“Key Informant Survey” of Production, Value, Losses and ... - DfID
“Key Informant Survey” of Production, Value, Losses and ... - DfID
“Key Informant Survey” of Production, Value, Losses and ... - DfID
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
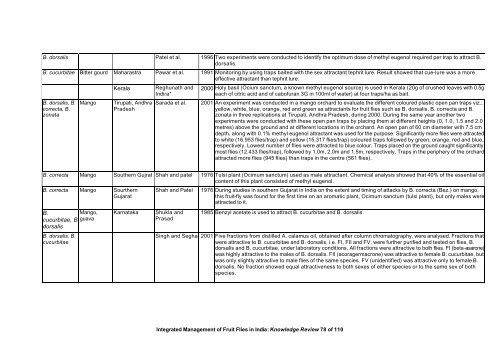
B. dorsalis Patel et al. 1996 Two experiments were conducted to identify the optimum dose <strong>of</strong> methyl eugenol required per trap to attract B.<br />
dorsalis.<br />
B. cucurbitae Bitter gourd Maharastra Pawar et al. 1991 Monitoring by using traps baited with the sex attractant tephrit lure. Result showed that cue-lure was a more<br />
effective attractant than tephrit lure.<br />
B. dorsalis, B.<br />
correcta, B.<br />
zonata<br />
Kerala Reghunath <strong>and</strong><br />
Indira*<br />
Mango Tirupati, Andhra<br />
Pradesh<br />
2000 Holy basil (Ocium sanctum, a known methyl eugenol source) is used in Kerala (20g <strong>of</strong> crushed leaves with 0.5g<br />
each <strong>of</strong> citric acid <strong>and</strong> <strong>of</strong> cab<strong>of</strong>uran 3G in 100ml <strong>of</strong> water) at four traps/ha as bait.<br />
Sarada et al. 2001 An experiment was conducted in a mango orchard to evaluate the different coloured plastic open pan traps viz.,<br />
yellow, white, blue, orange, red <strong>and</strong> green as attractants for fruit flies such as B. dorsalis, B. correcta <strong>and</strong> B.<br />
zonata in three replications at Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, during 2000. During the same year another two<br />
experiments were conducted with these open pan traps by placing them at different heights (0, 1.0, 1.5 <strong>and</strong> 2.0<br />
metres) above the ground <strong>and</strong> at different locations in the orchard. An open pan <strong>of</strong> 60 cm diameter with 7.5 cm<br />
depth, along with 0.1% methyl eugenol attractant was used for the purpose. Significantly more flies were attracted<br />
to white (16.953 flies/trap) <strong>and</strong> yellow (15.317 flies/trap) coloured traps followed by green, orange, red <strong>and</strong> blue,<br />
respectively. Lowest number <strong>of</strong> flies were attracted to blue colour. Traps placed on the ground caught significantly<br />
most flies (12.433 flies/trap), followed by 1.0m, 2.0m <strong>and</strong> 1.5m, respectively. Traps in the periphery <strong>of</strong> the orchard<br />
attracted more flies (945 flies) than traps in the centre (561 flies).<br />
B. correcta Mango Southern Gujrat Shah <strong>and</strong> patel 1976 Tulsi plant (Ocimum sanctum) used as male attractant. Chemical analysis showed that 40% <strong>of</strong> the essential oil<br />
content <strong>of</strong> this plant consisted <strong>of</strong> methyl eugenol.<br />
B. correcta Mango Sourthern<br />
Gujarat<br />
B.<br />
Mango,<br />
cucurbitae, B guava<br />
dorsalis<br />
B. dorsalis, B.<br />
cucurbitae<br />
Karnataka Shukla <strong>and</strong><br />
Prasad<br />
Shah <strong>and</strong> Patel 1976 During studies in southern Gujarat in India on the extent <strong>and</strong> timing <strong>of</strong> attacks by B. correcta (Bez.) on mango,<br />
this fruit-fly was found for the first time on an aromatic plant, Ocimum sanctum (tulsi plant), but only males were<br />
attracted to it.<br />
1985 Benzyl acetate is used to attract B. cucurbitae <strong>and</strong> B. dorsalis.<br />
Singh <strong>and</strong> Seghal 2001 Five fractions from distilled A. calamus oil, obtained after column chromatography, were analysed. Fractions that<br />
were attractive to B. cucurbitae <strong>and</strong> B. dorsalis, i.e. FI, FII <strong>and</strong> FV, were further purified <strong>and</strong> tested on flies, B.<br />
dorsalis <strong>and</strong> B. cucurbitae, under laboratory conditions. All fractions were attractive to both flies. FI (beta-asarone)<br />
was highly attractive to the males <strong>of</strong> B. dorsalis. FII (acoragermacrone) was attractive to female B. cucurbitae, but<br />
was only slightly attractive to male flies <strong>of</strong> the same species. FV (unidentified) was attractive only to female B.<br />
dorsalis. No fraction showed equal attractiveness to both sexes <strong>of</strong> either species or to the same sex <strong>of</strong> both<br />
species.<br />
Integrated Management <strong>of</strong> Fruit Flies in India: Knowledge Review 78 <strong>of</strong> 110