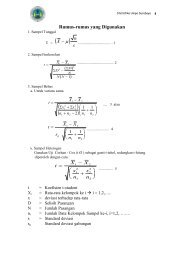
- Page 2 and 3:
HSRC SERIES IN METHODOLOGYSeries Ed
- Page 4 and 5:
All rights reserved. No part of thi
- Page 6 and 7:
PART 3Appendix 1M Ferreira — A so
- Page 8 and 9:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 10 and 11:
important methods of operationalizi
- Page 12 and 13:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 14 and 15:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 16 and 17:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 18 and 19:
Introduction: The scientific langua
- Page 20 and 21:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 22 and 23:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 24 and 25:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 26 and 27:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 28 and 29:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 30 and 31:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 32 and 33:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 34 and 35:
inevitably be found in the discipli
- Page 36 and 37:
At the project level, three general
- Page 38 and 39:
FIGURE 1.3Free download from www.hs
- Page 40 and 41:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 42 and 43:
context of a particular research tr
- Page 44 and 45:
Introduction: Social sciences resea
- Page 46 and 47:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 48 and 49:
all the factors which may pose a th
- Page 50 and 51:
(3) Conceptualization and operation
- Page 52 and 53:
negative influence on the person’
- Page 54 and 55:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 56 and 57:
CONDITIONS ORIENTATIONS ACTIONSINDI
- Page 58 and 59:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 60 and 61:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 62 and 63:
to indicate a causal relationship b
- Page 64 and 65:
flict with a point of view in which
- Page 66 and 67:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 68 and 69:
Our discussion of problem formulati
- Page 70 and 71:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 72 and 73:
IntroductionConcept and meaningConc
- Page 74 and 75:
ductivism, refers to the belief tha
- Page 76 and 77:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 78 and 79:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 80 and 81:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 82 and 83:
Social isolation1. Sometimes I feel
- Page 84 and 85:
manifestations of alienation, it ou
- Page 86 and 87:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 88 and 89:
found between theoretical and conce
- Page 90 and 91:
IntroductionSources of data, reacti
- Page 92 and 93:
that they have tradition, culture,
- Page 94 and 95:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 96 and 97:
categories. Finally, the research c
- Page 98 and 99:
affiliation, or presumed affiliatio
- Page 100 and 101:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 102 and 103:
pectancy effects was conducted by R
- Page 104 and 105:
ticipant’s perception of his or h
- Page 106 and 107:
(v) Questionnaire length effects(vi
- Page 108 and 109:
We have, in an earlier section, dra
- Page 110 and 111:
example of the double blind experim
- Page 112 and 113:
CONSTRUCTIVE REPLICATIONIn conclusi
- Page 114 and 115:
IntroductionAn example: The Reiger
- Page 116 and 117:
Coloured youths were fatally wounde
- Page 118 and 119:
ehaving violently towards some of t
- Page 120 and 121:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 122 and 123:
multivariate techniques are much mo
- Page 124 and 125:
tial validity. A closer inspection
- Page 126 and 127:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 128 and 129:
validity (as a rule we will not use
- Page 130 and 131:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 132 and 133:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 134 and 135:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 136 and 137:
CONTEXT EFFECTSIs it reasonable to
- Page 138 and 139:
analysis, text analysis, and case s
- Page 140 and 141:
IntroductionConceptsStatementsConno
- Page 142 and 143:
The schematic representation also g
- Page 144 and 145:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 146 and 147:
DICHOTOMOUS, POLYTOMIC AND CONTINUO
- Page 148 and 149:
People therefore, depending upon th
- Page 150 and 151:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 152 and 153:
higher than the mean scores on meth
- Page 154 and 155:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 156 and 157:
Source ofinformation Sender Recipie
- Page 158 and 159:
of the modellandum which are deemed
- Page 160 and 161:
phenomena or variables and, for thi
- Page 162 and 163:
i.e. from a collection of mutually
- Page 164 and 165:
Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 166 and 167:
system, the Aristotelian theory of
- Page 168 and 169:
IntroductionThe spectrum of the soc
- Page 170 and 171:
• How do scientist study underlyi
- Page 172 and 173:
the scope is more likely to be unde
- Page 174 and 175:
A number of comments will serve to
- Page 176 and 177:
ConceptsIn figure 7.2 below, qualit
- Page 178 and 179:
A research report is usually a logi
- Page 180 and 181:
to be found between qualitative and
- Page 182 and 183:
at which people are placed towards
- Page 184 and 185:
The different levels can probably b
- Page 186 and 187: proach should be canonized and anot
- Page 188 and 189: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 190 and 191: Goals of this chapterIntroductory r
- Page 192 and 193: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 194 and 195: is written, the wise researcher wou
- Page 196 and 197: Some of the characteristics that ar
- Page 198 and 199: falls within more than one discipli
- Page 200 and 201: earlier on. The aim of the project,
- Page 202 and 203: Example 3Title of projectAtlas of l
- Page 204 and 205: IntroductionThe context of reportin
- Page 206 and 207: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 208 and 209: METATHEORETICAL GUIDEIINESIt is gen
- Page 210 and 211: the researcher’s views, insuffici
- Page 212 and 213: Suggestions for further reading:Bes
- Page 214 and 215: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 216 and 217: 2. THEORETICAL ORIENTATIONMedical s
- Page 218 and 219: particular outpatient centre experi
- Page 220 and 221: 3. METHODOLOGICAL STRATEGYSymbolic
- Page 222 and 223: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 224 and 225: the organisation). Secondly, a larg
- Page 226 and 227: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 228 and 229: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 230 and 231: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 232 and 233: tations of the subjects; it is conc
- Page 234 and 235: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 238 and 239: 16. First half of 1981.17. Gold (19
- Page 240 and 241: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 242 and 243: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 244 and 245: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 246 and 247: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 248 and 249: 2. How is value-orientation defined
- Page 250 and 251: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 252 and 253: in practice. In contrast, pragmatis
- Page 254 and 255: ian style of management result in l
- Page 256 and 257: Quality of supervision of stoping g
- Page 258 and 259: TABLE IIIANALYSIS OF VARIANCE FOR M
- Page 260 and 261: FIGURE 2 — SECOND ORDER INTERACTI
- Page 262 and 263: A further consideration in the choi
- Page 264 and 265: gangs with supervision that was ass
- Page 266 and 267: percentage of transfers not being m
- Page 268 and 269: for all the relevant factors. Discu
- Page 270 and 271: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 272 and 273: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 274 and 275: Free download from www.hsrcpress.ac
- Page 276 and 277: WHITE, V.P. (ed.). 1983. Grant prop
- Page 278 and 279: connotation 58ff, 126ff- convention
- Page 280 and 281: hermeneutics 21heuristic function,
- Page 282 and 283: Naive inductivism 57naturalistic re
- Page 284 and 285: esearcher image 82-83researcher ori