Reviews in Computational Chemistry Volume 18
Reviews in Computational Chemistry Volume 18
Reviews in Computational Chemistry Volume 18
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
develop<strong>in</strong>g polarizable models. A vast literature exists <strong>in</strong> this area, with<br />
applications rang<strong>in</strong>g from the solvation of simple ions 27,82,202,217,2<strong>18</strong> and<br />
biomolecules 10 to hydrophobic hydration and the structure of water at <strong>in</strong>terfaces<br />
104,219,220 and <strong>in</strong> external electric fields. 206,220 Due to the wide variation<br />
<strong>in</strong> electrostatic environments encountered, it is not surpris<strong>in</strong>g to f<strong>in</strong>d that<br />
polarizable models generally (but not always) provide significant improvements<br />
over nonpolarizable models.<br />
Prote<strong>in</strong>s and Nucleic Acids<br />
For both prote<strong>in</strong>s and nucleic acids, there exist significant structuredeterm<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g,<br />
hydrogen-bond<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>teractions between groups with p electrons:<br />
the peptide group for prote<strong>in</strong>s and bases for nucleic acids. The extensive network<br />
of peptide hydrogen bonds <strong>in</strong> a-helices and b-sheets <strong>in</strong> prote<strong>in</strong>s and the<br />
base-pair stack<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the double helix of nucleic acids are stablized by polarization<br />
of electrons with some p character. This stabilization has been labeled<br />
p-bond cooperativity or resonance-assisted hydrogen bond<strong>in</strong>g. 221,222 The<br />
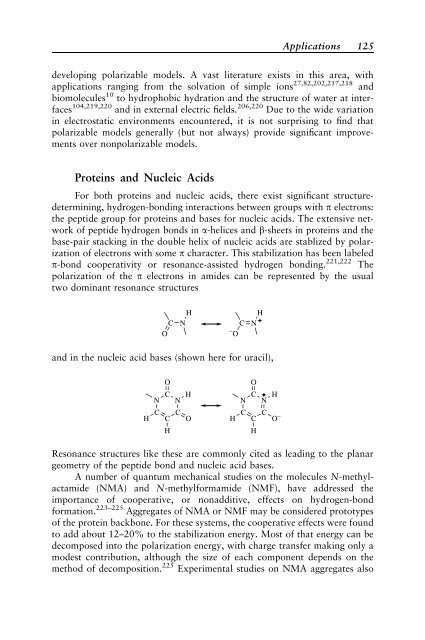
polarization of the p electrons <strong>in</strong> amides can be represented by the usual<br />
two dom<strong>in</strong>ant resonance structures<br />
H<br />
C N<br />
O<br />
H<br />
C N<br />
−O and <strong>in</strong> the nucleic acid bases (shown here for uracil),<br />
N<br />
O<br />
C<br />
N<br />
H<br />
H<br />
C C<br />
C<br />
H<br />
O<br />
N<br />
O<br />
C<br />
N<br />
H<br />
C C<br />
C O− H<br />
H<br />
Applications 125<br />
Resonance structures like these are commonly cited as lead<strong>in</strong>g to the planar<br />
geometry of the peptide bond and nucleic acid bases.<br />
A number of quantum mechanical studies on the molecules N-methylactamide<br />
(NMA) and N-methylformamide (NMF), have addressed the<br />
importance of cooperative, or nonadditive, effects on hydrogen-bond<br />
formation. 223–225 Aggregates of NMA or NMF may be considered prototypes<br />
of the prote<strong>in</strong> backbone. For these systems, the cooperative effects were found<br />
to add about 12–20% to the stabilization energy. Most of that energy can be<br />
decomposed <strong>in</strong>to the polarization energy, with charge transfer mak<strong>in</strong>g only a<br />
modest contribution, although the size of each component depends on the<br />
method of decomposition. 225 Experimental studies on NMA aggregates also