PostGIS Raster : Extending PostgreSQL for The Support of ... - CoDE
PostGIS Raster : Extending PostgreSQL for The Support of ... - CoDE
PostGIS Raster : Extending PostgreSQL for The Support of ... - CoDE
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Lines<br />
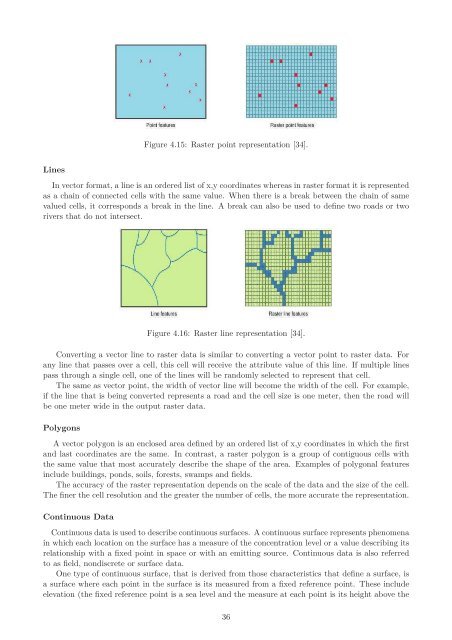
Figure 4.15: <strong>Raster</strong> point representation [34].<br />
In vector <strong>for</strong>mat, a line is an ordered list <strong>of</strong> x,y coordinates whereas in raster <strong>for</strong>mat it is represented<br />
as a chain <strong>of</strong> connected cells with the same value. When there is a break between the chain <strong>of</strong> same<br />
valued cells, it corresponds a break in the line. A break can also be used to define two roads or two<br />
rivers that do not intersect.<br />
Figure 4.16: <strong>Raster</strong> line representation [34].<br />
Converting a vector line to raster data is similar to converting a vector point to raster data. For<br />
any line that passes over a cell, this cell will receive the attribute value <strong>of</strong> this line. If multiple lines<br />
pass through a single cell, one <strong>of</strong> the lines will be randomly selected to represent that cell.<br />
<strong>The</strong> same as vector point, the width <strong>of</strong> vector line will become the width <strong>of</strong> the cell. For example,<br />
if the line that is being converted represents a road and the cell size is one meter, then the road will<br />
be one meter wide in the output raster data.<br />
Polygons<br />
A vector polygon is an enclosed area defined by an ordered list <strong>of</strong> x,y coordinates in which the first<br />
and last coordinates are the same. In contrast, a raster polygon is a group <strong>of</strong> contiguous cells with<br />
the same value that most accurately describe the shape <strong>of</strong> the area. Examples <strong>of</strong> polygonal features<br />
include buildings, ponds, soils, <strong>for</strong>ests, swamps and fields.<br />
<strong>The</strong> accuracy <strong>of</strong> the raster representation depends on the scale <strong>of</strong> the data and the size <strong>of</strong> the cell.<br />
<strong>The</strong> finer the cell resolution and the greater the number <strong>of</strong> cells, the more accurate the representation.<br />
Continuous Data<br />
Continuous data is used to describe continuous surfaces. A continuous surface represents phenomena<br />
in which each location on the surface has a measure <strong>of</strong> the concentration level or a value describing its<br />
relationship with a fixed point in space or with an emitting source. Continuous data is also referred<br />
to as field, nondiscrete or surface data.<br />
One type <strong>of</strong> continuous surface, that is derived from those characteristics that define a surface, is<br />
a surface where each point in the surface is its measured from a fixed reference point. <strong>The</strong>se include<br />
elevation (the fixed reference point is a sea level and the measure at each point is its height above the<br />
36