IBK Jahresbericht 2004-2006 - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion ...
IBK Jahresbericht 2004-2006 - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion ...
IBK Jahresbericht 2004-2006 - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion ...
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
FORSCHUNG<br />
Zustandsindikatoren <strong>für</strong> die Inspektions<strong>und</strong><br />
Unterhaltsplanung<br />
Projektleitung: Prof. Dr. M.H. Faber<br />
Mitarbeiterin: V. Malioka<br />
Projektpartner: Schweizerischer Nationalfonds,<br />
Bern.<br />
Die Auswahl von kosteneffizienten, präventiven<br />
<strong>und</strong> notwendigen Unterhaltsmassnahmen basiert in<br />
der Regel auf Zustandsbeurteilungen, die aufgr<strong>und</strong><br />
von Inspektionen, Tests <strong>und</strong> Beobachtungen gewonnen<br />
werden. Solche Zustandsbeurteilungen unterliegen<br />
grossen Unsicherheiten <strong>und</strong> sind im Allgemeinen<br />
nur Indikatoren über den Zustand der <strong>Konstruktion</strong>.<br />
Schädigung von Betonkonstruktionen<br />
treten in verschiedenen zeitlichen Phasen auf <strong>und</strong><br />
führen daher zu unterschiedlichen Konsequenzen.<br />
Diese Phasen können mittels Inspektionen beobachtet<br />
<strong>und</strong> unterschieden werden. Die Kosteneffizienz<br />
des Unterhalts <strong>und</strong> der Reparaturen ist davon<br />
abhängig, wann <strong>und</strong> wie diese Massnahmen durchgeführt<br />
wurden.<br />
Diese Arbeit konzentriert sich auf die Anwendung<br />
des Bayes’schen Ansatzes zur Qualitätskontrolle<br />
<strong>und</strong> zur Inspektions- <strong>und</strong> Unterhaltsplanung<br />
von Betonkonstruktionen basierend auf Zustandsindikatoren.<br />
Bis heute werden vorwiegend vier zerstörungsfreie<br />
Inspektionsmethoden angewandt: die<br />
Potenzialmessungen, durch Macrocell-Systeme, die<br />
Messung der Betonüberdeckung <strong>und</strong> die Bestimmung<br />
der Karbonatisierungstiefe mittels Phenolphthalein.<br />
Zwei Eigenschaften charakterisieren<br />
die Bedeutung <strong>und</strong> die Qualität des Indikators. Erstens<br />
die Stärke des Indikators, d.h. die Wahrscheinlichkeit,<br />
dass die Schädigung des Bauteils erreicht<br />
ist, falls eine Inspektion eine positive oder negative<br />
Indikation angibt. Zweitens die Likelihood des<br />
Indikators, d.h. die Wahrscheinlichkeit, dass eine<br />
Inspektion eine positive oder negative Indikation<br />
angibt, gegeben dass das Betonbauwerk in einem<br />
bestimmten Zustand ist [1].<br />
Condition Indicators for Inspection and<br />
Maintenance Planning<br />
The selection of cost efficient preventive and essential<br />
maintenance measures is normally based on<br />
condition assessments achieved through inspections,<br />
tests and monitoring. Such condition assessments<br />
are subject to significant uncertainties and in<br />
general at best provide indications rather than observations<br />
about the structure’s condition. Deterioration<br />
of concrete structures occur in a number of<br />
phases, leading to varying consequences. These<br />
phases can be observed and differentiated by means<br />
of inspections. Furthermore, the cost efficiency of<br />
maintenance and repair activities is highly dependent<br />
on when and how they are implemented.<br />
This research project focuses on the use of a<br />
Bayesian approach in quality control, inspection<br />
and maintenance planning of concrete structures<br />
based on condition indicators. Predominantly, four<br />
NDE methods have been applied up until today:<br />
half-cell potential, macrocell systems, concrete<br />
cover depth and phenolphthalein measurements.<br />
Two features characterise the relevance and the quality<br />
of an indicator. Firstly, the strength of the indicator,<br />
i.e. the probability of the (adverse) structural<br />
state of interest conditional upon a positive or negative<br />
indication. Secondly, the likelihood of the indicator,<br />
i.e. the probability of observing a positive or<br />
negative indication conditional on the (adverse)<br />
structural state of interest [1].<br />
[1] Malioka, V. and Faber, M.H. (2003). Condition indicators<br />
for inspection and maintenance planning. Proceedings<br />
to the 9th International Conference on Applications<br />
of Statistics and Probability in Civil Engineering<br />
ICASP9, Volume 2, pp. 1101-1108, San Francisco, USA,<br />
July 6-9, 2003.<br />
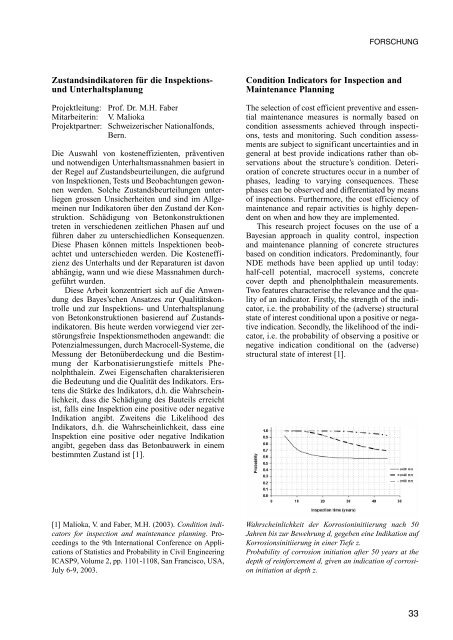
Wahrscheinlichkeit der Korrosioninitiierung nach 50<br />
Jahren bis zur Bewehrung d, gegeben eine Indikation auf<br />
Korrosionsinitiierung in einer Tiefe z.<br />
Probability of corrosion initiation after 50 years at the<br />
depth of reinforcement d, given an indication of corrosion<br />
initiation at depth z.<br />
33