“Key Informant Survey” of Production, Value, Losses and ... - DfID
“Key Informant Survey” of Production, Value, Losses and ... - DfID
“Key Informant Survey” of Production, Value, Losses and ... - DfID
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
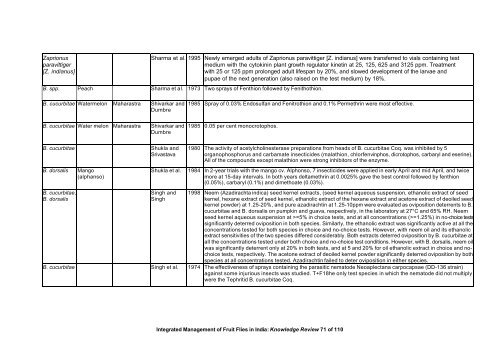
Zaprionus<br />
paravittiger<br />
[Z. indianus]<br />
Sharma et al. 1995 Newly emerged adults <strong>of</strong> Zaprionus paravittiger [Z. indianus] were transferred to vials containing test<br />
medium with the cytokinin plant growth regulator kinetin at 25, 125, 625 <strong>and</strong> 3125 ppm. Treatment<br />
with 25 or 125 ppm prolonged adult lifespan by 20%, <strong>and</strong> slowed development <strong>of</strong> the larvae <strong>and</strong><br />
pupae <strong>of</strong> the next generation (also raised on the test medium) by 18%.<br />
B. spp. Peach Sharma et al. 1973 Two sprays <strong>of</strong> Fenthion followed by Fenithothion.<br />
B. cucurbitae Watermelon Maharastra Shivarkar <strong>and</strong><br />
Dumbre<br />
B. cucurbitae Water melon Maharastra Shivarkar <strong>and</strong><br />
Dumbre<br />
B. cucurbitae Shukla <strong>and</strong><br />
Srivastava<br />
B. dorsalis Mango<br />
(alphanso)<br />
B. cucurbitae,<br />
B. dorsalis<br />
1985 Spray <strong>of</strong> 0.03% Endosulfan <strong>and</strong> Fenitrothion <strong>and</strong> 0.1% Permethrin were most effective.<br />
1985 0.05 per cent monocrotophos.<br />
1980 The activity <strong>of</strong> acetylcholinesterase preparations from heads <strong>of</strong> B. cucurbitae Coq. was inhibited by 5<br />
organophosphorus <strong>and</strong> carbamate insecticides (malathion, chlorfenvinphos, dicrotophos, carbaryl <strong>and</strong> eserine).<br />
All <strong>of</strong> the compounds except malathion were strong inhibitors <strong>of</strong> the enzyme.<br />
Shukla et al. 1984 In 2-year trials with the mango cv. Alphonso, 7 insecticides were applied in early April <strong>and</strong> mid April, <strong>and</strong> twice<br />
more at 15-day intervals. In both years deltamethrin at 0.0025% gave the best control followed by fenthion<br />
(0.05%), carbaryl (0.1%) <strong>and</strong> dimethoate (0.03%).<br />
Singh <strong>and</strong><br />
Singh<br />
1998 Neem (Azadirachta indica) seed kernel extracts, (seed kernel aqueous suspension, ethanolic extract <strong>of</strong> seed<br />
kernel, hexane extract <strong>of</strong> seed kernel, ethanolic extract <strong>of</strong> the hexane extract <strong>and</strong> acetone extract <strong>of</strong> deoiled seed<br />
kernel powder) at 1.25-20%, <strong>and</strong> pure azadirachtin at 1.25-10ppm were evaluated as oviposition deterrents to B.<br />
cucurbitae <strong>and</strong> B. dorsalis on pumpkin <strong>and</strong> guava, respectively, in the laboratory at 27°C <strong>and</strong> 65% RH. Neem<br />
seed kernel aqueous suspension at >=5% in choice tests, <strong>and</strong> at all concentrations (>=1.25%) in no-choice tests<br />
significantly deterred oviposition in both species. Similarly, the ethanolic extract was significantly active at all the<br />
concentrations tested for both species in choice <strong>and</strong> no-choice tests. However, with neem oil <strong>and</strong> its ethanolic<br />
extract sensitivities <strong>of</strong> the two species differed considerably. Both extracts deterred oviposition by B. cucurbitae at<br />
all the concentrations tested under both choice <strong>and</strong> no-choice test conditions. However, with B. dorsalis, neem oil<br />
was significantly deterrent only at 20% in both tests, <strong>and</strong> at 5 <strong>and</strong> 20% for oil ethanolic extract in choice <strong>and</strong> nochoice<br />
tests, respectively. The acetone extract <strong>of</strong> deoiled kernel powder significantly deterred oviposition by both<br />
species at all concentrations tested. Azadirachtin failed to deter oviposition in either species.<br />
B. cucurbitae Singh et al. 1974 The effectiveness <strong>of</strong> sprays containing the parasitic nematode Neoaplectana carpocapsae (DD-136 strain)<br />
against some injurious insects was studied. T+F18he only test species in which the nematode did not multiply<br />
were the Tephritid B. cucurbitae Coq.<br />
Integrated Management <strong>of</strong> Fruit Flies in India: Knowledge Review 71 <strong>of</strong> 110