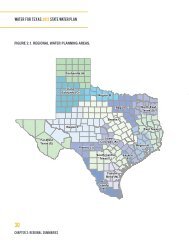
(GP/GT) for Additional Water Supply in the Lower Rio Grande
(GP/GT) for Additional Water Supply in the Lower Rio Grande
(GP/GT) for Additional Water Supply in the Lower Rio Grande
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
ill-I5<br />
The tube plates are usually rectangular and made of non-ferrous material compatible with <strong>the</strong> tubes.<br />
Intermediate tube support plates are spaced across <strong>the</strong> vessel to ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> tube separation and prevent<br />
vibration. In spite of cont<strong>in</strong>u<strong>in</strong>g research <strong>in</strong>to use of enhanced-profile tubes, pla<strong>in</strong> circular tubes are still<br />
<strong>the</strong> usual supply. In <strong>the</strong> cross-tube MSF plant, <strong>the</strong>re may be several seawater passes through each stage,<br />
with correspond<strong>in</strong>g complexity of <strong>the</strong> waterbox designs at each end of <strong>the</strong> tube bundle. Depend<strong>in</strong>g on<br />
temperature regime and fluid chemistry, water boxes are usually l<strong>in</strong>ed with ei<strong>the</strong>r epoxy res<strong>in</strong>, neoprene,<br />
butyl rubber or cupro-nickel and may <strong>in</strong>corporate sacrificial anodes to m<strong>in</strong>imize corrosion/erosion of tube<br />
ends and tube plates.<br />
Inside each evaporator stage <strong>the</strong>re are mist-separator pads, usually fill<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> whole horizontal crosssection<br />
adjacent to <strong>the</strong> distillate trays. These are normally of knitted sta<strong>in</strong>less steel or monel wire,<br />
supported on a sta<strong>in</strong>less steel framework. The area of <strong>the</strong> vessel shell above <strong>the</strong> mist-separator pad is<br />
generally less prone to corrosion than <strong>the</strong> ma<strong>in</strong> body of <strong>the</strong> flash chamber, s<strong>in</strong>ce it does not get splashed<br />
with br<strong>in</strong>e. It is <strong>the</strong>re<strong>for</strong>e customary not to apply any protective cladd<strong>in</strong>g or l<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g to <strong>the</strong> vessel above<br />
mist-separator level, except <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> hottest one or two stages, where carbon dioxide may be released from<br />
<strong>the</strong> br<strong>in</strong>e. These hottest stages are often l<strong>in</strong>ed throughout with sta<strong>in</strong>less steel and separately vented to <strong>the</strong><br />
ejector system.<br />
At <strong>the</strong> bottom of each stage, br<strong>in</strong>e boxes <strong>in</strong>corporat<strong>in</strong>g gates and weirs control <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>terstage flow and<br />
prevent "unseal<strong>in</strong>g" between stages dur<strong>in</strong>g start-up and load chang<strong>in</strong>g, when liquid levels tend to fluctuate<br />
widely. Because of <strong>the</strong> high br<strong>in</strong>e velocities and extreme turbulence, <strong>the</strong>se components are almost<br />
<strong>in</strong>variably made of sta<strong>in</strong>less steel.<br />
The br<strong>in</strong>e heater is usually a separate vessel <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>for</strong>m of conventional steam/water shell-and-tube<br />
cyl<strong>in</strong>drical heat exchanger, with carbon steel shell and non-ferrous tubes. It may have several passes on<br />
<strong>the</strong> br<strong>in</strong>e side and a number of steam entries at <strong>the</strong> top.<br />
The vent<strong>in</strong>g system often <strong>in</strong>corporates a separate hogg<strong>in</strong>g ejector <strong>for</strong> quick start-up and ei<strong>the</strong>r a two or<br />
three stage ejector system, with <strong>in</strong>termediate and f<strong>in</strong>al condensers <strong>for</strong> normal operation. Sophisticated<br />
materials and/or l<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>gs are often used to m<strong>in</strong>imize corrosion of <strong>the</strong> ejector system under <strong>the</strong> aggressive<br />
work<strong>in</strong>g conditions.<br />
To economize on <strong>in</strong>stallation area, cross-tube evaporator vessels are sometimes built <strong>in</strong> a two-tier<br />
arrangement. When consider<strong>in</strong>g plot layouts <strong>for</strong> both long and cross-tube MSF plants, allowance has to<br />
be made <strong>for</strong> tube-withdrawal space. Nearly all MSF plants are <strong>in</strong>stalled outdoors. In places with tropical<br />
or aggressive climates, some components such as pumps and control devices may have wea<strong>the</strong>r-protective<br />
canopies or sunshades. Very small plants can sometimes be shipped and delivered to site as fully-f<strong>in</strong>ished<br />
units and even <strong>for</strong> very large plants, special transport and handl<strong>in</strong>g facilities are often constructed as part<br />
of <strong>the</strong> project, such that f<strong>in</strong>ished modules weigh<strong>in</strong>g up to about 2,000 tons can be brought to site and<br />
placed on <strong>the</strong>ir foundations.<br />
5. Cogeneration of Electricity and <strong>Water</strong><br />
By far <strong>the</strong> largest use of MSF plant is <strong>in</strong> comb<strong>in</strong>ed-cycle (or dual-purpose) municipal <strong>in</strong>stallations<br />
produc<strong>in</strong>g both dr<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g water and electricity. By comb<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g power and water <strong>in</strong> a s<strong>in</strong>gle undertak<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
a number of capital and operation cost sav<strong>in</strong>gs can be achieved.