Single-Chip Low Cost Low Power RF-Transceiver (Rev. A)
Single-Chip Low Cost Low Power RF-Transceiver (Rev. A)
Single-Chip Low Cost Low Power RF-Transceiver (Rev. A)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
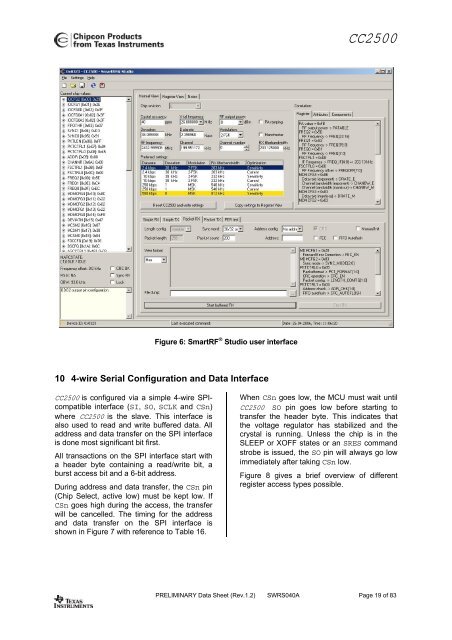
CC2500Figure 6: Smart<strong>RF</strong> ® Studio user interface10 4-wire Serial Configuration and Data InterfaceCC2500 is configured via a simple 4-wire SPIcompatibleinterface (SI, SO, SCLK and CSn)where CC2500 is the slave. This interface isalso used to read and write buffered data. Alladdress and data transfer on the SPI interfaceis done most significant bit first.All transactions on the SPI interface start witha header byte containing a read/write bit, aburst access bit and a 6-bit address.During address and data transfer, the CSn pin(<strong>Chip</strong> Select, active low) must be kept low. IfCSn goes high during the access, the transferwill be cancelled. The timing for the addressand data transfer on the SPI interface isshown in Figure 7 with reference to Table 16.When CSn goes low, the MCU must wait untilCC2500 SO pin goes low before starting totransfer the header byte. This indicates thatthe voltage regulator has stabilized and thecrystal is running. Unless the chip is in theSLEEP or XOFF states or an SRES commandstrobe is issued, the SO pin will always go lowimmediately after taking CSn low.Figure 8 gives a brief overview of differentregister access types possible.PRELIMINARY Data Sheet (<strong>Rev</strong>.1.2) SWRS040A Page 19 of 83









![td-res-4 [Compatibility Mode]](https://img.yumpu.com/45826987/1/184x260/td-res-4-compatibility-mode.jpg?quality=85)




