A new approach to species delimitation in Septoria - CBS - KNAW
A new approach to species delimitation in Septoria - CBS - KNAW
A new approach to species delimitation in Septoria - CBS - KNAW
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
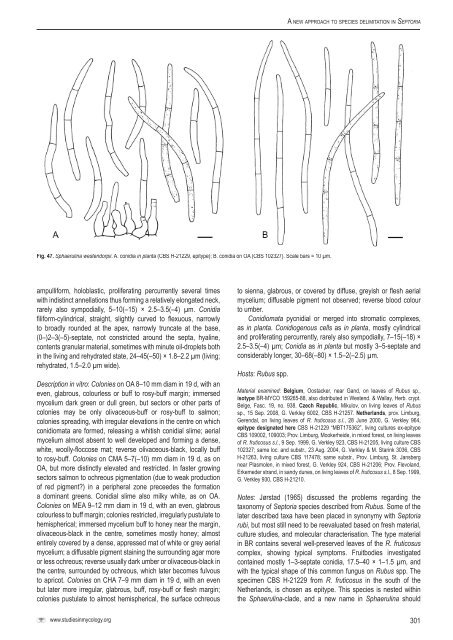
A <strong>new</strong> <strong>approach</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>species</strong> <strong>delimitation</strong> <strong>in</strong> Sep<strong>to</strong>riaFig. 47. Sphaerul<strong>in</strong>a westendorpii. A. conidia <strong>in</strong> planta (<strong>CBS</strong> H-21229, epitype); B. conidia on OA (<strong>CBS</strong> 102327). Scale bars = 10 µm.ampulliform, holoblastic, proliferat<strong>in</strong>g percurrently several timeswith <strong>in</strong>dist<strong>in</strong>ct annellations thus form<strong>in</strong>g a relatively elongated neck,rarely also sympodially, 5–10(–15) × 2.5–3.5(–4) µm. Conidiafiliform-cyl<strong>in</strong>drical, straight, slightly curved <strong>to</strong> flexuous, narrowly<strong>to</strong> broadly rounded at the apex, narrowly truncate at the base,(0–)2–3(–5)-septate, not constricted around the septa, hyal<strong>in</strong>e,contents granular material, sometimes with m<strong>in</strong>ute oil-droplets both<strong>in</strong> the liv<strong>in</strong>g and rehydrated state, 24–45(–50) × 1.8–2.2 µm (liv<strong>in</strong>g;rehydrated, 1.5–2.0 µm wide).Description <strong>in</strong> vitro: Colonies on OA 8–10 mm diam <strong>in</strong> 19 d, with aneven, glabrous, colourless or buff <strong>to</strong> rosy-buff marg<strong>in</strong>; immersedmycelium dark green or dull green, but sec<strong>to</strong>rs or other parts ofcolonies may be only olivaceous-buff or rosy-buff <strong>to</strong> salmon;colonies spread<strong>in</strong>g, with irregular elevations <strong>in</strong> the centre on whichconidiomata are formed, releas<strong>in</strong>g a whitish conidial slime; aerialmycelium almost absent <strong>to</strong> well developed and form<strong>in</strong>g a dense,white, woolly-floccose mat; reverse olivaceous-black, locally buff<strong>to</strong> rosy-buff. Colonies on CMA 5–7(–10) mm diam <strong>in</strong> 19 d, as onOA, but more dist<strong>in</strong>ctly elevated and restricted. In faster grow<strong>in</strong>gsec<strong>to</strong>rs salmon <strong>to</strong> ochreous pigmentation (due <strong>to</strong> weak productionof red pigment?) <strong>in</strong> a peripheral zone preceedes the formationa dom<strong>in</strong>ant greens. Conidial slime also milky white, as on OA.Colonies on MEA 9–12 mm diam <strong>in</strong> 19 d, with an even, glabrouscolourless <strong>to</strong> buff marg<strong>in</strong>; colonies restricted, irregularly pustulate <strong>to</strong>hemispherical; immersed mycelium buff <strong>to</strong> honey near the marg<strong>in</strong>,olivaceous-black <strong>in</strong> the centre, sometimes mostly honey; almostentirely covered by a dense, appressed mat of white or grey aerialmycelium; a diffusable pigment sta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the surround<strong>in</strong>g agar moreor less ochreous; reverse usually dark umber or olivaceous-black <strong>in</strong>the centre, surrounded by ochreous, which later becomes fulvous<strong>to</strong> apricot. Colonies on CHA 7–9 mm diam <strong>in</strong> 19 d, with an evenbut later more irregular, glabrous, buff, rosy-buff or flesh marg<strong>in</strong>;colonies pustulate <strong>to</strong> almost hemispherical, the surface ochreous<strong>to</strong> sienna, glabrous, or covered by diffuse, greyish or flesh aerialmycelium; diffusable pigment not observed; reverse blood colour<strong>to</strong> umber.Conidiomata pycnidial or merged <strong>in</strong><strong>to</strong> stromatic complexes,as <strong>in</strong> planta. Conidiogenous cells as <strong>in</strong> planta, mostly cyl<strong>in</strong>dricaland proliferat<strong>in</strong>g percurrently, rarely also sympodially, 7–15(–18) ×2.5–3.5(–4) µm; Conidia as <strong>in</strong> planta but mostly 3–5-septate andconsiderably longer, 30–68(–80) × 1.5–2(–2.5) µm.Hosts: Rubus spp.Material exam<strong>in</strong>ed: Belgium, Oostacker, near Gand, on leaves of Rubus sp.,isotype BR-MYCO 159265-88, also distributed <strong>in</strong> Westend. & Wallay, Herb. crypt.Belge, Fasc. 19, no. 938. Czech Republic, Mikulov, on liv<strong>in</strong>g leaves of Rubussp., 15 Sep. 2008, G. Verkley 6002, <strong>CBS</strong> H-21257. Netherlands, prov. Limburg,Gerendal, on liv<strong>in</strong>g leaves of R. fruticosus s.l., 28 June 2000, G. Verkley 964,epitype designated here <strong>CBS</strong> H-21229 “MBT175362”, liv<strong>in</strong>g cultures ex-epitype<strong>CBS</strong> 109002, 109003; Prov. Limburg, Mookerheide, <strong>in</strong> mixed forest, on liv<strong>in</strong>g leavesof R. fruticosus s.l., 9 Sep. 1999, G. Verkley 923, <strong>CBS</strong> H-21205, liv<strong>in</strong>g culture <strong>CBS</strong>102327; same loc. and substr., 23 Aug. 2004, G. Verkley & M. Star<strong>in</strong>k 3036, <strong>CBS</strong>H-21263, liv<strong>in</strong>g culture <strong>CBS</strong> 117478; same substr., Prov. Limburg, St. Jansbergnear Plasmolen, <strong>in</strong> mixed forest, G. Verkley 924, <strong>CBS</strong> H-21206; Prov. Flevoland,Erkemeder strand, <strong>in</strong> sandy dunes, on liv<strong>in</strong>g leaves of R. fruticosus s.l., 8 Sep. 1999,G. Verkley 930, <strong>CBS</strong> H-21210.Notes: Jørstad (1965) discussed the problems regard<strong>in</strong>g thetaxonomy of Sep<strong>to</strong>ria <strong>species</strong> described from Rubus. Some of thelater described taxa have been placed <strong>in</strong> synonymy with Sep<strong>to</strong>riarubi, but most still need <strong>to</strong> be reevaluated based on fresh material,culture studies, and molecular characterisation. The type material<strong>in</strong> BR conta<strong>in</strong>s several well-preserved leaves of the R. fruticosuscomplex, show<strong>in</strong>g typical symp<strong>to</strong>ms. Fruitbodies <strong>in</strong>vestigatedconta<strong>in</strong>ed mostly 1–3-septate conidia, 17.5–40 × 1–1.5 µm, andwith the typical shape of this common fungus on Rubus spp. Thespecimen <strong>CBS</strong> H-21229 from R. fruticosus <strong>in</strong> the south of theNetherlands, is chosen as epitype. This <strong>species</strong> is nested with<strong>in</strong>the Sphaerul<strong>in</strong>a-clade, and a <strong>new</strong> name <strong>in</strong> Sphaerul<strong>in</strong>a shouldwww.studies<strong>in</strong>mycology.org301