Organohalogen concentrations and a gross and histologic ...
Organohalogen concentrations and a gross and histologic ...
Organohalogen concentrations and a gross and histologic ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
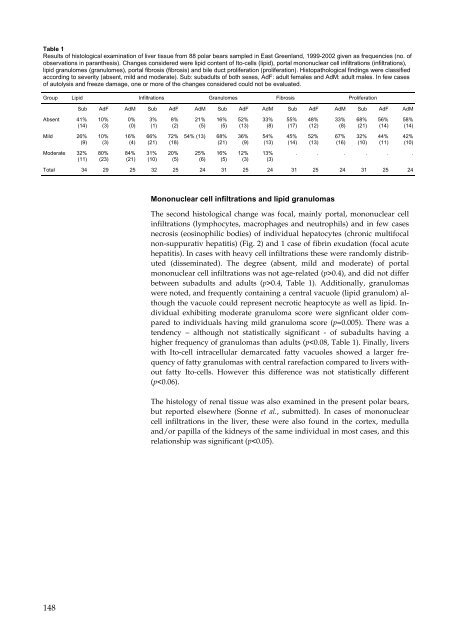
Table 1<br />
Results of <strong>histologic</strong>al examination of liver tissue from 88 polar bears sampled in East Greenl<strong>and</strong>, 1999-2002 given as frequencies (no. of<br />
observations in paranthesis). Changes considered were lipid content of Ito-cells (lipid), portal mononuclear cell infiltrations (infiltrations),<br />
lipid granulomes (granulomes), portal fibrosis (fibrosis) <strong>and</strong> bile duct proliferation (proliferation). Histopathological findings were classified<br />
according to severity (absent, mild <strong>and</strong> moderate). Sub: subadults of both sexes, AdF: adult females <strong>and</strong> AdM: adult males. In few cases<br />
of autolysis <strong>and</strong> freeze damage, one or more of the changes considered could not be evaluated.<br />
Group Lipid Infiltrations Granulomes Fibrosis Proliferation<br />
Absent 41%<br />
(14)<br />
Mild 26%<br />
(9)<br />
Moderate 32%<br />
(11)<br />
148<br />
Sub AdF AdM Sub AdF AdM Sub AdF AdM Sub AdF AdM Sub AdF AdM<br />
10%<br />
(3)<br />
10%<br />
(3)<br />
80%<br />
(23)<br />
0%<br />
(0)<br />
16%<br />
(4)<br />
84%<br />
(21)<br />
3%<br />
(1)<br />
66%<br />
(21)<br />
31%<br />
(10)<br />
8%<br />
(2)<br />
72%<br />
(18)<br />
20%<br />
(5)<br />
21%<br />
(5)<br />
16%<br />
(5)<br />
54% (13) 68%<br />
(21)<br />
25%<br />
(6)<br />
16%<br />
(5)<br />
52%<br />
(13)<br />
36%<br />
(9)<br />
12%<br />
(3)<br />
33%<br />
(8)<br />
54%<br />
(13)<br />
13%<br />
(3)<br />
Mononuclear cell infiltrations <strong>and</strong> lipid granulomas<br />
The second <strong>histologic</strong>al change was focal, mainly portal, mononuclear cell<br />
infiltrations (lymphocytes, macrophages <strong>and</strong> neutrophils) <strong>and</strong> in few cases<br />
necrosis (eosinophilic bodies) of individual hepatocytes (chronic multifocal<br />
non-suppurativ hepatitis) (Fig. 2) <strong>and</strong> 1 case of fibrin exudation (focal acute<br />
hepatitis). In cases with heavy cell infiltrations these were r<strong>and</strong>omly distributed<br />
(disseminated). The degree (absent, mild <strong>and</strong> moderate) of portal<br />
mononuclear cell infiltrations was not age-related (p>0.4), <strong>and</strong> did not differ<br />
between subadults <strong>and</strong> adults (p>0.4, Table 1). Additionally, granulomas<br />
were noted, <strong>and</strong> frequently containing a central vacuole (lipid granulom) although<br />
the vacuole could represent necrotic heaptocyte as well as lipid. Individual<br />
exhibiting moderate granuloma score were signficant older compared<br />
to individuals having mild granuloma score (p=0.005). There was a<br />
tendency – although not statistically significant - of subadults having a<br />
higher frequency of granulomas than adults (p