desarrollo y validación de metodología para minimizar la ...
desarrollo y validación de metodología para minimizar la ...
desarrollo y validación de metodología para minimizar la ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
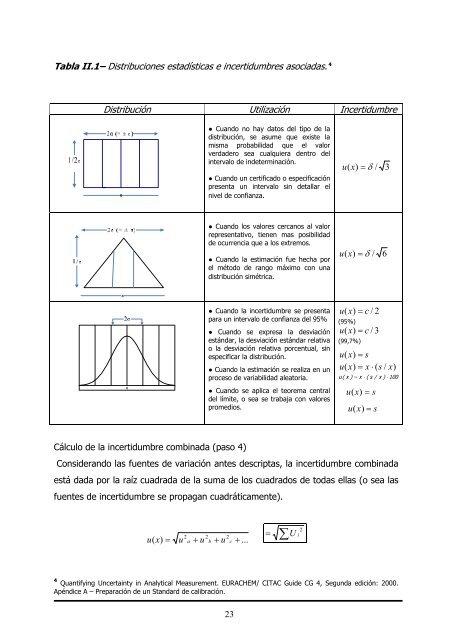
Tab<strong>la</strong> II.1– Distribuciones estadísticas e incertidumbres asociadas. 4<br />
Distribución Utilización Incertidumbre<br />
Cálculo <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> incertidumbre combinada (paso 4)<br />
Consi<strong>de</strong>rando <strong>la</strong>s fuentes <strong>de</strong> variación antes <strong>de</strong>scriptas, <strong>la</strong> incertidumbre combinada<br />
está dada por <strong>la</strong> raíz cuadrada <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> suma <strong>de</strong> los cuadrados <strong>de</strong> todas el<strong>la</strong>s (o sea <strong>la</strong>s<br />
fuentes <strong>de</strong> incertidumbre se propagan cuadráticamente).<br />
2 2 2<br />
u ( x)<br />
= u a + u b + u c + ... ∑ = U<br />
4 Quantifying Uncertainty in Analytical Measurement. EURACHEM/ CITAC Gui<strong>de</strong> CG 4, Segunda edición: 2000.<br />
Apéndice A – Pre<strong>para</strong>ción <strong>de</strong> un Standard <strong>de</strong> calibración.<br />
● Cuando no hay datos <strong>de</strong>l tipo <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong><br />
distribución, se asume que existe <strong>la</strong><br />
misma probabilidad que el valor<br />
verda<strong>de</strong>ro sea cualquiera <strong>de</strong>ntro <strong>de</strong>l<br />
intervalo <strong>de</strong> in<strong>de</strong>terminación.<br />
● Cuando un certificado o especificación<br />
presenta un intervalo sin <strong>de</strong>tal<strong>la</strong>r el<br />
nivel <strong>de</strong> confianza.<br />
● Cuando los valores cercanos al valor<br />
representativo, tienen mas posibilidad<br />
<strong>de</strong> ocurrencia que a los extremos.<br />
● Cuando <strong>la</strong> estimación fue hecha por<br />
el método <strong>de</strong> rango máximo con una<br />
distribución simétrica.<br />
● Cuando <strong>la</strong> incertidumbre se presenta<br />
<strong>para</strong> un intervalo <strong>de</strong> confianza <strong>de</strong>l 95%<br />
● Cuando se expresa <strong>la</strong> <strong>de</strong>sviación<br />
estándar, <strong>la</strong> <strong>de</strong>sviación estándar re<strong>la</strong>tiva<br />
o <strong>la</strong> <strong>de</strong>sviación re<strong>la</strong>tiva porcentual, sin<br />
especificar <strong>la</strong> distribución.<br />
● Cuando <strong>la</strong> estimación se realiza en un<br />
proceso <strong>de</strong> variabilidad aleatoria.<br />
● Cuando se aplica el teorema central<br />
<strong>de</strong>l límite, o sea se trabaja con valores<br />
promedios.<br />
23<br />
2<br />
i<br />
u ( x)<br />
= δ /<br />
u ( x)<br />
= δ /<br />
u ( x)<br />
= c / 2<br />
(95%)<br />
u ( x)<br />
= c / 3<br />
(99,7%)<br />
6<br />
3<br />
u ( x)<br />
= s<br />
u( x)<br />
= x ⋅ ( s / x)<br />
u ( x ) = x ⋅ ( s / x ) ⋅ 100<br />
u ( x)<br />
= s<br />
u (<br />
x)<br />
= s