Protocols - Hemorio
Protocols - Hemorio
Protocols - Hemorio
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
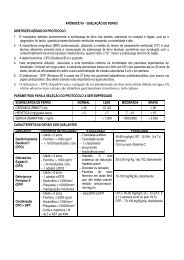
TREATMENT OF BLEEDING SITUATIONS<br />
SITUATIONS CONDUCTION FVIII FREQUENCY DURATION<br />
NASAL OR ORAL - Locals (topical thrombin,<br />
- - -<br />
MUCOSA<br />
cauterization, solution to rinse the<br />
BLEEDING<br />
mouth with)<br />
- antifibrinolytic<br />
- DDAVP<br />
DENTAL<br />
- DDAVP only dose + 20 IU/Kg Only dose -<br />
EXTRACTION antifibrinolytic (when indicated) When indicated<br />
MENOMETRORRH - Contraceptive<br />
20 IU/Kg Only dose -<br />
AGIA<br />
- Antifibrinolytic<br />
- NOR-etisteron<br />
10mg 2x/day during10d, after<br />
-10mg/day for 10d<br />
- DDAVP<br />
PREGNANCY<br />
- DDAVP<br />
- - -<br />
VWD TYPE 1 - antifibrinolytic is not indicated<br />
(4-5d, after<br />
childbirth, it might<br />
have some bleeding)<br />
- Normal birth<br />
PREGNANCY<br />
30 - 50 IU/kg 24/24h<br />
Until<br />
VWD TYPE 2<br />
(thrombocytopenia<br />
Normal birth<br />
In cases of<br />
Severe<br />
Thrombocytopenia is<br />
corrected and until<br />
may occur)<br />
Thrombocytopeni<br />
a<br />
scarring<br />
PREGNANCY<br />
VWD TYPE 3<br />
Normal birth or Cesarean section 40 - 60 IU/Kg 24/24h During 7 days<br />
MINOR<br />
SURGERIES<br />
Keep FVIII> 50U/dL until scarring 30 IU/Kg<br />
Once a Day in<br />
alternate days<br />
Until scarring<br />
MAJOR<br />
SURGERIES<br />
Keep FVII > 50U/dl 50 IU/Kg<br />
Once a day 1st to 4th In alternate days<br />
day<br />
5th until scarring<br />
AUXILLIARY DRUGS<br />
Epsilon Amino Caproic Acid (EACA, 50 mg/kg/dose, 4 times a day, P.O.) and tranexamic acid (15-20<br />
mg/kg/dose, 3 times a day, P.O.) are most frequently applied antifibrinolytics. The antifibrinolytics are very<br />
effective to control oral mucosa bleeding, epistaxis, menorrhages and after dental extraction. They may be<br />
used as only treatment, in minor severity bleeding in these sites, or associated to desmopressin, or factor<br />
concentrate, for more severe bleeding in pre- or post-operatory. Although they are more commonly used<br />
orally, antifibrinolytics can also be given through intravenous and topic routes. They are counter-indicated<br />
in cases of hematuria and present risk to anticipate vessel-occlusion events in post-thrombotic patients.<br />
Estrogen-progesterone associations increase FVW plasma levels, but with variable and not-predictable<br />
response pattern, are not applied with therapy purposes, although, they are useful to reduce intensity of<br />
menorrhages in women with VWD. Even in low doses, the combined tablets of estrogen-progesterone<br />
decrease endometrial proliferation and may be enough to control mild bleeding. Combination with higher<br />
doses may be used where there is no control with lower doses. Tablets can be continuously administered<br />
during several months to reduce menstruation frequency, The use of intravenous estrogen, such<br />
Premarin® 25 mg every 4 hours for up to 6 doses, maybe administered to stop one severe menorrhage.<br />
Intravaginal rings or IUD with estrogen + progesterone release or progesterone release alone are welltolerated<br />
in more mature women. Hysterectomy may be indicated for women with persistent menorrhage<br />
and to which completed family planning.<br />
NOTES:<br />
A – Pregnancy and Childbirth: As of 10 th week of pregnancy, FVIII and FVW levels increase<br />
spontaneously in VWD types 1 and 2, being able to achieve normal levels. Pregnant patients with VWD<br />
78