Organohalogen concentrations and a gross and histologic ...
Organohalogen concentrations and a gross and histologic ...
Organohalogen concentrations and a gross and histologic ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
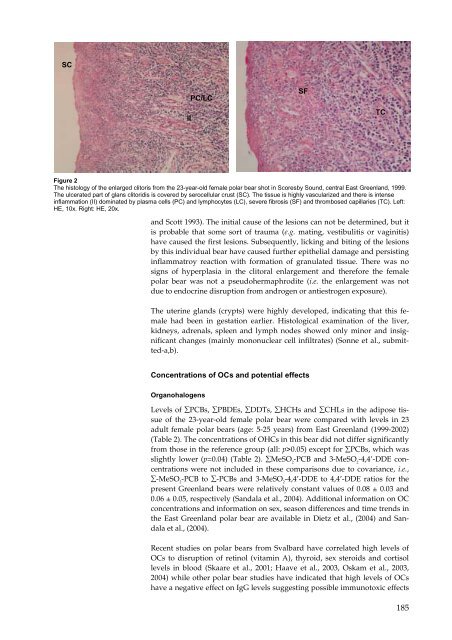
SC<br />
II<br />
PC/LC<br />
Figure 2<br />
The histology of the enlarged clitoris from the 23-year-old female polar bear shot in Scoresby Sound, central East Greenl<strong>and</strong>, 1999.<br />
The ulcerated part of glans clitoridis is covered by serocellular crust (SC). The tissue is highly vascularized <strong>and</strong> there is intense<br />
inflammation (II) dominated by plasma cells (PC) <strong>and</strong> lymphocytes (LC), severe fibrosis (SF) <strong>and</strong> thrombosed capillaries (TC). Left:<br />
HE, 10x. Right: HE, 20x.<br />
<strong>and</strong> Scott 1993). The initial cause of the lesions can not be determined, but it<br />
is probable that some sort of trauma (e.g. mating, vestibulitis or vaginitis)<br />
have caused the first lesions. Subsequently, licking <strong>and</strong> biting of the lesions<br />
by this individual bear have caused further epithelial damage <strong>and</strong> persisting<br />
inflammatroy reaction with formation of granulated tissue. There was no<br />
signs of hyperplasia in the clitoral enlargement <strong>and</strong> therefore the female<br />
polar bear was not a pseudohermaphrodite (i.e. the enlargement was not<br />
due to endocrine disruption from <strong>and</strong>rogen or antiestrogen exposure).<br />
The uterine gl<strong>and</strong>s (crypts) were highly developed, indicating that this female<br />
had been in gestation earlier. Histological examination of the liver,<br />
kidneys, adrenals, spleen <strong>and</strong> lymph nodes showed only minor <strong>and</strong> insignificant<br />
changes (mainly mononuclear cell infiltrates) (Sonne et al., submitted-a,b).<br />
Concentrations of OCs <strong>and</strong> potential effects<br />
<strong>Organohalogen</strong>s<br />
Levels of ∑PCBs, ∑PBDEs, ∑DDTs, ∑HCHs <strong>and</strong> ∑CHLs in the adipose tissue<br />
of the 23-year-old female polar bear were compared with levels in 23<br />
adult female polar bears (age: 5-25 years) from East Greenl<strong>and</strong> (1999-2002)<br />
(Table 2). The <strong>concentrations</strong> of OHCs in this bear did not differ significantly<br />
from those in the reference group (all: p>0.05) except for ∑PCBs, which was<br />
slightly lower (p=0.04) (Table 2). ∑MeSO 2 -PCB <strong>and</strong> 3-MeSO 2 -4,4’-DDE <strong>concentrations</strong><br />
were not included in these comparisons due to covariance, i.e.,<br />
∑-MeSO 2 -PCB to ∑-PCBs <strong>and</strong> 3-MeSO 2 -4,4’-DDE to 4,4’-DDE ratios for the<br />
present Greenl<strong>and</strong> bears were relatively constant values of 0.08 ± 0.03 <strong>and</strong><br />
0.06 ± 0.05, respectively (S<strong>and</strong>ala et al., 2004). Additional information on OC<br />
<strong>concentrations</strong> <strong>and</strong> information on sex, season differences <strong>and</strong> time trends in<br />
the East Greenl<strong>and</strong> polar bear are available in Dietz et al., (2004) <strong>and</strong> S<strong>and</strong>ala<br />
et al., (2004).<br />
Recent studies on polar bears from Svalbard have correlated high levels of<br />
OCs to disruption of retinol (vitamin A), thyroid, sex steroids <strong>and</strong> cortisol<br />
levels in blood (Skaare et al., 2001; Haave et al., 2003, Oskam et al., 2003,<br />
2004) while other polar bear studies have indicated that high levels of OCs<br />
have a negative effect on IgG levels suggesting possible immunotoxic effects<br />
SF<br />
TC<br />
185