PostGIS Raster : Extending PostgreSQL for The Support of ... - CoDE
PostGIS Raster : Extending PostgreSQL for The Support of ... - CoDE
PostGIS Raster : Extending PostgreSQL for The Support of ... - CoDE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Appendix F<br />
Continuous Surfaces<br />
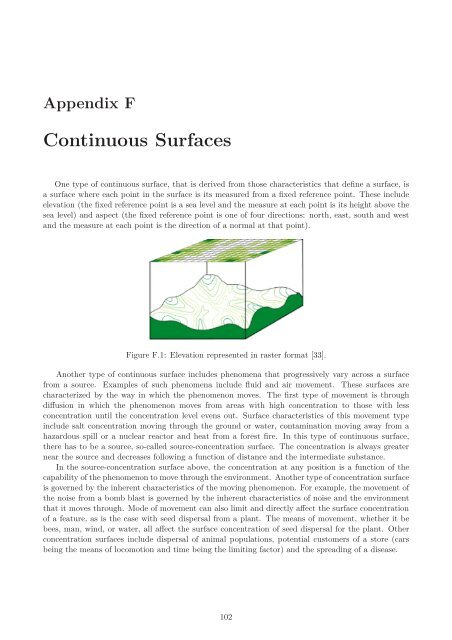
One type <strong>of</strong> continuous surface, that is derived from those characteristics that define a surface, is<br />
a surface where each point in the surface is its measured from a fixed reference point. <strong>The</strong>se include<br />
elevation (the fixed reference point is a sea level and the measure at each point is its height above the<br />
sea level) and aspect (the fixed reference point is one <strong>of</strong> four directions: north, east, south and west<br />
and the measure at each point is the direction <strong>of</strong> a normal at that point).<br />
Figure F.1: Elevation represented in raster <strong>for</strong>mat [33].<br />
Another type <strong>of</strong> continuous surface includes phenomena that progressively vary across a surface<br />
from a source. Examples <strong>of</strong> such phenomena include fluid and air movement. <strong>The</strong>se surfaces are<br />
characterized by the way in which the phenomenon moves. <strong>The</strong> first type <strong>of</strong> movement is through<br />
diffusion in which the phenomenon moves from areas with high concentration to those with less<br />
concentration until the concentration level evens out. Surface characteristics <strong>of</strong> this movement type<br />
include salt concentration moving through the ground or water, contamination moving away from a<br />
hazardous spill or a nuclear reactor and heat from a <strong>for</strong>est fire. In this type <strong>of</strong> continuous surface,<br />
there has to be a source, so-called source-concentration surface. <strong>The</strong> concentration is always greater<br />
near the source and decreases following a function <strong>of</strong> distance and the intermediate substance.<br />
In the source-concentration surface above, the concentration at any position is a function <strong>of</strong> the<br />
capability <strong>of</strong> the phenomenon to move through the environment. Another type <strong>of</strong> concentration surface<br />
is governed by the inherent characteristics <strong>of</strong> the moving phenomenon. For example, the movement <strong>of</strong><br />
the noise from a bomb blast is governed by the inherent characteristics <strong>of</strong> noise and the environment<br />
that it moves through. Mode <strong>of</strong> movement can also limit and directly affect the surface concentration<br />
<strong>of</strong> a feature, as is the case with seed dispersal from a plant. <strong>The</strong> means <strong>of</strong> movement, whether it be<br />
bees, man, wind, or water, all affect the surface concentration <strong>of</strong> seed dispersal <strong>for</strong> the plant. Other<br />
concentration surfaces include dispersal <strong>of</strong> animal populations, potential customers <strong>of</strong> a store (cars<br />
being the means <strong>of</strong> locomotion and time being the limiting factor) and the spreading <strong>of</strong> a disease.<br />
102