A new approach to species delimitation in Septoria - CBS - KNAW
A new approach to species delimitation in Septoria - CBS - KNAW
A new approach to species delimitation in Septoria - CBS - KNAW
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
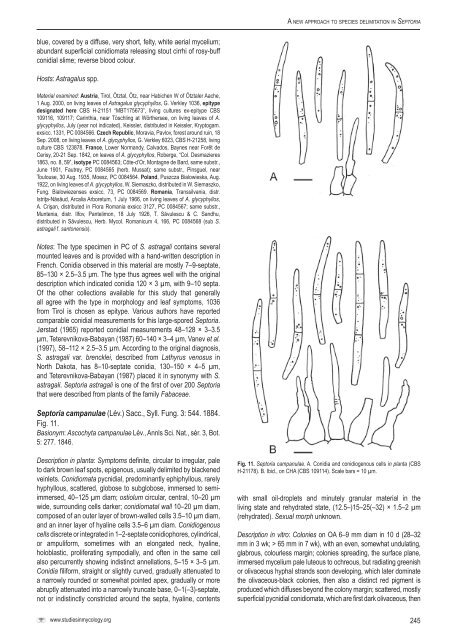
A <strong>new</strong> <strong>approach</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>species</strong> <strong>delimitation</strong> <strong>in</strong> Sep<strong>to</strong>riablue, covered by a diffuse, very short, felty, white aerial mycelium;abundant superficial conidiomata releas<strong>in</strong>g s<strong>to</strong>ut cirrhi of rosy-buffconidial slime; reverse blood colour.Hosts: Astragalus spp.Material exam<strong>in</strong>ed: Austria, Tirol, Ötztal, Ötz, near Habichen W of Ötztaler Aache,1 Aug. 2000, on liv<strong>in</strong>g leaves of Astragalus glycyphyllos, G. Verkley 1036, epitypedesignated here <strong>CBS</strong> H-21151 “MBT175673”, liv<strong>in</strong>g cultures ex-epitype <strong>CBS</strong>109116, 109117; Car<strong>in</strong>thia, near Töschl<strong>in</strong>g at Wörthersee, on liv<strong>in</strong>g leaves of A.glycyphyllos, July (year not <strong>in</strong>dicated), Keissler, distributed <strong>in</strong> Keissler, Kryp<strong>to</strong>gam.exsicc. 1331, PC 0084566. Czech Republic, Moravia, Pavlov, forest around ru<strong>in</strong>, 18Sep. 2008, on liv<strong>in</strong>g leaves of A. glycyphyllos, G. Verkley 6023, <strong>CBS</strong> H-21258, liv<strong>in</strong>gculture <strong>CBS</strong> 123878. France, Lower Normandy, Calvados, Baynes near Forêt deCerisy, 20-21 Sep. 1842, on leaves of A. glycyphyllos, Roberge, “Col. Desmazieres1863, no. 8, 59”, isotype PC 0084563; Côte-d’Or, Montagne de Bard, same substr.,June 1901, Fautrey, PC 0084565 (herb. Mussat); same substr., P<strong>in</strong>sguel, nearToulouse, 30 Aug. 1935, Moesz, PC 0084564. Poland, Puszcza Bialowieska, Aug.1922, on liv<strong>in</strong>g leaves of A. glycyphyllos, W. Siemaszko, distributed <strong>in</strong> W. Siemaszko,Fung. Bialowiezenses exsicc. 73, PC 0084569. Romania, Transsilvania, distr.Istriţa-Năsăud, Arcalia Arboretum, 1 July 1966, on liv<strong>in</strong>g leaves of A. glycyphyllos,A. Crişan, distributed <strong>in</strong> Flora Romania exsicc 3127, PC 0084567; same substr.,Muntenia, distr. Ilfov, Pantelimon, 18 July 1926, T. Săvulescu & C. Sandhu,distributed <strong>in</strong> Săvulescu, Herb. Mycol. Romanicum 4, 166, PC 0084568 (sub S.astragali f. san<strong>to</strong>nensis).Notes: The type specimen <strong>in</strong> PC of S. astragali conta<strong>in</strong>s severalmounted leaves and is provided with a hand-written description <strong>in</strong>French. Conidia observed <strong>in</strong> this material are mostly 7–9-septate,85–130 × 2.5–3.5 μm. The type thus agrees well with the orig<strong>in</strong>aldescription which <strong>in</strong>dicated conidia 120 × 3 µm, with 9–10 septa.Of the other collections available for this study that generallyall agree with the type <strong>in</strong> morphology and leaf symp<strong>to</strong>ms, 1036from Tirol is chosen as epitype. Various authors have reportedcomparable conidial measurements for this large-spored Sep<strong>to</strong>ria.Jørstad (1965) reported conidial measurements 48–128 × 3–3.5µm, Teterevnikova-Babayan (1987) 60–140 × 3–4 µm, Vanev et al.(1997), 58–112 × 2.5–3.5 µm. Accord<strong>in</strong>g <strong>to</strong> the orig<strong>in</strong>al diagnosis,S. astragali var. brencklei, described from Lathyrus venosus <strong>in</strong>North Dakota, has 8–10-septate conidia, 130–150 × 4–5 µm,and Teterevnikova-Babayan (1987) placed it <strong>in</strong> synonymy with S.astragali. Sep<strong>to</strong>ria astragali is one of the first of over 200 Sep<strong>to</strong>riathat were described from plants of the family Fabaceae.Sep<strong>to</strong>ria campanulae (Lév.) Sacc., Syll. Fung. 3: 544. 1884.Fig. 11.Basionym: Ascochyta campanulae Lév., Annls Sci. Nat., sér. 3, Bot.5: 277. 1846.Description <strong>in</strong> planta: Symp<strong>to</strong>ms def<strong>in</strong>ite, circular <strong>to</strong> irregular, pale<strong>to</strong> dark brown leaf spots, epigenous, usually delimited by blackenedve<strong>in</strong>lets. Conidiomata pycnidial, predom<strong>in</strong>antly ephiphyllous, rarelyhyphyllous, scattered, globose <strong>to</strong> subglobose, immersed <strong>to</strong> semiimmersed,40–125 µm diam; ostiolum circular, central, 10–20 µmwide, surround<strong>in</strong>g cells darker; conidiomatal wall 10–20 µm diam,composed of an outer layer of brown-walled cells 3.5–10 µm diam,and an <strong>in</strong>ner layer of hyal<strong>in</strong>e cells 3.5–6 µm diam. Conidiogenouscells discrete or <strong>in</strong>tegrated <strong>in</strong> 1–2-septate conidiophores, cyl<strong>in</strong>drical,or ampuliform, sometimes with an elongated neck, hyal<strong>in</strong>e,holoblastic, proliferat<strong>in</strong>g sympodially, and often <strong>in</strong> the same cellalso percurrently show<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>dist<strong>in</strong>ct annellations, 5–15 × 3–5 µm.Conidia filiform, straight or slightly curved, gradually attenuated <strong>to</strong>a narrowly rounded or somewhat po<strong>in</strong>ted apex, gradually or moreabruptly attenuated <strong>in</strong><strong>to</strong> a narrowly truncate base, 0–1(–3)-septate,not or <strong>in</strong>dist<strong>in</strong>ctly constricted around the septa, hyal<strong>in</strong>e, contentsFig. 11. Sep<strong>to</strong>ria campanulae. A. Conidia and conidiogenous cells <strong>in</strong> planta (<strong>CBS</strong>H-21178). B. Ibid., on CHA (<strong>CBS</strong> 109114). Scale bars = 10 µm.with small oil-droplets and m<strong>in</strong>utely granular material <strong>in</strong> theliv<strong>in</strong>g state and rehydrated state, (12.5–)15–25(–32) × 1.5–2 µm(rehydrated). Sexual morph unknown.Description <strong>in</strong> vitro: Colonies on OA 6–9 mm diam <strong>in</strong> 10 d (28–32mm <strong>in</strong> 3 wk; > 65 mm <strong>in</strong> 7 wk), with an even, somewhat undulat<strong>in</strong>g,glabrous, colourless marg<strong>in</strong>; colonies spread<strong>in</strong>g, the surface plane,immersed mycelium pale luteous <strong>to</strong> ochreous, but radiat<strong>in</strong>g greenishor olivaceous hyphal strands soon develop<strong>in</strong>g, which later dom<strong>in</strong>atethe olivaceous-black colonies, then also a dist<strong>in</strong>ct red pigment isproduced which diffuses beyond the colony marg<strong>in</strong>; scattered, mostlysuperficial pycnidial conidiomata, which are first dark olivaceous, thenwww.studies<strong>in</strong>mycology.org245