Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a PCM-Supported ...
Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a PCM-Supported ...
Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a PCM-Supported ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
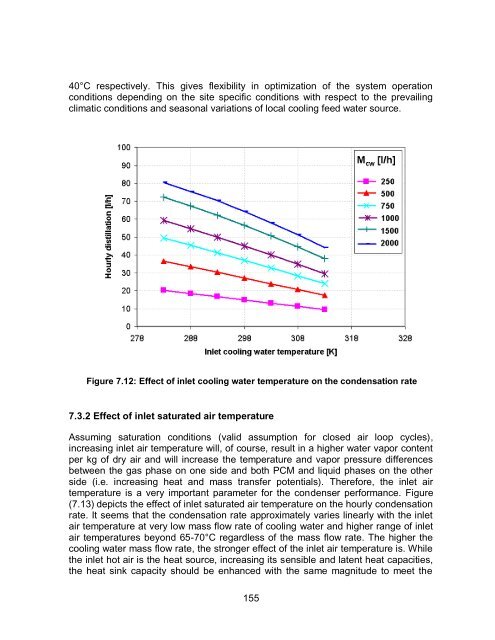
40°C respectively. This gives flexibility in optimization <strong>of</strong> the system operation<br />
conditions depending on the site specific conditions with respect to the prevailing<br />
climatic conditions <strong>and</strong> seasonal variations <strong>of</strong> local cooling feed water source.<br />
Figure 7.12: Effect <strong>of</strong> inlet cooling water temperature on the condensation rate<br />
7.3.2 Effect <strong>of</strong> inlet saturated air temperature<br />
Assuming saturation conditions (valid assumption for closed air loop cycles),<br />
increasing inlet air temperature will, <strong>of</strong> course, result in a higher water vapor content<br />
per kg <strong>of</strong> dry air <strong>and</strong> will increase the temperature <strong>and</strong> vapor pressure differences<br />
between the gas phase on one side <strong>and</strong> both <strong>PCM</strong> <strong>and</strong> liquid phases on the other<br />
side (i.e. increasing heat <strong>and</strong> mass transfer potentials). Therefore, the inlet air<br />
temperature is a very important parameter for the condenser performance. Figure<br />
(7.13) depicts the effect <strong>of</strong> inlet saturated air temperature on the hourly condensation<br />
rate. It seems that the condensation rate approximately varies linearly with the inlet<br />
air temperature at very low mass flow rate <strong>of</strong> cooling water <strong>and</strong> higher range <strong>of</strong> inlet<br />
air temperatures beyond 65-70°C regardless <strong>of</strong> the mass flow rate. The higher the<br />
cooling water mass flow rate, the stronger effect <strong>of</strong> the inlet air temperature is. While<br />
the inlet hot air is the heat source, increasing its sensible <strong>and</strong> latent heat capacities,<br />
the heat sink capacity should be enhanced with the same magnitude to meet the<br />
155