Organohalogen concentrations and a gross and histologic ...
Organohalogen concentrations and a gross and histologic ...
Organohalogen concentrations and a gross and histologic ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
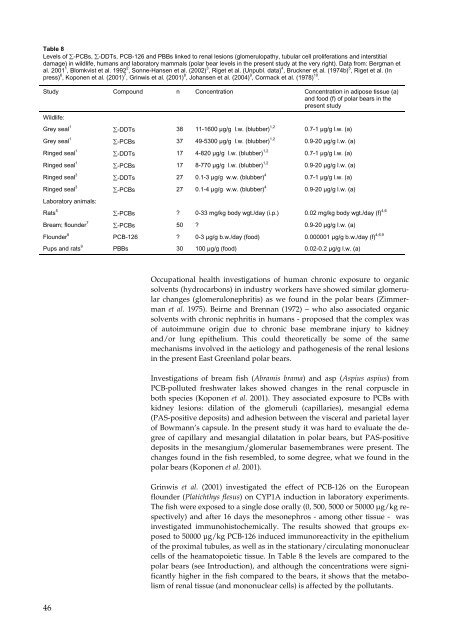
Table 8<br />
Levels of ∑-PCBs, ∑-DDTs, PCB-126 <strong>and</strong> PBBs linked to renal lesions (glomerulopathy, tubular cell proliferations <strong>and</strong> interstitial<br />
damage) in wildlife, humans <strong>and</strong> laboratory mammals (polar bear levels in the present study at the very right). Data from: Bergman et<br />
al. 2001 1 , Blomkvist et al. 1992 2 , Sonne-Hansen et al. (2002) 3 , Riget et al. (Unpubl. data) 4 , Bruckner et al. (1974b) 5 , Riget et al. (In<br />
press) 6 , Koponen et al. (2001) 7 , Grinwis et al. (2001) 8 , Johansen et al. (2004) 9 , Cormack et al. (1978) 10 .<br />
Study Compound n Concentration Concentration in adipose tissue (a)<br />
<strong>and</strong> food (f) of polar bears in the<br />
present study<br />
Wildlife:<br />
Grey seal 1<br />
Grey seal 1<br />
Ringed seal 1<br />
Ringed seal 1<br />
Ringed seal 3<br />
Ringed seal 3<br />
Laboratory animals:<br />
Rats 5<br />
Bream; flounder 7<br />
Flounder 8<br />
Pups <strong>and</strong> rats 9<br />
46<br />
∑-DDTs 38 11-1600 µg/g l.w. (blubber) 1,2<br />
∑-PCBs 37 49-5300 µg/g l.w. (blubber) 1,2<br />
∑-DDTs 17 4-820 µg/g l.w. (blubber) 1,2<br />
∑-PCBs 17 8-770 µg/g l.w. (blubber) 1,2<br />
∑-DDTs 27 0.1-3 µg/g w.w. (blubber) 4<br />
∑-PCBs 27 0.1-4 µg/g w.w. (blubber) 4<br />
0.7-1 µg/g l.w. (a)<br />
0.9-20 µg/g l.w. (a)<br />
0.7-1 µg/g l.w. (a)<br />
0.9-20 µg/g l.w. (a)<br />
0.7-1 µg/g l.w. (a)<br />
0.9-20 µg/g l.w. (a)<br />
∑-PCBs ? 0-33 mg/kg body wgt./day (i.p.) 0.02 mg/kg body wgt./day (f) 4,6<br />
∑-PCBs 50 ? 0.9-20 µg/g l.w. (a)<br />
PCB-126 ? 0-3 µg/g b.w./day (food) 0.000001 µg/g b.w./day (f) 4,6,9<br />
PBBs 30 100 µg/g (food) 0.02-0.2 µg/g l.w. (a)<br />
Occupational health investigations of human chronic exposure to organic<br />
solvents (hydrocarbons) in industry workers have showed similar glomerular<br />
changes (glomerulonephritis) as we found in the polar bears (Zimmerman<br />
et al. 1975). Beirne <strong>and</strong> Brennan (1972) – who also associated organic<br />
solvents with chronic nephritis in humans - proposed that the complex was<br />
of autoimmune origin due to chronic base membrane injury to kidney<br />
<strong>and</strong>/or lung epithelium. This could theoretically be some of the same<br />
mechanisms involved in the aetiology <strong>and</strong> pathogenesis of the renal lesions<br />
in the present East Greenl<strong>and</strong> polar bears.<br />
Investigations of bream fish (Abramis brama) <strong>and</strong> asp (Aspius aspius) from<br />
PCB-polluted freshwater lakes showed changes in the renal corpuscle in<br />
both species (Koponen et al. 2001). They associated exposure to PCBs with<br />
kidney lesions: dilation of the glomeruli (capillaries), mesangial edema<br />
(PAS-positive deposits) <strong>and</strong> adhesion between the visceral <strong>and</strong> parietal layer<br />
of Bowmann’s capsule. In the present study it was hard to evaluate the degree<br />
of capillary <strong>and</strong> mesangial dilatation in polar bears, but PAS-positive<br />
deposits in the mesangium/glomerular basemembranes were present. The<br />
changes found in the fish resembled, to some degree, what we found in the<br />
polar bears (Koponen et al. 2001).<br />
Grinwis et al. (2001) investigated the effect of PCB-126 on the European<br />
flounder (Platichthys flesus) on CYP1A induction in laboratory experiments.<br />
The fish were exposed to a single dose orally (0, 500, 5000 or 50000 µg/kg respectively)<br />
<strong>and</strong> after 16 days the mesonephros - among other tissue - was<br />
investigated immunohistochemically. The results showed that groups exposed<br />
to 50000 µg/kg PCB-126 induced immunoreactivity in the epithelium<br />
of the proximal tubules, as well as in the stationary/circulating mononuclear<br />
cells of the heamatopoietic tissue. In Table 8 the levels are compared to the<br />
polar bears (see Introduction), <strong>and</strong> although the <strong>concentrations</strong> were significantly<br />
higher in the fish compared to the bears, it shows that the metabolism<br />
of renal tissue (<strong>and</strong> mononuclear cells) is affected by the pollutants.