Full Report - Research for Development - Department for ...
Full Report - Research for Development - Department for ...
Full Report - Research for Development - Department for ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
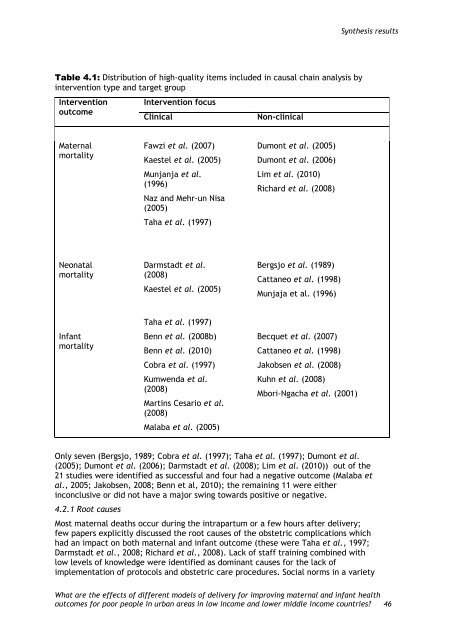
Table 4.1: Distribution of high-quality items included in causal chain analysis by<br />
intervention type and target group<br />
Intervention<br />
outcome<br />
Maternal<br />
mortality<br />
Neonatal<br />
mortality<br />
Infant<br />
mortality<br />
Intervention focus<br />
Clinical Non-clinical<br />
Fawzi et al. (2007)<br />
Kaestel et al. (2005)<br />
Munjanja et al.<br />
(1996)<br />
Naz and Mehr-un Nisa<br />
(2005)<br />
Taha et al. (1997)<br />
Darmstadt et al.<br />
(2008)<br />
Kaestel et al. (2005)<br />
Taha et al. (1997)<br />
Benn et al. (2008b)<br />
Benn et al. (2010)<br />
Cobra et al. (1997)<br />
Kumwenda et al.<br />
(2008)<br />
Martins Cesario et al.<br />
(2008)<br />
Malaba et al. (2005)<br />
Dumont et al. (2005)<br />
Dumont et al. (2006)<br />
Lim et al. (2010)<br />
Richard et al. (2008)<br />
Bergsjo et al. (1989)<br />
Cattaneo et al. (1998)<br />
Munjaja et al. (1996)<br />
Becquet et al. (2007)<br />
Cattaneo et al. (1998)<br />
Jakobsen et al. (2008)<br />
Kuhn et al. (2008)<br />
Mbori-Ngacha et al. (2001)<br />
Synthesis results<br />
Only seven (Bergsjo, 1989; Cobra et al. (1997); Taha et al. (1997); Dumont et al.<br />
(2005); Dumont et al. (2006); Darmstadt et al. (2008); Lim et al. (2010)) out of the<br />
21 studies were identified as successful and four had a negative outcome (Malaba et<br />
al., 2005; Jakobsen, 2008; Benn et al, 2010); the remaining 11 were either<br />
inconclusive or did not have a major swing towards positive or negative.<br />
4.2.1 Root causes<br />
Most maternal deaths occur during the intrapartum or a few hours after delivery;<br />
few papers explicitly discussed the root causes of the obstetric complications which<br />
had an impact on both maternal and infant outcome (these were Taha et al., 1997;<br />
Darmstadt et al., 2008; Richard et al., 2008). Lack of staff training combined with<br />
low levels of knowledge were identified as dominant causes <strong>for</strong> the lack of<br />
implementation of protocols and obstetric care procedures. Social norms in a variety<br />
What are the effects of different models of delivery <strong>for</strong> improving maternal and infant health<br />
outcomes <strong>for</strong> poor people in urban areas in low income and lower middle income countries? 46