THESIS - ROC CH ... - FINAL - resubmission.pdf - University of Guelph
THESIS - ROC CH ... - FINAL - resubmission.pdf - University of Guelph
THESIS - ROC CH ... - FINAL - resubmission.pdf - University of Guelph
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
cellulose and SPI. This high interfacial interaction seen should be expected as both cellulose<br />
and SPI have many groups to form hydrogen bonds (Chen and Liu 2008; Wu et al. 2009).<br />
Tensile Strength (Mpa)<br />
8<br />
7<br />
6<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
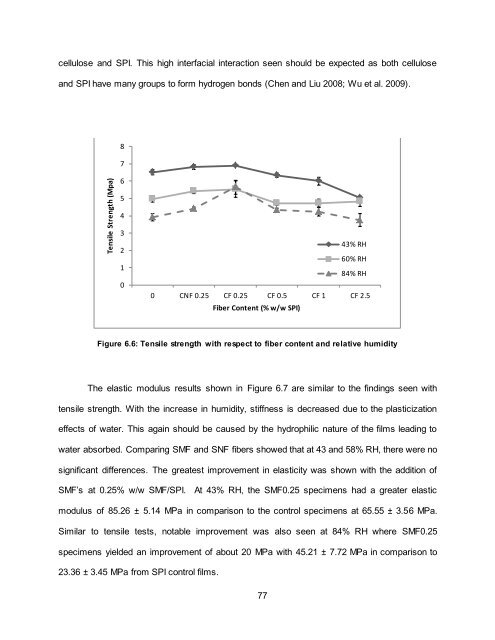
Figure 6.6: Tensile strength with respect to fiber content and relative humidity<br />
The elastic modulus results shown in Figure 6.7 are similar to the findings seen with<br />
tensile strength. With the increase in humidity, stiffness is decreased due to the plasticization<br />
effects <strong>of</strong> water. This again should be caused by the hydrophilic nature <strong>of</strong> the films leading to<br />
water absorbed. Comparing SMF and SNF fibers showed that at 43 and 58% RH, there were no<br />
significant differences. The greatest improvement in elasticity was shown with the addition <strong>of</strong><br />
SMF’s at 0.25% w/w SMF/SPI. At 43% RH, the SMF0.25 specimens had a greater elastic<br />
modulus <strong>of</strong> 85.26 ± 5.14 MPa in comparison to the control specimens at 65.55 ± 3.56 MPa.<br />
Similar to tensile tests, notable improvement was also seen at 84% RH where SMF0.25<br />
specimens yielded an improvement <strong>of</strong> about 20 MPa with 45.21 ± 7.72 MPa in comparison to<br />
23.36 ± 3.45 MPa from SPI control films.<br />
0 CNF 0.25 CF 0.25 CF 0.5 CF 1 CF 2.5<br />
Fiber Content (% w/w SPI)<br />
77<br />
43% RH<br />
60% RH<br />
84% RH