Full Report - Subregional Office for East and North-East Asia - escap
Full Report - Subregional Office for East and North-East Asia - escap
Full Report - Subregional Office for East and North-East Asia - escap
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL SURVEY OF ASIA AND THE PACIFIC 2013<br />
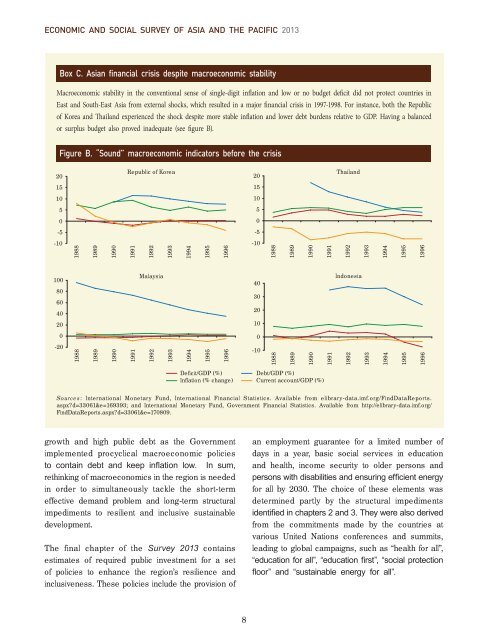
Box C. <strong>Asia</strong>n financial crisis despite macroeconomic stability<br />
Macroeconomic stability in the conventional sense of single-digit inflation <strong>and</strong> low or no budget deficit did not protect countries in<br />
<strong>East</strong> <strong>and</strong> South-<strong>East</strong> <strong>Asia</strong> from external shocks, which resulted in a major financial crisis in 1997-1998. For instance, both the Republic<br />
of Korea <strong>and</strong> Thail<strong>and</strong> experienced the shock despite more stable inflation <strong>and</strong> lower debt burdens relative to GDP. Having a balanced<br />
or surplus budget also proved inadequate (see figure B).<br />
Figure B. “Sound” macroeconomic indicators be<strong>for</strong>e the crisis<br />
Republic of Korea<br />
Thail<strong>and</strong><br />
20<br />
Republic of Korea<br />
20<br />
Thail<strong>and</strong><br />
15<br />
15<br />
10<br />
10<br />
5<br />
5<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-5<br />
-5<br />
-10<br />
1988<br />
1989<br />
1990<br />
1991<br />
1992<br />
1993<br />
Malaysia<br />
1994<br />
1995<br />
1996<br />
-10<br />
Malaysia<br />
1988<br />
1989<br />
1990<br />
1991<br />
1992<br />
Indonesia<br />
1993<br />
1994<br />
1995<br />
1996<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
-20<br />
1988<br />
1989<br />
1990<br />
Malaysia 100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
-20<br />
1991<br />
1992<br />
1993 1988<br />
1994 1989<br />
1995 1990<br />
1996 1991<br />
1992<br />
Indonesia<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
-10<br />
1993<br />
1988<br />
1994<br />
1989<br />
1995<br />
1990<br />
1996<br />
1991<br />
1992<br />
1993<br />
1994<br />
1995<br />
1996<br />
Deficit/GDP (%) Debt/GDP Deficit/GDP (%) (%) Debt/GDP (%)<br />
Inflation (% change) Current Inflation account/GDP (% change) (%) Current account/GDP (%)<br />
Sources: International Monetary Fund, International Financial Statistics. Available from elibrary-data.imf.org/FindData<strong>Report</strong>s.<br />
aspx?d=33061&e=169393; <strong>and</strong> International Monetary Fund, Government Financial Statistics. Available from http://elibrary-data.imf.org/<br />
FindData<strong>Report</strong>s.aspx?d=33061&e=170809.<br />
growth <strong>and</strong> high public debt as the Government<br />
implemented procyclical macroeconomic policies<br />
to contain debt <strong>and</strong> keep inflation low. In sum,<br />
rethinking of macroeconomics in the region is needed<br />
in order to simultaneously tackle the short-term<br />
effective dem<strong>and</strong> problem <strong>and</strong> long-term structural<br />
impediments to resilient <strong>and</strong> inclusive sustainable<br />
development.<br />
The final chapter of the Survey 2013 contains<br />
estimates of required public investment <strong>for</strong> a set<br />
of policies to enhance the region’s resilience <strong>and</strong><br />
inclusiveness. These policies include the provision of<br />
an employment guarantee <strong>for</strong> a limited number of<br />
days in a year, basic social services in education<br />
<strong>and</strong> health, income security to older persons <strong>and</strong><br />
persons with disabilities <strong>and</strong> ensuring efficient energy<br />
<strong>for</strong> all by 2030. The choice of these elements was<br />
determined partly by the structural impediments<br />
identified in chapters 2 <strong>and</strong> 3. They were also derived<br />
from the commitments made by the countries at<br />
various United Nations conferences <strong>and</strong> summits,<br />
leading to global campaigns, such as “health <strong>for</strong> all”,<br />
“education <strong>for</strong> all”, “education first”, “social protection<br />
floor” <strong>and</strong> “sustainable energy <strong>for</strong> all”.<br />
8