Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
9.4 Installation<br />
The design of wind turbine requires the installation to be manual, i.e. without the need of<br />
a crane. The tower design complies with the requirement by u<strong>sin</strong>g a tilt-up construction<br />
with a gin pole. The principal installation method is shown on figure 9.8 and described<br />
below:<br />
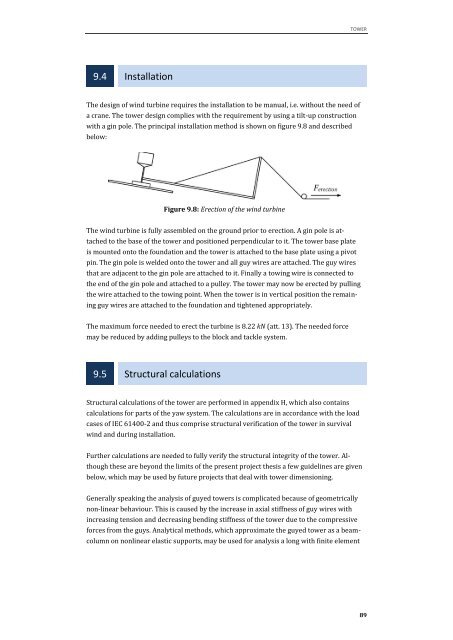
Figure 9.8: Erection of the wind turbine<br />
The wind turbine is fully assembled on the ground prior to erection. A gin pole is at-<br />
tached to the base of the tower and positioned perpendicular to it. The tower base plate<br />
is mounted onto the foundation and the tower is attached to the base plate u<strong>sin</strong>g a pivot<br />
pin. The gin pole is welded onto the tower and all guy wires are attached. The guy wires<br />
that are adjacent to the gin pole are attached to it. Finally a towing wire is connected to<br />
the end of the gin pole and attached to a pulley. The tower may now be erected by pulling<br />
the wire attached to the towing point. When the tower is in vertical position the remain-<br />
ing guy wires are attached to the foundation and tightened appropriately.<br />
The maximum force needed to erect the turbine is 8.22 kN (att. 13). The needed force<br />
may be reduced by adding pulleys to the block and tackle system.<br />
9.5 Structural calculations<br />
Structural calculations of the tower are performed in appendix H, which also contains<br />
calculations for parts of the yaw system. The calculations are in accordance with the load<br />
cases of IEC 61400-2 and thus comprise structural verification of the tower in survival<br />
wind and during installation.<br />
Further calculations are needed to fully verify the structural integrity of the tower. Al-<br />
though these are beyond the limits of the present project thesis a few guidelines are given<br />
below, which may be used by future projects that deal with tower dimensioning.<br />
Generally speaking the analysis of guyed towers is complicated because of geometrically<br />
non-linear behaviour. This is caused by the increase in axial stiffness of guy wires with<br />
increa<strong>sin</strong>g tension and decrea<strong>sin</strong>g bending stiffness of the tower due to the compressive<br />
forces from the guys. Analytical methods, which approximate the guyed tower as a beam-<br />
column on nonlinear elastic supports, may be used for analysis a long with finite element<br />
TOWER<br />
89