BIOLOGY - microscopia.info
BIOLOGY - microscopia.info
BIOLOGY - microscopia.info
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Overhead Transparency Atlases<br />
105<br />
Replicating DNA molecule II. - IV. DNA and RNA - Differences between DNA and RNA - Fractionation of cell components<br />
by centrifugation - Synthesizing ability of components - Function of ribosomes - Structure of ribosomes - Amino<br />
acid-tRNA-complexes - Specifity of tRNA - Kinds of RNA in the cell - Experiments with artificial messengers - Polysomes<br />
on bacterial DNA - Electron micrograph of RNA-phages - Coat protein-gene of an RNA-phage - Summary:<br />
replication, transcription, translation - V. Genetic code and mutation - Colinearity between nucleotide- and amino-acid<br />
sequence - Frame shift mutations - Triplet-binding test - The genetic code - Relations between codon and anticodon -<br />
Begin of protein synthesis - Section of phage RNA - Chemical mutagenesis - Effect of mutations - VI. Synthesis,<br />
structure, and function of proteins - Protein-synthesizing complex I - Protein-synthesizing complex II - Secondary structure<br />
of proteins: a-helix - Secondary structure of proteins: b-pleated sheath - Tertiary structure of a protein: b-chain of<br />
hemoglobin - Sickle cell anemia, erythrocytes - Molecular interpretation.<br />
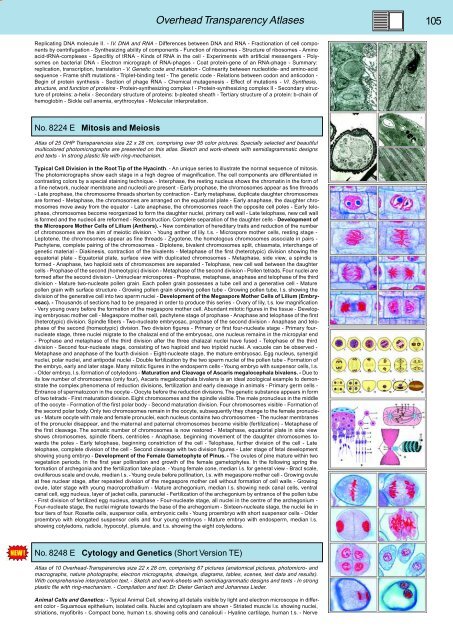
No. 8224 E Mitosis and Meiosis<br />
Atlas of 25 OHP Transparencies size 22 x 28 cm, comprising over 95 color pictures. Specially selected and beautiful<br />
multicolored photomicrographs are presented on this atlas. Sketch and work-sheets with semidiagrammatic designs<br />
and texts - In strong plastic file with ring-mechanism.<br />
Typical Cell Division in the Root Tip of the Hyacinth. - An unique series to illustrate the normal sequence of mitosis.<br />
The photomicrographs show each stage in a high degree of magnification. The cell components are differentiated in<br />
contrasting colors by a special staining technique. - Interphase, the resting nucleus shows the chromatin in the form of<br />
a fine network, nuclear membrane and nucleoli are present - Early prophase, the chromosomes appear as fine threads<br />
- Late prophase, the chromosome threads shorten by contraction - Early metaphase, duplicate daughter chromosomes<br />
are formed - Metaphase, the chromosomes are arranged on the equatorial plate - Early anaphase, the daughter chromosomes<br />
move away from the equator - Late anaphase, the chromosomes reach the opposite cell poles - Early telophase,<br />
chromosomes become reorganized to form the daughter nuclei, primary cell wall - Late telophase, new cell wall<br />
is formed and the nucleoli are reformed - Reconstruction. Complete separation of the daughter cells - Development of<br />
the Microspore Mother Cells of Lilium (Anthers). - New combination of hereditary traits and reduction of the number<br />
of chromosomes are the aim of meiotic division. - Young anther of lily. t.s. - Microspore mother cells, resting stage -<br />
Leptotene, the chromosomes appear as fine threads - Zygotene, the homologous chromosomes associate in pairs -<br />
Pachytene, complete pairing of the chromosomes - Diplotene, bivalent chromosomes split, chiasmata, interchange of<br />
genetic material - Diakinesis, contraction of the bivalents - Metaphase of the first (heterotypic) division showing the<br />
equatorial plate - Equatorial plate, surface view with duplicated chromosomes - Metaphase, side view, a spindle is<br />
formed - Anaphase, two haploid sets of chromosomes are separated - Telophase, new cell wall between the daughter<br />
cells - Prophase of the second (homeotypic) division - Metaphase of the second division - Pollen tetrads. Four nuclei are<br />
formed after the second division - Uninuclear microspores - Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase of the third<br />
division - Mature two-nucleate pollen grain. Each pollen grain possesses a tube cell and a generative cell - Mature<br />
pollen grain with surface structure - Growing pollen grain showing pollen tube - Growing pollen tube, l.s. showing the<br />
division of the generative cell into two sperm nuclei - Development of the Megaspore Mother Cells of Lilium (Embryosac).<br />
- Thousands of sections had to be prepared in order to produce this series - Ovary of lily, t.s. low magnification<br />
- Very young ovary before the formation of the megaspore mother cell. Abundant mitotic figures in the tissue - Developing<br />
embryosac mother cell - Megaspore mother cell, pachytene stage of prophase - Anaphase and telophase of the first<br />
(heterotypic) division. Spindle fibers - Two-nucleate embryosac, prophase of the second division - Anaphase and telophase<br />
of the second (homeotypic) division. Two division figures - Primary or first four-nucleate stage - Primary fournucleate<br />
stage, three nuclei migrate to the chalazal end of the embryosac, one nucleus remains in the micropylar end<br />
- Prophase and metaphase of the third division after the three chalazal nuclei have fused - Telophase of the third<br />
division - Second four-nucleate stage, consisting of two haploid and two triploid nuclei. A vacuole can be observed -<br />
Metaphase and anaphase of the fourth division - Eight-nucleate stage, the mature embryosac. Egg nucleus, synergid<br />
nuclei, polar nuclei, and antipodal nuclei - Double fertilization by the two sperm nuclei of the pollen tube - Formation of<br />
the embryo, early and later stage. Many mitotic figures in the endosperm cells - Young embryo with suspensor cells, l.s.<br />
- Older embryo, l.s. formation of cotyledons - Maturation and Cleavage of Ascaris megalocephala bivalens. - Due to<br />
its low number of chromosomes (only four), Ascaris megalocephala bivalens is an ideal zoological example to demonstrate<br />
the complex phenomena of reduction divisions, fertilization and early cleavage in animals - Primary germ cells -<br />
Entrance of spermatozoon in the oocyte - Oocyte before the reduction divisions. The genetic substance appears in form<br />
of two tetrads - First maturation division. Eight chromosomes and the spindle visible. The male pronucleus in the middle<br />
of the oocyte - Formation of the first polar body - Second maturation division. Four chromosomes visible - Formation of<br />
the second polar body. Only two chromosomes remain in the oocyte, subsequently they change to the female pronucleus<br />
- Mature oocyte with male and female pronuclei, each nucleus contains two chromosomes - The nuclear membranes<br />
of the pronuclei disappear, and the maternal and paternal chromosomes become visible (fertilization) - Metaphase of<br />
the first cleavage. The somatic number of chromosomes is now restored - Metaphase, equatorial plate in side view<br />
shows chromosomes, spindle fibers, centrioles - Anaphase, beginning movement of the daughter chromosomes towards<br />
the poles - Early telophase, beginning constriction of the cell - Telophase, further division of the cell - Late<br />
telophase, complete division of the cell - Second cleavage with two division figures - Later stage of fetal development<br />
showing young embryo - Development of the Female Gametophyte of Pinus. - The ovules of pine mature within two<br />
vegetation periods. In the first year pollination and growth of the female gametophytes. In the following spring the<br />
formation of archegonia and the fertilization take place. - Young female cone, median l.s. for general view - Bract scale,<br />
ovuliferous scale and ovule, median l.s. - Young ovule before pollination, l.s. with megaspore mother cell - Growing ovule<br />
at free nuclear stage, after repeated division of the megaspore mother cell without formation of cell walls - Growing<br />
ovule, later stage with young macroprothallium - Mature archegonium, median l.s. showing neck canal cells, ventral<br />
canal cell, egg nucleus, layer of jacket cells, paranuclei - Fertilization of the archegonium by entrance of the pollen tube<br />
- First division of fertilized egg nucleus, anaphase - Four-nucleate stage, all nuclei in the centre of the archegonium -<br />
Four-nucleate stage, the nuclei migrate towards the base of the archegonium - Sixteen-nucleate stage, the nuclei lie in<br />
four tiers of four. Rosette cells, suspensor cells, embryonic cells - Young proembryo with short suspensor cells - Older<br />
proembryo with elongated suspensor cells and four young embryos - Mature embryo with endosperm, median l.s.<br />
showing cotyledons, radicle, hypocotyl, plumule, and t.s. showing the eight cotyledons.<br />
No. 8248 E Cytology and Genetics (Short Version TE)<br />
Atlas of 10 Overhead-Transparencies size 22 x 28 cm, comprising 67 pictures (anatomical pictures, photomicro- and<br />
macrographs, nature photographs, electron micrographs, drawings, diagrams, tables, scenes, test data and results).<br />
With comprehensive interpretation text. - Sketch and work-sheets with semidiagrammatic designs and texts - In strong<br />
plastic file with ring-mechanism. - Compilation and text: Dr. Dieter Gerlach and Johannes Lieder.<br />
Animal Cells and Genetics: - Typical Animal Cell, showing all details visible by light and electron microscope in different<br />
color - Squamous epithelium, isolated cells. Nuclei and cytoplasm are shown - Striated muscle l.s. showing nuclei,<br />
striations, myofibrils - Compact bone, human t.s. showing cells and canaliculi - Hyaline cartilage, human t.s. - Nerve