NEW_Accomplishments.indd - IRIS
NEW_Accomplishments.indd - IRIS
NEW_Accomplishments.indd - IRIS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2006 <strong>IRIS</strong> 5-YEAR PROPOSAL SURFACE OF THE EARTH: GLOBAL STUDIES<br />
Systematic High-Resolution Imaging of the Karadere-Düzce Branch of the North<br />
Anatolian Fault<br />
Zhigang Peng • University of Southern California, now at University of California, Los Angeles<br />
Yehuda Ben-Zion • University of Southern California<br />
The spatial extent and material properties of the damaged fault zone rock have important implications for many aspects of<br />
earthquake behavior. Fault zone structures with material discontinuity interfaces and low-velocity layers of damaged fault zone<br />
rock can produce several indicative wave propagation signals, including scattering, anisotropy, non-linearity, and guided head<br />
and trapped waves. We perform a systematic analysis of such signals from seismic data recorded by a PASSCAL seismic network<br />
deployed along and around the Karadere-Düzce branch of the north Anatolian fault during the 1999 Mw 7.4 İzmit and Mw<br />
7.1 Düzce earthquake sequences. Our results can be summarized as follows: The observed fault zone trapped waves are generated<br />
by relatively shallow structures that extend generally only over the top ~3-4 km of the crust. The shallow trapping structure<br />
is ~100 m wide and is surrounded by broader (~ 1 km) anisotropic and scattering zones that are also confined primarily to the top<br />
3 km. The average delay times for ray paths that propagate along the rupture zone are larger than for the other paths. The apparent<br />
crack density in the damaged shallow fault zone rock is about 7%. Systematic analyses of anisotropy and scattering measured<br />
from waveforms generated from repeating earthquakes do not show precursory temporal evolution of properties before the<br />
Düzce mainshock. The anisotropy results show small co-seismic changes. However, the scattering results show clear co-seismic<br />
changes and post-seismic logarithmic recovery after the Düzce mainshock. A strong correlation between the co-seismic delays<br />
and intensities of the strong ground motion generated by the Düzce mainshock implies that the radiated seismic waves produce<br />
the velocity reductions in the top portion of the shallow crust.<br />
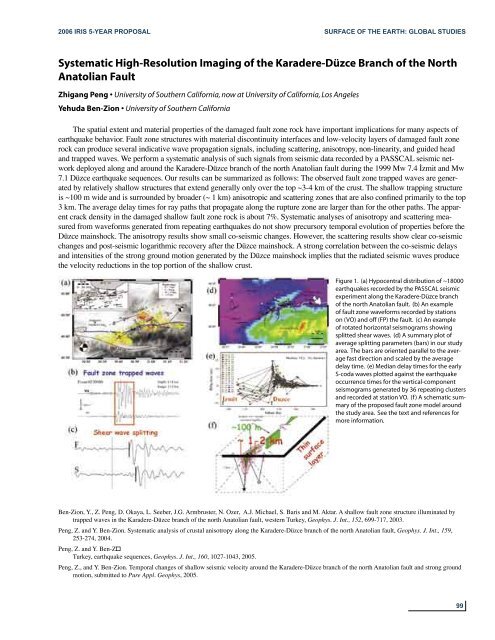
Figure 1. (a) Hypocentral distribution of ~18000<br />
earthquakes recorded by the PASSCAL seismic<br />
experiment along the Karadere-Düzce branch<br />
of the north Anatolian fault. (b) An example<br />
of fault zone waveforms recorded by stations<br />
on (VO) and off (FP) the fault. (c) An example<br />
of rotated horizontal seismograms showing<br />
splitted shear waves. (d) A summary plot of<br />
average splitting parameters (bars) in our study<br />
area. The bars are oriented parallel to the average<br />
fast direction and scaled by the average<br />
delay time. (e) Median delay times for the early<br />
S-coda waves plotted against the earthquake<br />
occurrence times for the vertical-component<br />
seismograms generated by 36 repeating clusters<br />
and recorded at station VO. (f ) A schematic summary<br />
of the proposed fault zone model around<br />
the study area. See the text and references for<br />
more information.<br />
Ben-Zion, Y., Z. Peng, D. Okaya, L. Seeber, J.G. Armbruster, N. Ozer, A.J. Michael, S. Baris and M. Aktar. A shallow fault zone structure illuminated by<br />
trapped waves in the Karadere-Düzce branch of the north Anatolian fault, western Turkey, Geophys. J. Int., 152, 699-717, 2003.<br />
Peng, Z. and Y. Ben-Zion. Systematic analysis of crustal anisotropy along the Karadere-Düzce branch of the north Anatolian fault, Geophys. J. Int., 159,<br />
253-274, 2004.<br />
Peng, Z. and Y. Ben-Z<br />
Turkey, earthquake sequences, Geophys. J. Int., 160, 1027-1043, 2005.<br />
Peng, Z., and Y. Ben-Zion. Temporal changes of shallow seismic velocity around the Karadere-Düzce branch of the north Anatolian fault and strong ground<br />
motion, submitted to Pure Appl. Geophys, 2005.<br />
99