Download - Maize
Download - Maize
Download - Maize
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
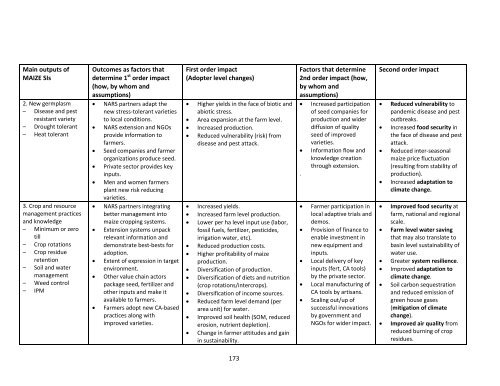
Main outputs of<br />
MAIZE SIs<br />
2. New germplasm<br />
– Disease and pest<br />
resistant variety<br />
– Drought tolerant<br />
– Heat tolerant<br />
3. Crop and resource<br />
management practices<br />
and knowledge<br />
– Minimum or zero<br />
till<br />
– Crop rotations<br />
– Crop residue<br />
retention<br />
– Soil and water<br />
management<br />
– Weed control<br />
– IPM<br />
Outcomes as factors that<br />
determine 1 st order impact<br />
(how, by whom and<br />
assumptions)<br />
NARS partners adapt the<br />
new stress‐tolerant varieties<br />
to local conditions.<br />
NARS extension and NGOs<br />
provide information to<br />
farmers.<br />
Seed companies and farmer<br />
organizations produce seed.<br />
Private sector provides key<br />
inputs.<br />
Men and women farmers<br />
plant new risk reducing<br />
varieties.<br />
NARS partners integrating<br />
better management into<br />
maize cropping systems.<br />
Extension systems unpack<br />
relevant information and<br />
demonstrate best‐bests for<br />
adoption.<br />
Extent of expression in target<br />
environment.<br />
Other value chain actors<br />
package seed, fertilizer and<br />
other inputs and make it<br />
available to farmers.<br />
Farmers adopt new CA‐based<br />
practices along with<br />
improved varieties.<br />
First order impact<br />
(Adopter level changes)<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Higher yields in the face of biotic and<br />
abiotic stress.<br />
Area expansion at the farm level.<br />
Increased production.<br />
Reduced vulnerability (risk) from<br />
disease and pest attack.<br />
Increased yields.<br />
Increased farm level production.<br />
Lower per ha level input use (labor,<br />
fossil fuels, fertilizer, pesticides,<br />
irrigation water, etc).<br />
Reduced production costs.<br />
Higher profitability of maize<br />
production.<br />
Diversification of production.<br />
Diversification of diets and nutrition<br />
(crop rotations/intercrops).<br />
Diversification of income sources.<br />
Reduced farm level demand (per<br />
area unit) for water.<br />
Improved soil health (SOM, reduced<br />
erosion, nutrient depletion).<br />
Change in farmer attitudes and gain<br />
in sustainability.<br />
Factors that determine<br />
2nd order impact (how,<br />
by whom and<br />
assumptions)<br />
Increased participation<br />
of seed companies for<br />
production and wider<br />
diffusion of quality<br />
seed of improved<br />
varieties.<br />
Information flow and<br />
knowledge creation<br />
through extension.<br />
.<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Farmer participation in<br />
local adaptive trials and<br />
demos.<br />
Provision of finance to<br />
enable investment in<br />
new equipment and<br />
inputs.<br />
Local delivery of key<br />
inputs (fert, CA tools)<br />
by the private sector.<br />
Local manufacturing of<br />
CA tools by artisans.<br />
Scaling out/up of<br />
successful innovations<br />
by government and<br />
NGOs for wider impact.<br />
Second order impact<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Reduced vulnerability to<br />
pandemic disease and pest<br />
outbreaks.<br />
Increased food security in<br />
the face of disease and pest<br />
attack.<br />
Reduced inter‐seasonal<br />
maize price fluctuation<br />
(resulting from stability of<br />
production).<br />
Increased adaptation to<br />
climate change.<br />
Improved food security at<br />
farm, national and regional<br />
scale.<br />
Farm level water saving<br />
that may also translate to<br />
basin level sustainability of<br />
water use.<br />
Greater system resilience.<br />
Improved adaptation to<br />
climate change.<br />
Soil carbon sequestration<br />
and reduced emission of<br />
green house gases<br />
(mitigation of climate<br />
change).<br />
Improved air quality from<br />
reduced burning of crop<br />
residues.<br />
173