IBK Jahresbericht 2004-2006 - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion ...
IBK Jahresbericht 2004-2006 - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion ...
IBK Jahresbericht 2004-2006 - Institut für Baustatik und Konstruktion ...
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
FORSCHUNG<br />
Beulverhalten von Stahlquerschnitten bei<br />
Brandeinwirkung<br />
Projektleitung:<br />
Mitarbeiter:<br />
Prof. Dr. M. Fontana<br />
M. Knobloch.<br />
Die Brandbemessung erlangt zunehmend Bedeutung<br />
<strong>für</strong> die sichere <strong>und</strong> wirtschaftliche <strong>Konstruktion</strong><br />
von Stahlbauten. Neben brandgerechter konstruktiver<br />
Ausbildung müssen realitätsnahe Bemessungsmodelle<br />
<strong>für</strong> die sichere <strong>und</strong> wirtschaftliche<br />
Bemessung von Stahlquerschnitten im Brandfall,<br />
insbesondere <strong>für</strong> Stabilitätsfälle geschaffen werden.<br />
Ungeschützte dünnwandige Stahlbauteile besitzen<br />
eine hohe Wärmeleitfähigkeit <strong>und</strong> eine geringe<br />
Massigkeit <strong>und</strong> erwärmen sich im Brandfall<br />
schnell. Festigkeit <strong>und</strong> Steifigkeit des Stahls nehmen<br />
bei erhöhten Temperaturen deutlich ab. Das<br />
Spannungs-Dehnungsverhalten wird nichtlinear. Im<br />
Brandfall muss daher der traglastmindernde Einfluss<br />
des Beulens <strong>für</strong> mehr Querschnitte berücksichtigt<br />
werden als bei Normaltemperatur, weil<br />
Traglaststeigerungen infolge von Plastifizierungen<br />
erst bei großen Dehnungen erreicht werden.<br />
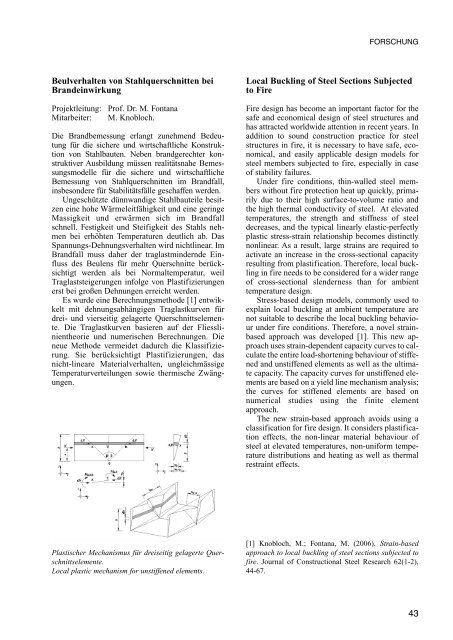
Es wurde eine Berechnungsmethode [1] entwikkelt<br />
mit dehnungsabhängigen Traglastkurven <strong>für</strong><br />
drei- <strong>und</strong> vierseitig gelagerte Querschnittselemente.<br />
Die Traglastkurven basieren auf der Fliesslinientheorie<br />
<strong>und</strong> numerischen Berechnungen. Die<br />
neue Methode vermeidet dadurch die Klassifizierung.<br />
Sie berücksichtigt Plastifizierungen, das<br />
nicht-lineare Materialverhalten, ungleichmässige<br />
Temperaturverteilungen sowie thermische Zwängungen.<br />
Local Buckling of Steel Sections Subjected<br />
to Fire<br />
Fire design has become an important factor for the<br />
safe and economical design of steel structures and<br />
has attracted worldwide attention in recent years. In<br />
addition to so<strong>und</strong> construction practice for steel<br />
structures in fire, it is necessary to have safe, economical,<br />
and easily applicable design models for<br />
steel members subjected to fire, especially in case<br />
of stability failures.<br />
Under fire conditions, thin-walled steel members<br />
without fire protection heat up quickly, primarily<br />
due to their high surface-to-volume ratio and<br />
the high thermal conductivity of steel. At elevated<br />
temperatures, the strength and stiffness of steel<br />
decreases, and the typical linearly elastic-perfectly<br />
plastic stress-strain relationship becomes distinctly<br />
nonlinear. As a result, large strains are required to<br />
activate an increase in the cross-sectional capacity<br />
resulting from plastification. Therefore, local buckling<br />
in fire needs to be considered for a wider range<br />
of cross-sectional slenderness than for ambient<br />
temperature design.<br />
Stress-based design models, commonly used to<br />
explain local buckling at ambient temperature are<br />
not suitable to describe the local buckling behaviour<br />
<strong>und</strong>er fire conditions. Therefore, a novel strainbased<br />
approach was developed [1]. This new approach<br />
uses strain-dependent capacity curves to calculate<br />
the entire load-shortening behaviour of stiffened<br />
and unstiffened elements as well as the ultimate<br />
capacity. The capacity curves for unstiffened elements<br />
are based on a yield line mechanism analysis;<br />
the curves for stiffened elements are based on<br />
numerical studies using the finite element<br />
approach.<br />
The new strain-based approach avoids using a<br />
classification for fire design. It considers plastification<br />
effects, the non-linear material behaviour of<br />
steel at elevated temperatures, non-uniform temperature<br />
distributions and heating as well as thermal<br />
restraint effects.<br />
Plastischer Mechanismus <strong>für</strong> dreiseitig gelagerte Querschnittselemente.<br />
Local plastic mechanism for unstiffened elements.<br />
[1] Knobloch, M.; Fontana, M. (<strong>2006</strong>). Strain-based<br />
approach to local buckling of steel sections subjected to<br />
fire. Journal of Constructional Steel Research 62(1-2),<br />
44-67.<br />
43