Introduction to Soil Chemistry
Introduction to Soil Chemistry
Introduction to Soil Chemistry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
56 soil basics iii<br />
2–<br />
S2O3 S 0<br />
H 2 S<br />
Oxidation<br />
Reduction<br />
2–<br />
SO3 R–SO 3 H<br />
R–SH<br />
2–<br />
SO4 BIOLOGICAL AND ORGANIC CHEMICALS OF SOIL<br />
3.4. BIOCHEMICAL<br />
R–S–R<br />
R–OSO 3 H<br />
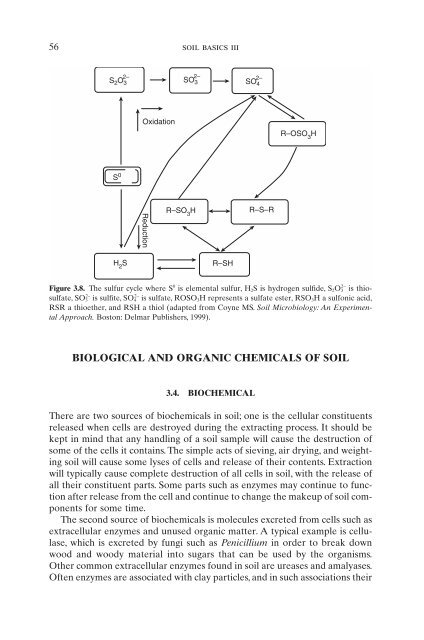
Figure 3.8. The sulfur cycle where S 0 is elemental sulfur, H2S is hydrogen sulfide, S2O3 2- is thiosulfate,<br />
SO3 2- is sulfite, SO4 2- is sulfate, ROSO3H represents a sulfate ester, RSO3H a sulfonic acid,<br />
RSR a thioether, and RSH a thiol (adapted from Coyne MS. <strong>Soil</strong> Microbiology: An Experimental<br />
Approach. Bos<strong>to</strong>n: Delmar Publishers, 1999).<br />
There are two sources of biochemicals in soil; one is the cellular constituents<br />
released when cells are destroyed during the extracting process. It should be<br />
kept in mind that any handling of a soil sample will cause the destruction of<br />
some of the cells it contains. The simple acts of sieving, air drying, and weighting<br />
soil will cause some lyses of cells and release of their contents. Extraction<br />
will typically cause complete destruction of all cells in soil, with the release of<br />
all their constituent parts. Some parts such as enzymes may continue <strong>to</strong> function<br />
after release from the cell and continue <strong>to</strong> change the makeup of soil components<br />
for some time.<br />
The second source of biochemicals is molecules excreted from cells such as<br />
extracellular enzymes and unused organic matter. A typical example is cellulase,<br />
which is excreted by fungi such as Penicillium in order <strong>to</strong> break down<br />
wood and woody material in<strong>to</strong> sugars that can be used by the organisms.<br />
Other common extracellular enzymes found in soil are ureases and amalyases.<br />
Often enzymes are associated with clay particles, and in such associations their