- Page 1 and 2:
click for previous page iv Table of
- Page 3 and 4:
vi Page Brachaeluridae . . . . . .
- Page 5 and 6:
688 Cephalopods Introduction and Ge
- Page 7 and 8:
690 Cephalopods Principal PRINCIPAL
- Page 9 and 10:
692 Cephalopods To examine the cont
- Page 11 and 12:
694 Cephalopods Chitin(ous) - a hor
- Page 13 and 14:
696 Cephalopods Ink sac - the struc
- Page 15 and 16:
698 Cephalopods Spermatophore groov
- Page 17 and 18:
700 Cephalopods 6a. Fins small and
- Page 19 and 20:
702 Cephalopods 15a. Surface of man
- Page 21 and 22:
704 Cephalopods 23a. Arms short, ty
- Page 23 and 24:
706 Cephalopods Order SEPIIDA - Cut
- Page 25 and 26:
708 Cephalopods List of Familes LIS
- Page 27 and 28:
710 Cephalopods Key to the species
- Page 29 and 30:
712 Cephalopods Sepiolidae SEPIOLID
- Page 31 and 32:
714 Cephalopods Eupryma morsei (Ver
- Page 33 and 34:
716 Cephalopods Rossia bipapillata
- Page 35 and 36:
718 Cephalopods Sepiolina nipponens
- Page 37 and 38:
720 Cephalopods Sepiadarium kochii
- Page 39 and 40:
722 Cephalopods Spirulidae SPIRULID
- Page 41 and 42:
724 Cephalopods anterior last locul
- Page 43 and 44:
726 Cephalopods it may be necessary
- Page 45 and 46:
728 Cephalopods 4a. Five to 6 wine-
- Page 47 and 48:
730 Cephalopods 11a. Tentacular clu
- Page 49 and 50:
732 Cephalopods 23a. Hectocotylus w
- Page 51 and 52:
734 Cephalopods List of species occ
- Page 53 and 54:
736 Cephalopods Sepiidae Sepia acul
- Page 55 and 56:
click for previous page 738 Cephalo
- Page 57 and 58:
740 Cephalopods Sepia brevimana Ste
- Page 59 and 60:
742 Cephalopods Sepia esculenta Hoy
- Page 61 and 62:
744 Cephalopods Sepia latimanus Quo
- Page 63 and 64:
746 Cephalopods Sepia opipara (Ired
- Page 65 and 66:
748 Cephalopods Sepia pharaonis Ehr
- Page 67 and 68:
click for previous page 750 Cephalo
- Page 69 and 70:
752 Cephalopods Sepia rozella (Ired
- Page 71 and 72:
754 Cephalopods Sepia stellifera Ho
- Page 73 and 74:
756 Cephalopods Sepiella inermis F
- Page 75 and 76:
758 Cephalopods Sepia bartletti (Ir
- Page 77 and 78:
760 Cephalopods Sepia mestus Gray,
- Page 79 and 80:
762 Cephalopods Sepia vossi Khromov
- Page 81 and 82:
click for previous page 764 Cephalo
- Page 83 and 84:
766 Cephalopods Loligo reesi (Voss,
- Page 85 and 86:
768 Cephalopods 6a. Gladius relativ
- Page 87 and 88:
770 Cephalopods ventral view Fig. 1
- Page 89 and 90:
772 Cephalopods Nipponololigo beka
- Page 91 and 92:
774 Cephalopods “Photololigo chin
- Page 93 and 94:
776 Cephalopods “Photololigo edul
- Page 95 and 96:
778 Cephalopods “Sepioteuthis les
- Page 97 and 98:
780 Cephalopods Loliolus affinis St
- Page 99 and 100:
782 Cephalopods Similar families oc
- Page 101 and 102:
784 Cephalopods Onychoteuthidae ONY
- Page 103 and 104:
786 Cephalopods List of species occ
- Page 105 and 106:
click for previous page 788 Cephalo
- Page 107 and 108:
790 Cephalopods 4a. Mantle very sle
- Page 109 and 110:
792 Cephalopods Nototodarus hawaiie
- Page 111 and 112:
794 Cephalopods Sthenoteuthis ouala
- Page 113 and 114:
796 Cephalopods Todaropsis eblanae
- Page 115 and 116:
798 Cephalopods Chiroteuthidae CHIR
- Page 117 and 118:
click for previous page 800 Cephalo
- Page 119 and 120:
802 Cephalopods Ocythoidae (suborde
- Page 121 and 122:
804 Cephalopods 5a. Distinctly elon
- Page 123 and 124:
806 Cephalopods 14a. Small, elongat
- Page 125 and 126:
808 Cephalopods 22a. Pale longitudi
- Page 127 and 128:
810 Cephalopods Cistopus indicus (R
- Page 129 and 130:
812 Cephalopods Octopus cyanea Gray
- Page 131 and 132:
814 Cephalopods Octopus cf. luteus
- Page 133 and 134:
816 Cephalopods Octopus nocturnus N
- Page 135 and 136:
818 Cephalopods Octopus tetricus Go
- Page 137 and 138:
820 Cephalopods Ameloctopus litoral
- Page 139 and 140:
822 Cephalopods Octopus abaculus No
- Page 141 and 142:
824 Cephalopods Octopus australis H
- Page 143 and 144:
826 Cephalopods Octopus polyzenia G
- Page 145 and 146:
828 Stomatopods Technical Terms and
- Page 147 and 148:
830 Stomatopods propodus of HARPIOS
- Page 149 and 150:
832 Stomatopods ODONTODACTYLIDAE Od
- Page 151 and 152:
834 Stomatopods Odontodactylus scyl
- Page 153 and 154:
836 Stomatopods 2a. Antennal protop
- Page 155 and 156:
838 Stomatopods Harpiosquillidae HA
- Page 157 and 158:
840 Stomatopods 8a. Rostral plate l
- Page 159 and 160:
842 Stomatopods Squillidae SQUILLID
- Page 161 and 162:
844 Stomatopods 7a. Dorsal surface
- Page 163 and 164:
846 Stomatopods Cloridopsis scorpio
- Page 165 and 166:
848 Stomatopods Oratosquillina grav
- Page 167 and 168:
click for previous page SHRIMPS AND
- Page 169 and 170:
Technical Terms and Measurements 85
- Page 171 and 172:
General Remarks 855 The terms “sh
- Page 173 and 174:
List of Families 857 List of Famili
- Page 175 and 176:
Infraorder Penaeidae, Superfamily S
- Page 177 and 178:
Sergestidae 861 6a. Lower antennula
- Page 179 and 180:
Sergestidae 863 Acetes intermedius
- Page 181 and 182:
Sergestidae 865 Acetes vulgaris Han
- Page 183 and 184:
Superfamily Penaeoidea 867 Caridea:
- Page 185 and 186: Aristeidae 869 Similar families occ
- Page 187 and 188: Aristeidae 871 List of species occu
- Page 189 and 190: Aristeidae 873 Aristeus virilis (Ba
- Page 191 and 192: Solenoceridae 875 Solenoceridae SOL
- Page 193 and 194: Solenoceridae 877 Stenopodidae: thi
- Page 195 and 196: Solenoceridae 879 9a. Anterior end
- Page 197 and 198: Solenoceridae 881 Haliporoides sibo
- Page 199 and 200: Solenoceridae 883 Solenocera crassi
- Page 201 and 202: Solenoceridae 885 Solenocera alfons
- Page 203 and 204: Solenoceridae 887 Solenocera koelbe
- Page 205 and 206: click for previous page Penaeidae 8
- Page 207 and 208: Penaeidae 891 Sergestidae: size sma
- Page 209 and 210: Penaeidae 893 9a. Carapace without
- Page 211 and 212: Penaeidae 895 2a. Rostrum armed wit
- Page 213 and 214: Penaeidae 897 17a. In males, basial
- Page 215 and 216: Penaeidae 899 5a. Epigastric spine
- Page 217 and 218: Penaeidae 901 2a. In males, petasma
- Page 219 and 220: Penaeidae 903 9a. Adrostral crest e
- Page 221 and 222: Penaeidae 905 Metapenaeopsis mannar
- Page 223 and 224: click for previous page Penaeidae 9
- Page 225 and 226: Penaeidae 909 Metapenaeus anchistus
- Page 227 and 228: Penaeidae 911 Metapenaeus intermedi
- Page 229 and 230: Penaeidae 913 Parapenaeopsis hardwi
- Page 231 and 232: Penaeidae 915 Penaeus esculentus Ha
- Page 233 and 234: Penaeidae 917 Penaeus japonicus Bat
- Page 235: Penaeidae 919 Penaeus longistylus K
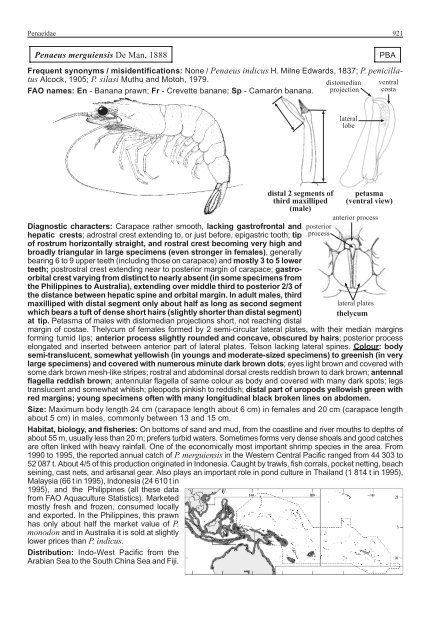
- Page 239 and 240: Penaeidae 923 Penaeus penicillatus
- Page 241 and 242: Penaeidae 925 Penaeus semisulcatus
- Page 243 and 244: Penaeidae 927 Trachypenaeus curviro
- Page 245 and 246: Penaeidae 929 Atypopenaeus formosus
- Page 247 and 248: Penaeidae 931 Metapenaeopsis novaeg
- Page 249 and 250: Penaeidae 933 Metapenaeopsis wellsi
- Page 251 and 252: Penaeidae 935 Metapenaeus conjunctu
- Page 253 and 254: Penaeidae 937 Metapenaeus eboracens
- Page 255 and 256: Penaeidae 939 Metapenaeus lysianass
- Page 257 and 258: click for previous page Penaeidae 9
- Page 259 and 260: Penaeidae 943 Parapenaeopsis gracil
- Page 261 and 262: Penaeidae 945 Parapenaeopsis tenell
- Page 263 and 264: Penaeidae 947 Parapenaeus longipes
- Page 265 and 266: Penaeidae 949 Trachypenaeus gonospi
- Page 267 and 268: Penaeidae 951 Trachypenaeus villalu
- Page 269 and 270: Sicyoniidae 953 Solenoceridae: body
- Page 271 and 272: Stenopodidae 955 Stenopodidae Infra
- Page 273 and 274: Infraorder Caridea 957 Infraorder C
- Page 275 and 276: Infraorder Caridea 959 Superfamily
- Page 277 and 278: Atyidae/Hippolytidae 961 Caridina w
- Page 279 and 280: Hymenoceridae 963 Hymenoceridae HYM
- Page 281 and 282: Palaemonidae 965 Exopalaemon stylif
- Page 283 and 284: click for previous page Palaemonida
- Page 285 and 286: Palaemonidae/Pandalidae 969 Palaemo
- Page 287 and 288:
Rhynchocinetidae 971 Rhynchocinetid
- Page 289 and 290:
974 Lobsters Technical Terms and Me
- Page 291 and 292:
976 Lobsters General Remarks GENERA
- Page 293 and 294:
978 Lobsters ENOPLOMETOPIDAE Page 9
- Page 295 and 296:
980 Lobsters List of FamiliesLIST a
- Page 297 and 298:
click for previous page 982 Lobster
- Page 299 and 300:
984 Lobsters Palinuridae: carapace
- Page 301 and 302:
986 Lobsters 6a. Abdomen smooth, wi
- Page 303 and 304:
988 Lobsters Acanthacaris tenuimana
- Page 305 and 306:
990 Lobsters Metanephrops thomsoni
- Page 307 and 308:
992 Lobsters Metanephrops andamanic
- Page 309 and 310:
994 Lobsters Metanephrops velutinus
- Page 311 and 312:
996 Lobsters Similar families occur
- Page 313 and 314:
998 Lobsters 3a. Carapace with 5 me
- Page 315 and 316:
1000 Lobsters Enoplometopus holthui
- Page 317 and 318:
1002 Lobsters Enoplometopidae: body
- Page 319 and 320:
1004 Lobsters Palibythus magnificus
- Page 321 and 322:
1006 Lobsters gonopore female leg 1
- Page 323 and 324:
1008 Lobsters Synaxidae: body very
- Page 325 and 326:
1010 Lobsters Key to the species of
- Page 327 and 328:
1012 Lobsters Key to the species of
- Page 329 and 330:
1014 Lobsters 8a. Antennular plate
- Page 331 and 332:
1016 Lobsters Panulirus homarus (Li
- Page 333 and 334:
1018 Lobsters Panulirus ornatus (Fa
- Page 335 and 336:
1020 Lobsters Panulirus polyphagus
- Page 337 and 338:
1022 Lobsters Justitia chani Poupin
- Page 339 and 340:
1024 Lobsters Linuparus sordidus Br
- Page 341 and 342:
1026 Lobsters Panulirus pascuensis
- Page 343 and 344:
click for previous page 1028 Lobste
- Page 345 and 346:
1030 Lobsters 5a. Medium size (adul
- Page 347 and 348:
1032 Lobsters 2a. Articulated parts
- Page 349 and 350:
1034 Lobsters Ibacus ciliatus (Von
- Page 351 and 352:
1036 Lobsters Ibacus pubescens Holt
- Page 353 and 354:
click for previous page 1038 Lobste
- Page 355 and 356:
1040 Lobsters Thenus orientalis (Lu
- Page 357 and 358:
1042 Lobsters Parribacus holthuisi
- Page 359 and 360:
click for previous page CRABS by P.
- Page 361 and 362:
Technical Terms and Measurements 10
- Page 363 and 364:
General Remarks 1049 Poisonous Crab
- Page 365 and 366:
General Remarks 1051 Adult male and
- Page 367 and 368:
General Remarks 1053 longitudinally
- Page 369 and 370:
Imported Crabs of Commercial Import
- Page 371 and 372:
Guide to Families 1057 CALAPPIDAE P
- Page 373 and 374:
Guide to Families 1059 PORTUNIDAE P
- Page 375 and 376:
Guide to Families/Key to Brachyura
- Page 377 and 378:
Key to Brachyura 1063 Fig. 9 Cyclod
- Page 379 and 380:
Key to Brachyura 1065 13a. Opening
- Page 381 and 382:
Key to Brachyura 1067 18a. Antennae
- Page 383 and 384:
Key to Brachyura 1069 Fig. 46 Atele
- Page 385 and 386:
Key to Brachyura 1071 30a. Last pai
- Page 387 and 388:
Key to Brachyura 1073 strongly recu
- Page 389 and 390:
Key to Brachyura 1075 42a. Longitud
- Page 391 and 392:
Key to Anomura 1077 48a. Male first
- Page 393 and 394:
Key to Anomura 1079 a) Fig. 103 Coe
- Page 395 and 396:
List of Families 1081 * CHEIRAGONID
- Page 397 and 398:
click for previous page Infraorder
- Page 399 and 400:
Dromiidae 1085 Dromiidae DROMIIDAE
- Page 401 and 402:
Dromiidae 1087 Dromia dormia (Linna
- Page 403 and 404:
Raninidae 1089 Raninidae RANINIDAE
- Page 405 and 406:
Calappidae 1091 Calappidae CALAPPID
- Page 407 and 408:
Calappidae 1093 3a. Entire posterio
- Page 409 and 410:
Calappidae 1095 Matuta victor (Fabr
- Page 411 and 412:
Calappidae 1097 Calappa hepatica (L
- Page 413 and 414:
Xanthidae 1099 Key to species of in
- Page 415 and 416:
Xanthidae 1101 Etisus splendidus Ra
- Page 417 and 418:
click for previous page Eriphiidae
- Page 419 and 420:
Eriphiidae 1105 6a. Dorsal surface
- Page 421 and 422:
Eriphiidae 1107 Menippe rumphii (Fa
- Page 423 and 424:
Eriphiidae 1109 Myomenippe fornasin
- Page 425 and 426:
Carpiliidae 1111 Carpilius convexus
- Page 427 and 428:
Pilumnidae 1113 A single species of
- Page 429 and 430:
click for previous page Portunidae
- Page 431 and 432:
Portunidae 1117 6a. Posterior borde
- Page 433 and 434:
Portunidae 1119 16a. Carapace with
- Page 435 and 436:
Portunidae 1121 Charybdis japonica
- Page 437 and 438:
Portunidae 1123 Podophthalmus vigil
- Page 439 and 440:
Portunidae 1125 Portunus sanguinole
- Page 441 and 442:
Portunidae 1127 The differences in
- Page 443 and 444:
Portunidae 1129 Thalamita crenata (
- Page 445 and 446:
Portunidae 1131 Charybdis annulata
- Page 447 and 448:
Geryonidae 1133 3a. Anterolateral m
- Page 449 and 450:
Geryonidae 1135 Chaceon australis M
- Page 451 and 452:
Majidae 1137 Schizophrys aspera (H.
- Page 453 and 454:
Grapsidae 1139 2a. Carapace squaris
- Page 455 and 456:
Grapsidae 1141 Key to food species
- Page 457 and 458:
Grapsidae 1143 Episesarma versicolo
- Page 459 and 460:
Grapsidae 1145 Episesarma chengtong
- Page 461 and 462:
click for previous page Gecarcinida
- Page 463 and 464:
Gecarcinidae 1149 Cardisoma carnife
- Page 465 and 466:
Gecarcinidae 1151 Cardisoma hirtipe
- Page 467 and 468:
Ocypodidae 1153 Ocypode ceratophtha
- Page 469 and 470:
Infraorder Anomura - Coenobitidae 1
- Page 471 and 472:
1158 Holothurians General Remarks G
- Page 473 and 474:
1160 Holothurians dentritic peltate
- Page 475 and 476:
1162 Holothurians oral tentacles ge
- Page 477 and 478:
1164 Holothurians Interradii (or in
- Page 479 and 480:
1166 Holothurians 11a. Tables with
- Page 481 and 482:
1168 Holothurians Actinopyga maurit
- Page 483 and 484:
1170 Holothurians Actinopyga palaue
- Page 485 and 486:
1172 Holothurians Bohadschia argus
- Page 487 and 488:
1174 Holothurians Bohadschia vitien
- Page 489 and 490:
1176 Holothurians Holothuria (Halod
- Page 491 and 492:
1178 Holothurians Holothuria (Merte
- Page 493 and 494:
1180 Holothurians Holothuria (Metri
- Page 495 and 496:
1182 Holothurians Holothuria (Micro
- Page 497 and 498:
1184 Holothurians Pearsonothuria gr
- Page 499 and 500:
1186 Holothurians Stichopus chloron
- Page 501 and 502:
1188 Holothurians Stichopus variega
- Page 503 and 504:
1190 Holothurians Thelenota anax Cl
- Page 505 and 506:
1192 Hagfishes MYXINIDAE Hagfishes
- Page 507 and 508:
1194 Sharks Technical Terms and Mea
- Page 509 and 510:
1196 Sharks General Remarks GENERAL
- Page 511 and 512:
1198 Sharks Key to Families KEY TO
- Page 513 and 514:
1200 Sharks 12a. No lobe and groove
- Page 515 and 516:
1202 Sharks 21a. First dorsal fin l
- Page 517 and 518:
1204 Sharks PRISTIOPHORIDAE: Sawsha
- Page 519 and 520:
1206 Sharks PSEUDOTRIAKIDAE: False
- Page 521 and 522:
click for previous page 1208 Sharks
- Page 523 and 524:
1210 Sharks Heptranchias perlo (Bon
- Page 525 and 526:
1212 Sharks Key to the species of E
- Page 527 and 528:
1214 Sharks Squatinidae: trunk much
- Page 529 and 530:
1216 Sharks 11a. Diagonal distance
- Page 531 and 532:
1218 Sharks 20a. Upper teeth relati
- Page 533 and 534:
1220 Sharks 29a. Denticles on sides
- Page 535 and 536:
1222 Sharks Etmopterus molleri Whi
- Page 537 and 538:
1224 Sharks Centrophorus niaukang T
- Page 539 and 540:
1226 Sharks Etmopterus brachyurus S
- Page 541 and 542:
1228 Sharks Euprotomicrus bispinatu
- Page 543 and 544:
1230 Sharks Squalus megalops (Macle
- Page 545 and 546:
1232 Sharks Squalus sp. F [Last and
- Page 547 and 548:
1234 Sharks Key to the species of P
- Page 549 and 550:
1236 Sharks Rays (Batoidea): pector
- Page 551 and 552:
1238 Sharks HETERODONTIDAE Bullhead
- Page 553 and 554:
1240 Sharks Heterodontus galeatus (
- Page 555 and 556:
1242 Sharks List of species occurri
- Page 557 and 558:
1244 Sharks Key to the species of B
- Page 559 and 560:
1246 Sharks Similar families occurr
- Page 561 and 562:
1248 Sharks Orectolobus ornatus (de
- Page 563 and 564:
1250 Sharks Ginglymostomatidae: pre
- Page 565 and 566:
1252 Sharks 7a. Black spot behind g
- Page 567 and 568:
1254 Sharks Chiloscyllium hasselti
- Page 569 and 570:
1256 Sharks Chiloscyllium plagiosum
- Page 571 and 572:
1258 Sharks Hemiscyllium freycineti
- Page 573 and 574:
1260 Sharks GINGLYMOSTOMATIDAE Nurs
- Page 575 and 576:
1262 Sharks A single species in thi
- Page 577 and 578:
1264 Sharks Odontaspididae ODONTASP
- Page 579 and 580:
1266 Sharks Carcharias taurus Rafin
- Page 581 and 582:
1268 Sharks A single species in thi
- Page 583 and 584:
1270 Sharks Key to the species of A
- Page 585 and 586:
1272 Sharks Alopias superciliosus (
- Page 587 and 588:
1274 Sharks LAMNIDAE Mackerel shark
- Page 589 and 590:
1276 Sharks Carcharodon carcharias
- Page 591 and 592:
1278 Sharks Isurus paucus Guitart M
- Page 593 and 594:
1280 Sharks Key to the species of S
- Page 595 and 596:
1282 Sharks 13a. Pectoral fin broad
- Page 597 and 598:
1284 Sharks 25a. Labial furrows ver
- Page 599 and 600:
1286 Sharks Apristurus herklotsi (F
- Page 601 and 602:
1288 Sharks Atelomycterus macleayi
- Page 603 and 604:
1290 Sharks Galeus gracilis Compagn
- Page 605 and 606:
1292 Sharks Scyliorhinus garmani (F
- Page 607 and 608:
1294 Sharks Triakidae: no gill rake
- Page 609 and 610:
1296 Sharks A single species in thi
- Page 611 and 612:
1298 Sharks Proscylliidae: gill rak
- Page 613 and 614:
1300 Sharks 9a. Snout bluntly round
- Page 615 and 616:
1302 Sharks Galeorhinus galeus (Lin
- Page 617 and 618:
1304 Sharks Mustelus antarcticus G
- Page 619 and 620:
1306 Sharks Similar families occurr
- Page 621 and 622:
1308 Sharks Chaenogaleus macrostoma
- Page 623 and 624:
1310 Sharks Hemipristis elongatus (
- Page 625 and 626:
click for previous page 1312 Sharks
- Page 627 and 628:
1314 Sharks Odontaspididae: fifth g
- Page 629 and 630:
1316 Sharks 6a. Second dorsal-fin o
- Page 631 and 632:
1318 Sharks 12a. Head very flat and
- Page 633 and 634:
1320 Sharks 22a. Second dorsal fin
- Page 635 and 636:
1322 Sharks 30a. Usually 11 lower a
- Page 637 and 638:
1324 Sharks List of species occurri
- Page 639 and 640:
1326 Sharks Carcharhinus altimus (S
- Page 641 and 642:
1328 Sharks Carcharhinus amblyrhync
- Page 643 and 644:
1330 Sharks Carcharhinus borneensis
- Page 645 and 646:
1332 Sharks Carcharhinus brevipinna
- Page 647 and 648:
1334 Sharks Carcharhinus dussumieri
- Page 649 and 650:
1336 Sharks Carcharhinus fitzroyens
- Page 651 and 652:
1338 Sharks Carcharhinus hemiodon (
- Page 653 and 654:
1340 Sharks Carcharhinus limbatus (
- Page 655 and 656:
1342 Sharks Carcharhinus macloti (M
- Page 657 and 658:
1344 Sharks Carcharhinus obscurus (
- Page 659 and 660:
1346 Sharks Carcharhinus sealei (Pi
- Page 661 and 662:
1348 Sharks Carcharhinus tilstoni (
- Page 663 and 664:
1350 Sharks Lamiopsis temmincki (M
- Page 665 and 666:
1352 Sharks Negaprion acutidens (R
- Page 667 and 668:
1354 Sharks Rhizoprionodon acutus (
- Page 669 and 670:
1356 Sharks Rhizoprionodon taylori
- Page 671 and 672:
1358 Sharks Triaenodon obesus (Rüp
- Page 673 and 674:
1360 Sharks Glyphis sp. B En - Born
- Page 675 and 676:
1362 Sharks 2a. Anterior margin of
- Page 677 and 678:
1364 Sharks Sphyrna lewini (Griffit
- Page 679 and 680:
1366 Sharks Sphyrna zygaena (Linnae
- Page 681 and 682:
1368 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 683 and 684:
1370 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 685 and 686:
1372 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 687 and 688:
1374 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 689 and 690:
1376 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 691 and 692:
1378 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 693 and 694:
1380 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 695 and 696:
1382 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 697 and 698:
1384 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 699 and 700:
1386 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 701 and 702:
1388 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 703 and 704:
1390 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 705 and 706:
1392 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 707 and 708:
1394 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 709 and 710:
1396 The Living Marine Resources of
- Page 711 and 712:
FAO SPECIES IDENTIFICATION GUIDE FO
- Page 713:
Carpenter, K.E.; Niem, V.H. (eds) F