Dissertation - HQ
Dissertation - HQ
Dissertation - HQ
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
126 Oceanography vs. behaviour<br />
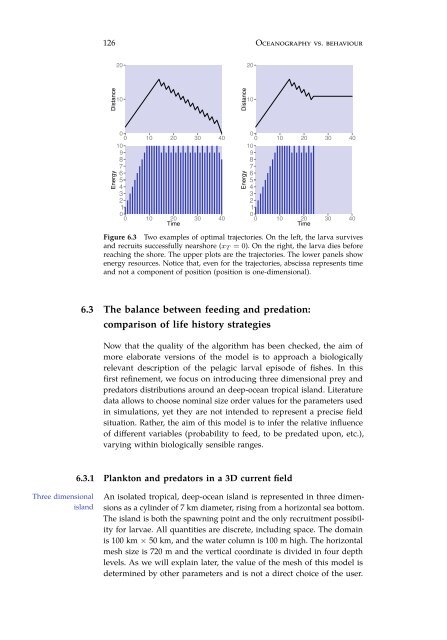
Figure 6.3 Two examples of optimal trajectories. On the left, the larva survives<br />
and recruits successfully nearshore (x T = 0). On the right, the larva dies before<br />
reaching the shore. The upper plots are the trajectories. The lower panels show<br />
energy resources. Notice that, even for the trajectories, abscissa represents time<br />
and not a component of position (position is one-dimensional).<br />
6.3 The balance between feeding and predation:<br />
comparison of life history strategies<br />
Now that the quality of the algorithm has been checked, the aim of<br />
more elaborate versions of the model is to approach a biologically<br />
relevant description of the pelagic larval episode of fishes. In this<br />
first refinement, we focus on introducing three dimensional prey and<br />
predators distributions around an deep-ocean tropical island. Literature<br />
data allows to choose nominal size order values for the parameters used<br />
in simulations, yet they are not intended to represent a precise field<br />
situation. Rather, the aim of this model is to infer the relative influence<br />
of different variables (probability to feed, to be predated upon, etc.),<br />
varying within biologically sensible ranges.<br />
6.3.1 Plankton and predators in a 3D current field<br />
Three dimensional<br />
island<br />
An isolated tropical, deep-ocean island is represented in three dimensions<br />
as a cylinder of 7 km diameter, rising from a horizontal sea bottom.<br />
The island is both the spawning point and the only recruitment possibility<br />
for larvae. All quantities are discrete, including space. The domain<br />
is 100 km × 50 km, and the water column is 100 m high. The horizontal<br />
mesh size is 720 m and the vertical coordinate is divided in four depth<br />
levels. As we will explain later, the value of the mesh of this model is<br />
determined by other parameters and is not a direct choice of the user.