You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Pfeiffer <strong>Vacuum</strong><br />
Page 42<br />
<strong>Vacuum</strong> <strong>Technology</strong><br />
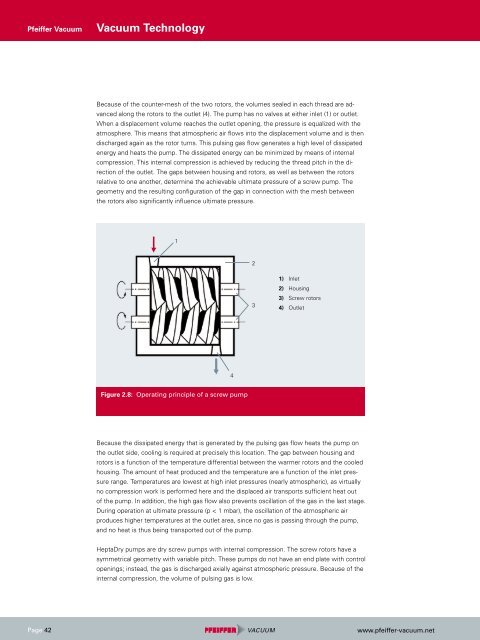
Because of the counter-mesh of the two rotors, the volumes sealed in each thread are advanced<br />
along the rotors to the outlet (4). The pump has no valves at either inlet (1) or outlet.<br />
When a displacement volume reaches the outlet opening, the pressure is equalized with the<br />
atmosphere. This means that atmospheric air flows into the displacement volume and is then<br />
discharged again as the rotor turns. This pulsing gas flow generates a high level of dissipated<br />
energy and heats the pump. The dissipated energy can be minimized by means of internal<br />
compression. This internal compression is achieved by reducing the thread pitch in the direction<br />
of the outlet. The gaps between housing and rotors, as well as between the rotors<br />
relative to one another, determine the achievable ultimate pressure of a screw pump. The<br />
geometry and the resulting configuration of the gap in connection with the mesh between<br />
the rotors also significantly influence ultimate pressure.<br />
Figure 2.8: Operating principle of a screw pump<br />
1<br />
4<br />
1) Inlet<br />
2) Housing<br />
3) Screw rotors<br />
4) Outlet<br />
Because the dissipated energy that is generated by the pulsing gas flow heats the pump on<br />
the outlet side, cooling is required at precisely this location. The gap between housing and<br />
rotors is a function of the temperature differential between the warmer rotors and the cooled<br />
housing. The amount of heat produced and the temperature are a function of the inlet pressure<br />
range. Temperatures are lowest at high inlet pressures (nearly atmospheric), as virtually<br />
no compression work is performed here and the displaced air transports sufficient heat out<br />
of the pump. In addition, the high gas flow also prevents oscillation of the gas in the last stage.<br />
During operation at ultimate pressure (p < 1 mbar), the oscillation of the atmospheric air<br />
produces higher temperatures at the outlet area, since no gas is passing through the pump,<br />
and no heat is thus being transported out of the pump.<br />
HeptaDry pumps are dry screw pumps with internal compression. The screw rotors have a<br />
symmetrical geometry with variable pitch. These pumps do not have an end plate with control<br />
openings; instead, the gas is discharged axially against atmospheric pressure. Because of the<br />
internal compression, the volume of pulsing gas is low.<br />
2<br />
3<br />
www.pfeiffer-vacuum.net