Census Analytical Report - Uganda Bureau of Statistics
Census Analytical Report - Uganda Bureau of Statistics
Census Analytical Report - Uganda Bureau of Statistics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
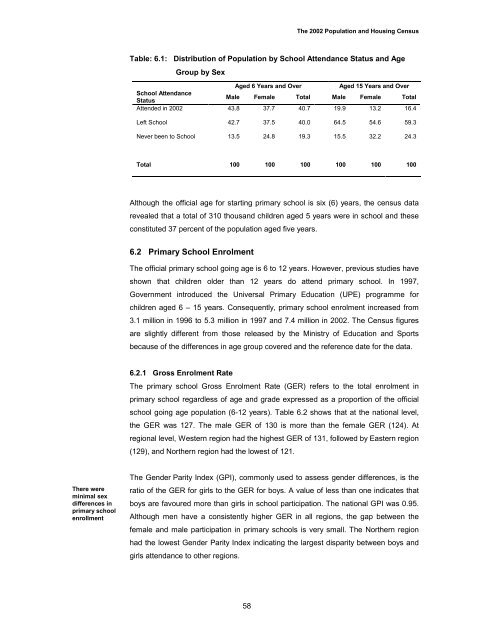
The 2002 Population and Housing <strong>Census</strong>Table: 6.1: Distribution <strong>of</strong> Population by School Attendance Status and AgeGroup by SexAged 6 Years and OverAged 15 Years and OverSchool AttendanceStatusMale Female Total Male Female TotalAttended in 2002 43.8 37.7 40.7 19.9 13.2 16.4Left School 42.7 37.5 40.0 64.5 54.6 59.3Never been to School 13.5 24.8 19.3 15.5 32.2 24.3Total 100 100 100 100 100 100Although the <strong>of</strong>ficial age for starting primary school is six (6) years, the census datarevealed that a total <strong>of</strong> 310 thousand children aged 5 years were in school and theseconstituted 37 percent <strong>of</strong> the population aged five years.6.2 Primary School EnrolmentThe <strong>of</strong>ficial primary school going age is 6 to 12 years. However, previous studies haveshown that children older than 12 years do attend primary school. In 1997,Government introduced the Universal Primary Education (UPE) programme forchildren aged 6 – 15 years. Consequently, primary school enrolment increased from3.1 million in 1996 to 5.3 million in 1997 and 7.4 million in 2002. The <strong>Census</strong> figuresare slightly different from those released by the Ministry <strong>of</strong> Education and Sportsbecause <strong>of</strong> the differences in age group covered and the reference date for the data.6.2.1 Gross Enrolment RateThe primary school Gross Enrolment Rate (GER) refers to the total enrolment inprimary school regardless <strong>of</strong> age and grade expressed as a proportion <strong>of</strong> the <strong>of</strong>ficialschool going age population (6-12 years). Table 6.2 shows that at the national level,the GER was 127. The male GER <strong>of</strong> 130 is more than the female GER (124). Atregional level, Western region had the highest GER <strong>of</strong> 131, followed by Eastern region(129), and Northern region had the lowest <strong>of</strong> 121.There wereminimal sexdifferences inprimary schoolenrollmentThe Gender Parity Index (GPI), commonly used to assess gender differences, is theratio <strong>of</strong> the GER for girls to the GER for boys. A value <strong>of</strong> less than one indicates thatboys are favoured more than girls in school participation. The national GPI was 0.95.Although men have a consistently higher GER in all regions, the gap between thefemale and male participation in primary schools is very small. The Northern regionhad the lowest Gender Parity Index indicating the largest disparity between boys andgirls attendance to other regions.58