3+4+Supplementum/2012 - Společnost pro pojivové tkáně
3+4+Supplementum/2012 - Společnost pro pojivové tkáně
3+4+Supplementum/2012 - Společnost pro pojivové tkáně
- TAGS
- www.pojivo.cz
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
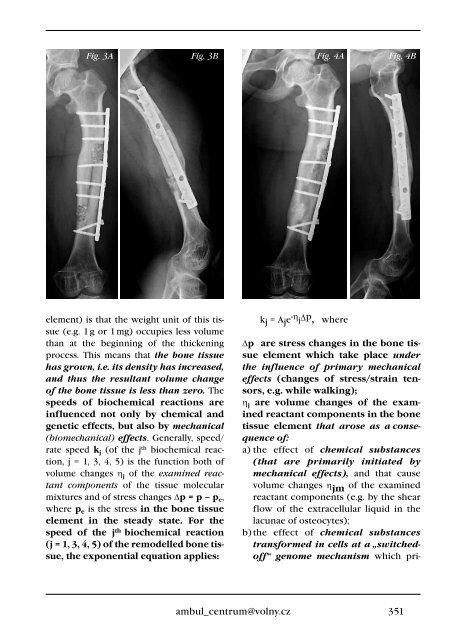
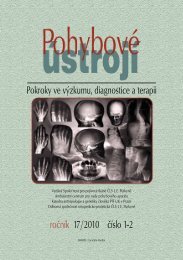
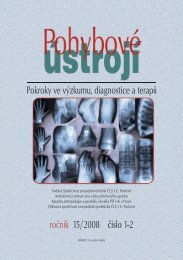
Fig. 3A Fig. 3B Fig. 4A<br />
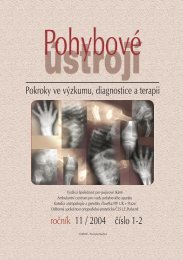
Fig. 4B<br />
element) is that the weight unit of this tissue<br />
(e.g. 1 g or 1 mg) occupies less volume<br />
than at the beginning of the thickening<br />
<strong>pro</strong>cess. This means that the bone tissue<br />
has grown, i.e. its density has increased,<br />
and thus the resultant volume change<br />
of the bone tissue is less than zero. The<br />
speeds of biochemical reactions are<br />
influenced not only by chemical and<br />
genetic effects, but also by mechanical<br />
(biomechanical) effects. Generally, speed/<br />
rate speed k j (of the j th biochemical reaction,<br />
j = 1, 3, 4, 5) is the function both of<br />
volume changes η j of the examined reactant<br />
components of the tissue molecular<br />
mixtures and of stress changes ∆p = p – p e,<br />
where p e is the stress in the bone tissue<br />
element in the steady state. for the<br />
speed of the j th biochemical reaction<br />
(j = 1, 3, 4, 5) of the remodelled bone tissue,<br />
the exponential equation applies:<br />
ambul_centrum@volny.cz<br />
kj = Aje -η j∆p , where<br />
∆p are stress changes in the bone tissue<br />
element which take place under<br />
the influence of primary mechanical<br />
effects (changes of stress/strain tensors,<br />
e.g. while walking);<br />
ηj are volume changes of the examined<br />
reactant components in the bone<br />
tissue element that arose as a consequence<br />
of:<br />
a) the effect of chemical substances<br />
(that are primarily initiated by<br />
mechanical effects), and that cause<br />
volume changes ηjm of the examined<br />
reactant components (e.g. by the shear<br />
flow of the extracellular liquid in the<br />
lacunae of osteocytes);<br />
b) the effect of chemical substances<br />
transformed in cells at a „switchedoff“<br />
genome mechanism which pri-<br />
351