SOFT 2004 Meeting Abstracts - Society of Forensic Toxicologists
SOFT 2004 Meeting Abstracts - Society of Forensic Toxicologists
SOFT 2004 Meeting Abstracts - Society of Forensic Toxicologists
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
M15 <br />
DRUG DETECTION IN ORAL FLUID: IDENTIFICATION OF POLY DRUG USE BY EIA AND GC<br />
MS<br />
Joe Clarke 2 *, Lolita Tsanaclisl , and John Wicks! : !Tricho-Tech Limited, The Cardiff Medicentre, Heath Park,<br />
Cardiff, CF14 4UJ, United Kingdom.; 2Altrix Healthcare Pic, Birchwood Science Park, Warrington, WA3 7BP,<br />
United Kingdom.<br />
The analysis <strong>of</strong> drugs <strong>of</strong> abuse in oral fluid is becoming more widely used and accepted across a number <strong>of</strong><br />
testing disciplines, particularly because <strong>of</strong> its simplicity to collect in relation to urine. Commonly abused and<br />
prescribed drugs are known to be detectable in oral fluid. The objective <strong>of</strong> this study was to assess the prevalence<br />
<strong>of</strong> a number <strong>of</strong> drugs in oral fluid with specimens collected from known and unknown drug users. The cut-<strong>of</strong>f<br />
levels for oral fluid are much lower then those for urine. Certain analytical methods that are used with urine<br />
samples, including immunoassay and GC-MS, are not necessarily applicable for screening oral fluid specimens.<br />
This study provides a compilation <strong>of</strong> data for the confirmation by GC-MSIEI, GC-MS/CI or GC-MS/MS <strong>of</strong> oral<br />
fluid for a wide range <strong>of</strong> analytes. Oral fluid specimens (N=8911) were collected with prior consent from various<br />
establishments in the U.K including private companies, rehabilitation clinics, and criminal justice services using<br />
the Intercept® DOA collection device (OraSure Technologies, USA) according to manufacturer's instructions.<br />
Specimens were initially screened for a combination <strong>of</strong> Opiates, Cocaine metabolites, Cannabinoids,<br />
Amphetamines, Benzodiazepines and Methadone using separate OraSure Technologies Inc. micro-plate enzyme<br />
immunoassays and Buprenorphine (Diagnostix Ltd, Canada), according to manufacturer's instructions.<br />
For the confirmation analysis by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS), the samples were cleaned<br />
using Oasis® MCX Cartridges and derivatised with TFA or BSTFA (Sigma, Poole, UK). The derivatised<br />
extracts were injected onto either gas-chromatograph HP5973 for GC-MSIEI and GC-MS/CI (Agilent, Berkshire,<br />
UK) or Varian Inc. Saturn for GC-MS/MS (Walton-on-Thames, UK) equipped with capillary column 15mxO.25<br />
mm Varian, Factor Four. The dynamic range was from 2 to 2000 ng/mL. Three ions for the drugs and two ions<br />
for the internal standards were monitored. The confirmation rate for each drug group, relative to applied cut-<strong>of</strong>f<br />
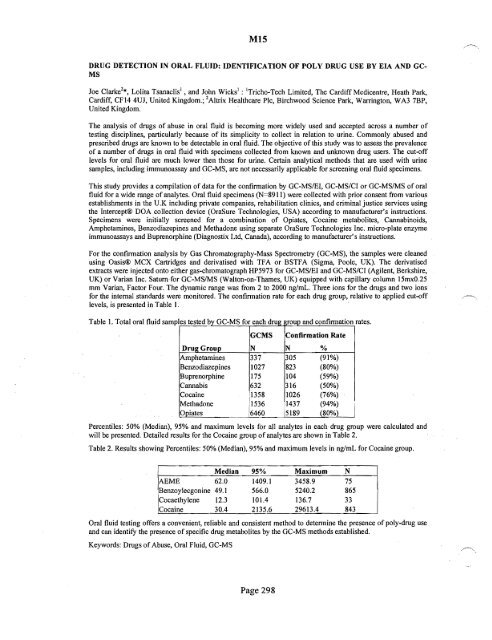
levels, is presented in Table I.<br />
.r--"<br />
Table 1. Total oral fluid sampl es teste db)y GC.MSt)oreachdrug ~oup and con fiIrmatlon rates.<br />
GCMS<br />
Confirmation Rate<br />
Drug Group N N %<br />
Amphetamines 337 305 (91%)<br />
Benzodiazepines 1027 823 (80%)<br />
Buprenorphine 175 104 (59%)<br />
Cannabis 632 316 (50%)<br />
Cocaine 1358 1026 (76%)<br />
1<br />
Methadone 1536 11437 (94%)<br />
Omates 116460 15189 (80%t I<br />
Percentiles: 50% (Median), 95% and maximum levels for all analytes in each drug group were calculated and<br />
will be presented. Detailed results for the Cocaine group <strong>of</strong> analytes are shown in Table 2.<br />
Table 2. Results showing Percentiles: 50% (Median), 95% and maximum levels in ng/mL for Cocaine group.<br />
Median 95% Maximum N<br />
AEME 62.0 1409.1 3458.9 75<br />
BenzoyJecgonine 49.1 566.0 5240.2 865<br />
Cocaethylene 12.3 101.4 136.7 33<br />
Cocaine 3004 2135.6 29613.4 843<br />
Oral fluid testing <strong>of</strong>fers a convenient, reliable and consistent method to determine the presence <strong>of</strong> poly-drug use<br />
and can identifY the presence <strong>of</strong> specific drug metabolites by the GC-MS methods established.<br />
Keywords: Drugs <strong>of</strong> Abuse, Oral Fluid, GC·MS<br />
Page 298