2009 METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS...Magnetic torque experim<strong>en</strong>ts on the magnetic-field-induced organicsuperconductor λ-(BETS) 2 FeCl 4Layered organic superconductors have upper critical fieldsexceeding the theoretical Pauli limit for superconductivitywh<strong>en</strong> the magnetic field is applied parallel to the layers.Theory predicts th<strong>en</strong> the possibility of a Fulde-Ferrel-Larkin-Ovchinnikov (FFLO) superconducting state[Fulde and Ferrel, Phys. Rev. 135, A550 (1964);Larkin and Ovchinnikov, Sov. Phys. JETP 20, 762(1965)]. Besi<strong>des</strong> κ-(BEDT-TTF) 2 Cu(NCS) 2 , the two dim<strong>en</strong>sionalfield-induced superconductor λ-(BETS) 2 FeCl 4 ,where BETS is bis(ethyl<strong>en</strong>edithio)tetrasel<strong>en</strong>afulval<strong>en</strong>e, is acandidate which fulfils all necessary conditions. Wh<strong>en</strong> themagnetic field is applied parallel to the metallic layers, asuperconducting phase appears above 17 T below 1 K.In our first experim<strong>en</strong>t we focused on the critical field at17 T. Figure 98 shows torque data tak<strong>en</strong> at differ<strong>en</strong>t temperaturesduring field sweeps. Surprisingly, a broad kinklikeanomaly appears only above 22 T indicating the transitioninto the field-induced superconducting state. Below200 mK a pronounced hysteresis appears. The experim<strong>en</strong>tsshow no evid<strong>en</strong>ce for additional phase transitions withinthe superconducting state. The phase diagram clearly differsfrom that reported by Uji et al. A misalignm<strong>en</strong>t of thesample can be ruled out. A possible explanation may befound in the rather rapid cooling conditions in our experim<strong>en</strong>twhich is known to cause anion-disorder effects in 1Dorganic superconductors. The result stimulates further experim<strong>en</strong>tsunder more controlled experim<strong>en</strong>tal conditions.This field-induced superconductivity is well understoodin the framework of the Fischer theory, based on theJaccarino-Peter effect. Uji et al. reported possible FFLOstates at the two critical fields based on dip structures inthe resistivity [Uji et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 157001(2006) and refer<strong>en</strong>ces therein]. This motivated us to lookfor a thermodynamic phase transition betwe<strong>en</strong> the homog<strong>en</strong>eoussuperconducting phase and the FFLO states bymeans of magnetic torque experim<strong>en</strong>ts using a capacitancecantilever technique. The probe was equipped with a rotator,which allowed us to align the layers parallel to the fielddirection with a precision of 0.001 ◦ . Single crystals of λ-(BETS) 2 FeCl 4 were grown by the standard electrochemicaloxidation technique.Figure 98: Magnet torque of λ-(BETS) 2 FeCl 4 is plotted as afunction of field at differ<strong>en</strong>t temperatures.I. SheikinR. Lortz (The Hong Kong University of Sci<strong>en</strong>ce and Technology, Kowloon, Hong Kong), Y. Nakazawa ( University ofOsaka, Osaka, Japan), B. Zhou, A. Kobayashi, H. Kobayashi (Nihon University, Tokyo, Japan)71
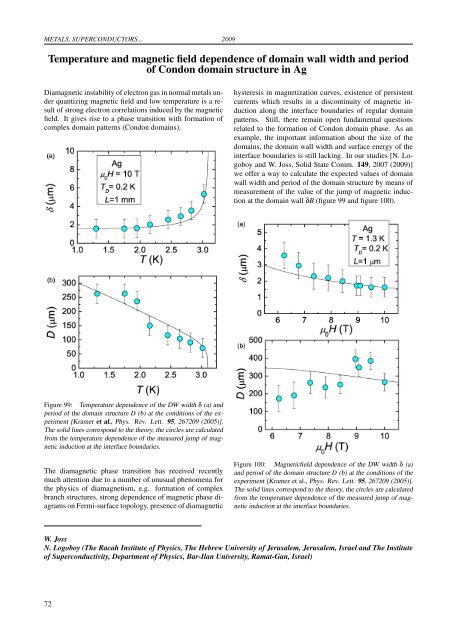
METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Temperature and magnetic field dep<strong>en</strong>d<strong>en</strong>ce of domain wall width and periodof Condon domain structure in AgDiamagnetic instability of electron gas in normal metals underquantizing magnetic field and low temperature is a resultof strong electron correlations induced by the magneticfield. It gives rise to a phase transition with formation ofcomplex domain patterns (Condon domains).hysteresis in magnetization curves, exist<strong>en</strong>ce of persist<strong>en</strong>tcurr<strong>en</strong>ts which results in a discontinuity of magnetic inductionalong the interface boundaries of regular domainpatterns. Still, there remain op<strong>en</strong> fundam<strong>en</strong>tal questionsrelated to the formation of Condon domain phase. As anexample, the important information about the size of thedomains, the domain wall width and surface <strong>en</strong>ergy of theinterface boundaries is still lacking. In our studies [N. Logoboyand W. Joss, Solid State Comm. 149, 2007 (2009)]we offer a way to calculate the expected values of domainwall width and period of the domain structure by means ofmeasurem<strong>en</strong>t of the value of the jump of magnetic inductionat the domain wall δB (figure 99 and figure 100).Figure 99: Temperature dep<strong>en</strong>d<strong>en</strong>ce of the DW width δ (a) andperiod of the domain structure D (b) at the conditions of the experim<strong>en</strong>t[Kramer et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 267209 (2005)].The solid lines correspond to the theory, the circles are calculatedfrom the temperature dep<strong>en</strong>d<strong>en</strong>ce of the measured jump of magneticinduction at the interface boundaries.The diamagnetic phase transition has received rec<strong>en</strong>tlymuch att<strong>en</strong>tion due to a number of unusual ph<strong>en</strong>om<strong>en</strong>a forthe physics of diamagnetism, e.g. formation of complexbranch structures, strong dep<strong>en</strong>d<strong>en</strong>ce of magnetic phase diagramson Fermi-surface topology, pres<strong>en</strong>ce of diamagneticFigure 100: Magneticfield dep<strong>en</strong>d<strong>en</strong>ce of the DW width δ (a)and period of the domain structure D (b) at the conditions of theexperim<strong>en</strong>t [Kramer et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 267209 (2005)].The solid lines correspond to the theory, the circles are calculatedfrom the temperature dep<strong>en</strong>d<strong>en</strong>ce of the measured jump of magneticinduction at the interface boundaries.W. JossN. Logoboy (The Racah Institute of Physics, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel and The Instituteof Superconductivity, Departm<strong>en</strong>t of Physics, Bar-Ilan University, Ramat-Gan, Israel)72
- Page 1 and 2:
LABORATOIRE NATIONAL DES CHAMPS MAG
- Page 4 and 5:
TABLE OF CONTENTSPreface 1Carbon Al
- Page 6 and 7:
Coexistence of closed orbit and qua
- Page 8:
2009PrefaceDear Reader,You have bef
- Page 12 and 13:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESInvestigation
- Page 14 and 15:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESPropagative L
- Page 16 and 17:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESEdge fingerpr
- Page 18 and 19:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESObservation o
- Page 20 and 21:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESImproving gra
- Page 22 and 23:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESHow perfect c
- Page 24 and 25:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESTuning the el
- Page 26 and 27:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESElectric fiel
- Page 28 and 29: 2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESMagnetotransp
- Page 30 and 31: 2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESGraphite from
- Page 32: 2009Two-Dimensional Electron Gas25
- Page 35 and 36: TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Di
- Page 37 and 38: TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Sp
- Page 39 and 40: TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Cr
- Page 41 and 42: TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Re
- Page 43 and 44: TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009In
- Page 45 and 46: TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Ho
- Page 47 and 48: TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Te
- Page 50 and 51: 2009 SEMICONDUCTORS AND NANOSTRUCTU
- Page 52 and 53: 2009 SEMICONDUCTORS AND NANOSTRUCTU
- Page 54 and 55: 2009 SEMICONDUCTORS AND NANOSTRUCTU
- Page 56 and 57: 2009 SEMICONDUCTORS AND NANOSTRUCTU
- Page 58 and 59: 2009 SEMICONDUCTORS AND NANOSTRUCTU
- Page 60: 2009Metals, Superconductors and Str
- Page 63 and 64: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Anom
- Page 65 and 66: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Magn
- Page 67 and 68: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS ... 2009Coe
- Page 69 and 70: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS ... 2009Fie
- Page 71 and 72: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009High
- Page 73 and 74: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Angu
- Page 75 and 76: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Magn
- Page 77: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Meta
- Page 81 and 82: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 200974
- Page 84 and 85: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSY b 3+ → Er
- Page 86 and 87: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSMagnetotranspo
- Page 88 and 89: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSHigh field tor
- Page 90 and 91: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSNuclear magnet
- Page 92 and 93: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSStructural ana
- Page 94 and 95: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSEnhancement ma
- Page 96 and 97: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSInvestigation
- Page 98 and 99: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSField-induced
- Page 100 and 101: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSMagnetic prope
- Page 102: 2009Biology, Chemistry and Soft Mat
- Page 105 and 106: BIOLOGY, CHEMISTRY AND SOFT MATTER
- Page 108 and 109: 2009 APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITYMagne
- Page 110 and 111: 2009 APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITYPhtha
- Page 112: 2009Magneto-Science105
- Page 115 and 116: MAGNETO-SCIENCE 2009Study of the in
- Page 117 and 118: MAGNETO-SCIENCE 2009Magnetohydrodyn
- Page 119 and 120: MAGNETO-SCIENCE 2009112
- Page 122 and 123: 2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 124 and 125: 2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 126 and 127: 2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 128 and 129:
2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 130 and 131:
2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 132 and 133:
2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 134 and 135:
2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 136 and 137:
2009 PROPOSALSProposals for Magnet
- Page 138 and 139:
2009 PROPOSALSSpin-Jahn-Teller effe
- Page 140 and 141:
2009 PROPOSALSQuantum Oscillations
- Page 142 and 143:
2009 PROPOSALSThermoelectric tensor
- Page 144 and 145:
2009 PROPOSALSDr. EscoffierCyclotro
- Page 146 and 147:
2009 PROPOSALSHigh field magnetotra
- Page 148 and 149:
2009 THESESPhD Theses 20091. Nanot
- Page 150 and 151:
2009 PUBLICATIONS[21] O. Drachenko,
- Page 152 and 153:
2009 PUBLICATIONS[75] S. Nowak, T.
- Page 154 and 155:
Contributors of the LNCMI to the Pr
- Page 156 and 157:
Institut Jean Lamour, Nancy : 68Ins
- Page 158 and 159:
Lawrence Berkeley National Laborato