Reviews in Computational Chemistry Volume 18
Reviews in Computational Chemistry Volume 18
Reviews in Computational Chemistry Volume 18
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
0<br />
12 16 20 24 28 32<br />
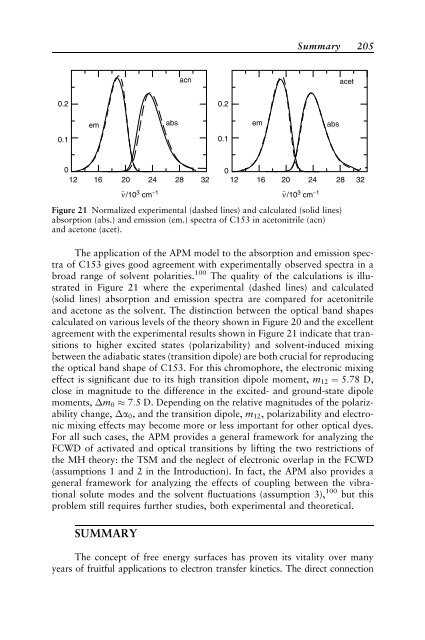
The application of the APM model to the absorption and emission spectra<br />
of C153 gives good agreement with experimentally observed spectra <strong>in</strong> a<br />
broad range of solvent polarities. 100 The quality of the calculations is illustrated<br />
<strong>in</strong> Figure 21 where the experimental (dashed l<strong>in</strong>es) and calculated<br />
(solid l<strong>in</strong>es) absorption and emission spectra are compared for acetonitrile<br />
and acetone as the solvent. The dist<strong>in</strong>ction between the optical band shapes<br />
calculated on various levels of the theory shown <strong>in</strong> Figure 20 and the excellent<br />
agreement with the experimental results shown <strong>in</strong> Figure 21 <strong>in</strong>dicate that transitions<br />
to higher excited states (polarizability) and solvent-<strong>in</strong>duced mix<strong>in</strong>g<br />
between the adiabatic states (transition dipole) are both crucial for reproduc<strong>in</strong>g<br />
the optical band shape of C153. For this chromophore, the electronic mix<strong>in</strong>g<br />
effect is significant due to its high transition dipole moment, m12 ¼ 5:78 D,<br />
close <strong>in</strong> magnitude to the difference <strong>in</strong> the excited- and ground-state dipole<br />
moments, m0 7:5 D. Depend<strong>in</strong>g on the relative magnitudes of the polarizability<br />
change, a0, and the transition dipole, m12, polarizability and electronic<br />
mix<strong>in</strong>g effects may become more or less important for other optical dyes.<br />
For all such cases, the APM provides a general framework for analyz<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
FCWD of activated and optical transitions by lift<strong>in</strong>g the two restrictions of<br />
the MH theory: the TSM and the neglect of electronic overlap <strong>in</strong> the FCWD<br />
(assumptions 1 and 2 <strong>in</strong> the Introduction). In fact, the APM also provides a<br />
general framework for analyz<strong>in</strong>g the effects of coupl<strong>in</strong>g between the vibrational<br />
solute modes and the solvent fluctuations (assumption 3), 100 but this<br />
problem still requires further studies, both experimental and theoretical.<br />
SUMMARY<br />
acn<br />
em abs em abs<br />
−<br />
ν /10 3 cm −1<br />
0<br />
12 16 20 24 28 32<br />
The concept of free energy surfaces has proven its vitality over many<br />
years of fruitful applications to electron transfer k<strong>in</strong>etics. The direct connection<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
Summary 205<br />
− ν /10 3 cm −1<br />
Figure 21 Normalized experimental (dashed l<strong>in</strong>es) and calculated (solid l<strong>in</strong>es)<br />
absorption (abs.) and emission (em.) spectra of C153 <strong>in</strong> acetonitrile (acn)<br />
and acetone (acet).<br />
acet