Energy in Australia
Energy-in-Australia-2015
Energy-in-Australia-2015
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
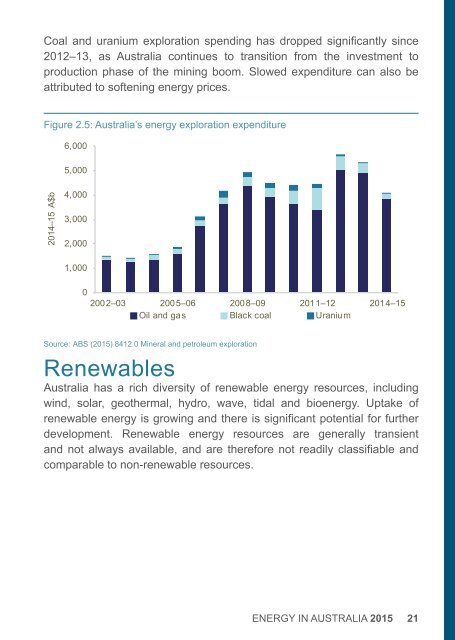
Coal and uranium exploration spend<strong>in</strong>g has dropped significantly s<strong>in</strong>ce<br />
2012–13, as <strong>Australia</strong> cont<strong>in</strong>ues to transition from the <strong>in</strong>vestment to<br />
production phase of the m<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g boom. Slowed expenditure can also be<br />
attributed to soften<strong>in</strong>g energy prices.<br />
Figure 2.5: <strong>Australia</strong>’s energy exploration expenditure<br />
6,000<br />
5,000<br />
2014–15 A$b<br />
4,000<br />
3,000<br />
2,000<br />
1,000<br />
0<br />
2002–03 2005–06 2008–09 2011–12 2014–15<br />
Oil and gas Black coal Uranium<br />
Source: ABS (2015) 8412.0 M<strong>in</strong>eral and petroleum exploration<br />
Renewables<br />
<strong>Australia</strong> has a rich diversity of renewable energy resources, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g<br />
w<strong>in</strong>d, solar, geothermal, hydro, wave, tidal and bioenergy. Uptake of<br />
renewable energy is grow<strong>in</strong>g and there is significant potential for further<br />
development. Renewable energy resources are generally transient<br />
and not always available, and are therefore not readily classifiable and<br />
comparable to non-renewable resources.<br />
ENERGY IN AUSTRALIA 2015 21