Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a PCM-Supported ...
Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a PCM-Supported ...
Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a PCM-Supported ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
the specified boundary <strong>and</strong> weather conditions, especially that the distillate rate also<br />
decreases below the optimum point at G/L hw =0.67. The optimum theoretical mass<br />
flow ratio would be selected as the intersection point at G/L hw =1.8. However, it is<br />
believed that the right decision depends on the energy source <strong>and</strong> cost, for instance<br />
if the energy is supplied through a waste heat source or has a very low cost the<br />
decision then maybe to adopt the highest distillation rate as the main criterion. It can<br />
also be observed that the impact <strong>of</strong> increasing G/L hw is more pronounced on the<br />
distillate rate than the GOR between the intersection point <strong>and</strong> the maximum<br />
distillation rate. Thus the optimum point would be selected as the mean value<br />
between G/L hw =0.67 <strong>and</strong> G/L hw =1, i.e. ≈0.8-0.9.<br />
8.3.5 Effect <strong>of</strong> cooling water flow rate<br />
Due to existence <strong>of</strong> an<br />
additional heat exchanger at<br />
inlet <strong>of</strong> the condenser to bring<br />
the cooling water temperature<br />
down to the ambient<br />
conditions, the condenser<br />
performance is expected to<br />
be always better at higher<br />
mass flow rates <strong>of</strong> the<br />
coolant. But the mass flow<br />
rate has a strong effect on<br />
the outlet cooling water<br />
temperature, which in turn is<br />
extremely important since it<br />
determines the amount <strong>of</strong><br />
latent heat recovery through<br />
the main heat exchanger<br />
downstream <strong>of</strong> the<br />
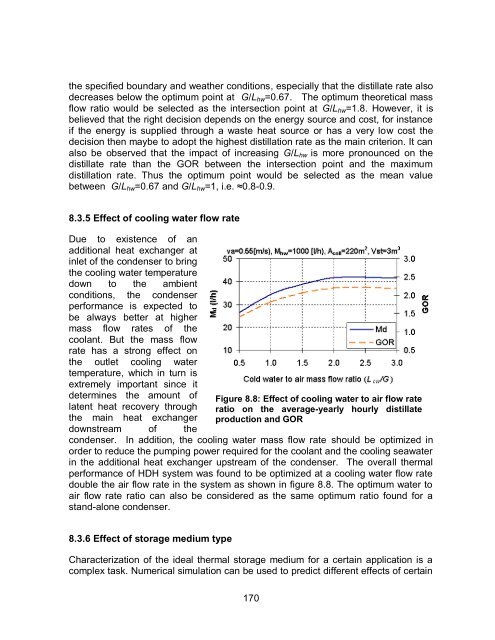
Figure 8.8: Effect <strong>of</strong> cooling water to air flow rate<br />
ratio on the average-yearly hourly distillate<br />
production <strong>and</strong> GOR<br />
condenser. In addition, the cooling water mass flow rate should be optimized in<br />
order to reduce the pumping power required for the coolant <strong>and</strong> the cooling seawater<br />
in the additional heat exchanger upstream <strong>of</strong> the condenser. The overall thermal<br />
performance <strong>of</strong> HDH system was found to be optimized at a cooling water flow rate<br />
double the air flow rate in the system as shown in figure 8.8. The optimum water to<br />
air flow rate ratio can also be considered as the same optimum ratio found for a<br />
st<strong>and</strong>-alone condenser.<br />
8.3.6 Effect <strong>of</strong> storage medium type<br />
Characterization <strong>of</strong> the ideal thermal storage medium for a certain application is a<br />
complex task. <strong>Numerical</strong> simulation can be used to predict different effects <strong>of</strong> certain<br />
170