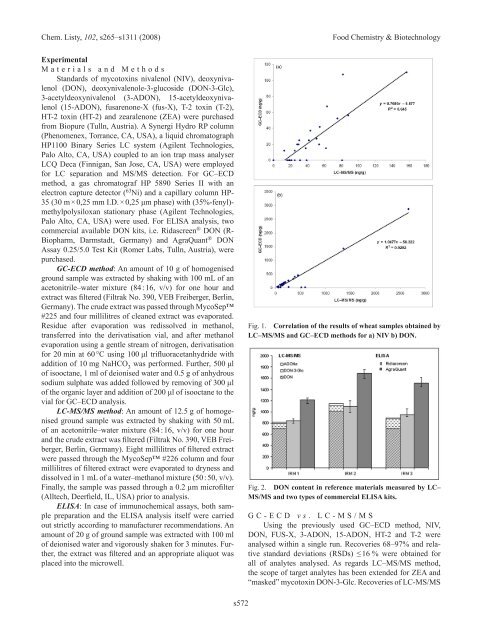
Fig. 1. Correlation of the results of wheat samples obtained by<br />
LC–MS/MS and GC–ECD methods for a) NIV b) DON.<br />
Fig. 2. DON content in reference materials measured by LC–<br />
MS/MS and two types of commercial ELISA kits.<br />
G C - E C D v s . L C - M S / M S<br />
Using the previously used GC–ECD method, nIV,<br />
DOn, FUS-X, 3-ADOn, 15-ADOn, HT-2 and T-2 were<br />
analysed within a single run. Recoveries 68–97% and relative<br />
standard deviations (RSDs) ≤ 16 % were obtained for<br />
all of analytes analysed. As regards LC–MS/MS method,<br />
the scope of target analytes has been extended for ZEA and<br />
“masked” mycotoxin DOn-3-Glc. Recoveries of LC-MS/MS