Coherent Backscattering from Multiple Scattering Systems - KOPS ...
Coherent Backscattering from Multiple Scattering Systems - KOPS ...
Coherent Backscattering from Multiple Scattering Systems - KOPS ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2.7 The theory of coherent backscattering<br />
diffuson / cooperon<br />
2<br />
1.8<br />
1.6<br />
1.4<br />
1.2<br />
1<br />
0.8<br />
0.6<br />
diffuson α d<br />
(θ)<br />
cooperon α c<br />
(θ)<br />
α d<br />
(θ) + α c<br />
(θ)<br />
0.4<br />
0.2<br />
0<br />
−90 −60 −30 0 30 60 90<br />
scattering angle [deg]<br />
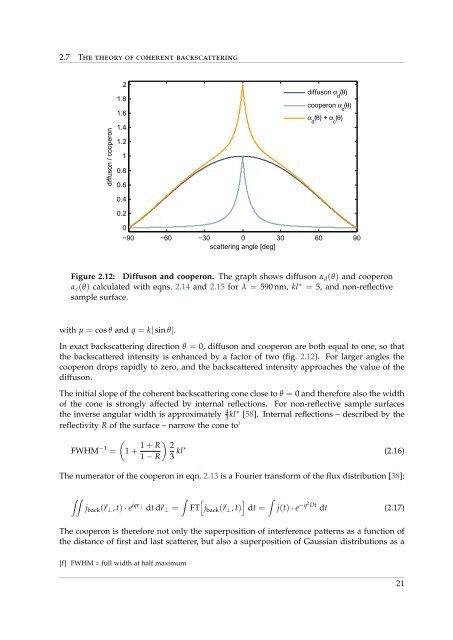
Figure 2.12: Diffuson and cooperon. The graph shows diffuson α d (θ) and cooperon<br />
α c (θ) calculated with eqns. 2.14 and 2.15 for λ = 590 nm, kl ∗ = 5, and non-reflective<br />
sample surface.<br />
with µ = cos θ and q = k| sin θ|.<br />
In exact backscattering direction θ = 0, diffuson and cooperon are both equal to one, so that<br />
the backscattered intensity is enhanced by a factor of two (fig. 2.12). For larger angles the<br />
cooperon drops rapidly to zero, and the backscattered intensity approaches the value of the<br />
diffuson.<br />
The initial slope of the coherent backscattering cone close to θ = 0 and therefore also the width<br />
of the cone is strongly affected by internal reflections. For non-reflective sample surfaces<br />
the inverse angular width is approximately 4 3 kl∗ [58]. Internal reflections – described by the<br />
reflectivity R of the surface – narrow the cone to f<br />
FWHM −1 =<br />
(<br />
1 + 1 + R ) 2<br />
1 − R 3 kl∗ (2.16)<br />
The numerator of the cooperon in eqn. 2.13 is a Fourier transform of the flux distribution [38]:<br />
∫∫<br />
∫<br />
j back (⃗r ⊥ , t) · e iqr ⊥<br />
dt d⃗r ⊥ =<br />
[ ] ∫<br />
FT j back (⃗r ⊥ , t) dt =<br />
j(t) · e −q2 Dt dt (2.17)<br />
The cooperon is therefore not only the superposition of interference patterns as a function of<br />
the distance of first and last scatterer, but also a superposition of Gaussian distributions as a<br />
[f] FWHM = full width at half maximum<br />
21