Pre-Phase A Report - Lisa - Nasa
Pre-Phase A Report - Lisa - Nasa
Pre-Phase A Report - Lisa - Nasa
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
130 Chapter 5 Payload Design<br />
Once a particular diameter of the primary mirror is given, the intensity at the beam axis<br />
in the far field is highest when the Gaussian diameter of the outgoing beam equals the<br />
diameter of the primary mirror. The beam is then truncated at the 1/e2 contour line of its<br />
intensity. In this case the power picked up at the far spacecraft is given by Eq. (3.1). For<br />
reasons of cost and weight a diameter of only 30 cm for the primary mirrors was chosen;<br />
it is adequate for the envisaged sensitivity level.<br />
Coupling of changes in beam orientation to the interferometer signal is minimal when the<br />
center of curvature of the wavefront at the receiving spacecraft sits inside the emitting<br />
spacecraft. For the wavefront of a laser beam in the far field the center of curvature<br />
coincides with the focus of the beam. The outgoing wavefront has therefore to be flat.<br />
The final quality of the plane wavefront leaving the telescope is specified as λ/10 .<br />
5.8.2 Telescope concept<br />
The telescope widens the diameter of the beam from a few mm to 30 cm. Since the<br />
space available is very limited, spherical optics would cause huge aberrations. Therefore<br />
conical sections are used for the mirror surfaces instead of spherical ones. In this case<br />
the imaging properties for point sources can in principle be perfect, if the focus of the<br />
beam is positioned exactly at the focus of the particular mirror. This is the idea behind<br />
the original Cassegrain telescope, where the primary is chosen to be a paraboloid and<br />
the secondary a hyperboloid. Unfortunately, the tolerances for misalignments and the<br />
usable field of view are very small in this case. There are several improvements over the<br />
original Cassegrain, e.g. the Ritchey-Chretien telescope, minimising the first three Seidel<br />
aberrations.<br />
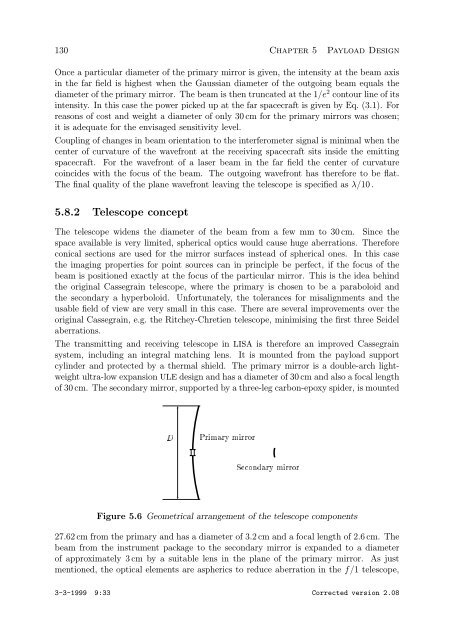
The transmitting and receiving telescope in LISA is therefore an improved Cassegrain<br />
system, including an integral matching lens. It is mounted from the payload support<br />
cylinder and protected by a thermal shield. The primary mirror is a double-arch lightweight<br />
ultra-low expansion ULE design and has a diameter of 30 cm and also a focal length<br />
of 30 cm. The secondary mirror, supported by a three-leg carbon-epoxy spider, is mounted<br />
D Primary mirror<br />
Secondary mirror<br />
Figure 5.6 Geometrical arrangement of the telescope components<br />
27.62 cm from the primary and has a diameter of 3.2 cm and a focal length of 2.6 cm. The<br />
beam from the instrument package to the secondary mirror is expanded to a diameter<br />
of approximately 3 cm by a suitable lens in the plane of the primary mirror. As just<br />
mentioned, the optical elements are aspherics to reduce aberration in the f/1 telescope,<br />
3-3-1999 9:33 Corrected version 2.08