2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSField-induced transitions in RECo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 (RE = Dy, Eu)One interesting family of perovskites is RE(TM,Mn)O 3 inwhich the Mn atom has be<strong>en</strong> partially substituted by atransition-metal elem<strong>en</strong>t TM like Co giving rise to Mn 4+ -Co 2+ ferromagnetic interactions. In addition, if the RE elem<strong>en</strong>tbears a large magnetic mom<strong>en</strong>t, th<strong>en</strong> the RE sublatticemay interact with the ordered TM-Mn sublattice [Peñaet al., J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 312, 78 (2007); Antuneset al., J. Europ. Ceram. Soc. 27, 3927 (2007)]. Inthis work we pres<strong>en</strong>t the magnetic properties of bulk ceramicsamples EuCo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 and DyCo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 .Nickel-containing samples of similar composition (Ni/Mn= 0.50/0.50) are measured for comparison. Samples wereprepared by solid state synthesis from the correspondingsubmicronic powder oxi<strong>des</strong>. They were characterized byX-ray diffraction showing pure perovskite orthorhombicstructure (Pbnm). Magnetic measurem<strong>en</strong>ts were performedon specim<strong>en</strong>s cut from ceramic bulks.ZFC curve follows a similar behaviour as the Eu case, thatis canted antiferromagnetism since the magnetic propertiesof the Co-Mn sublattice predominate. Wh<strong>en</strong> the sampleis field cooled the Co-Mn sublattice orders at T C = 85 K,a lower temperature as the Eu-case because of the smallerionic radius of the Dy ion compared to Eu.The magnetization loop is shown in figure 130(a) forEuCo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 sample. We notice five steep transitionson the hysteresis curves. The magnetization valuemeasured at 20 T is lower than the theoretical value(M S = 3.87 µ B ) if we consider all the spins of Mn 4+and Co 2+ aligned and no contribution from Eu 3+ . ForEuNi 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 there are no step-like transitions. Themeasured value of the magnetization at 20 T is also lowerthan the calculated value of 3.35 µ B if all spins of transitionmetals are aligned on the field direction. This suggeststhat Eu 3+ in these systems is a classical case of VanVleck magnetism. For DyCo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 (figure 130(b))we can see two field transitions (near 2 T and 5 T) andthe magnetization measured at 20 T reaches the theoreticalvalue (M S = 6.76 µ B ) if we consider a ferrimagneticmodel of two sublattices (rare earth and transition metalones) fully aligned, one in opposition to the other. For theDyNi 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 sample we do not see any field-inducedanomaly on the hysteresis curves up to 20 T.Figure 129: Thermal dep<strong>en</strong>d<strong>en</strong>ce of the ZFC-FC magnetizationfor EuCo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 and DyCo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 measured at0.025 T.Temperature dep<strong>en</strong>d<strong>en</strong>ce of the magnetization is shown infigure 129 for EuCo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 and DyCo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 .Samples were first cooled under no magnetic field, th<strong>en</strong>the static field of 0.025 T was applied and samples allowedwarming until 300 K (ZFC). Th<strong>en</strong>, they were subsequ<strong>en</strong>tlycooled under the same static field (FC). ZFC branch forEu sample shows that, upon warming, the Co-Mn sublatticeorders in an antiferromagnetic state with a small ferromagneticcompon<strong>en</strong>t due to non-linearity of the spins. Thelow magnetic mom<strong>en</strong>t of Eu and the low external field appliedto the sample, result in almost no contribution fromEu. During the FC procedure, the transition metal sublatticeorders ferromagnetically at T C = 130 K. For the Dysample we can notice that the ZFC curve starts from a finitevalue at 2 K and decreases to almost zero wh<strong>en</strong> thetemperature increases. This is just due to the Curie-Weissbehaviour of Dy 3+ that follows 1/T law, typical of freespinnon-correlated mom<strong>en</strong>ts. For higher temperatures, theFigure 130: Magnetization loop at2.5K for (a) EuCo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 (insert: EuNi 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 ) and(b) DyCo 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 (insert: DyNi 0.50 Mn 0.50 O 3 ).A. B. AntunesO. Peña (Sci<strong>en</strong>ces Chimiques de R<strong>en</strong>nes, Université de R<strong>en</strong>nes 1, R<strong>en</strong>nes, France), C. Moure, A. Moure (Electrocerámicas,Instituto de Cerámica y Vidrio, CSIC, Madrid, Spain)91
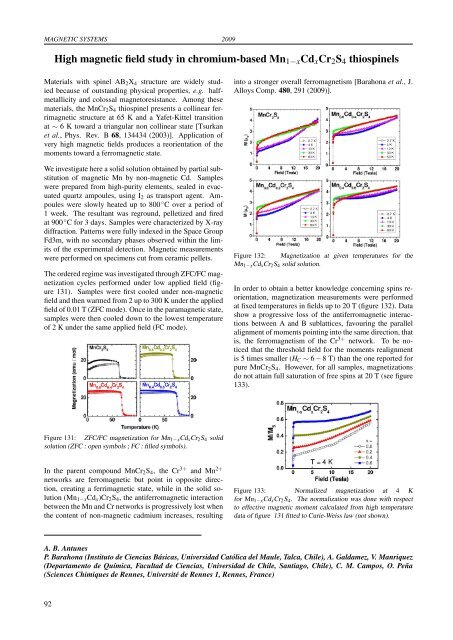
MAGNETIC SYSTEMS 2009High magnetic field study in chromium-based Mn 1−x Cd x Cr 2 S 4 thiospinelsMaterials with spinel AB 2 X 4 structure are widely studiedbecause of outstanding physical properties, e.g. halfmetallicityand colossal magnetoresistance. Among thesematerials, the MnCr 2 S 4 thiospinel pres<strong>en</strong>ts a collinear ferrimagneticstructure at 65 K and a Yafet-Kittel transitionat ∼ 6 K toward a triangular non collinear state [Tsurkanet al., Phys. Rev. B 68, 134434 (2003)]. Application ofvery high magnetic fields produces a reori<strong>en</strong>tation of themom<strong>en</strong>ts toward a ferromagnetic state.We investigate here a solid solution obtained by partial substitutionof magnetic Mn by non-magnetic Cd. Sampleswere prepared from high-purity elem<strong>en</strong>ts, sealed in evacuatedquartz ampoules, using I 2 as transport ag<strong>en</strong>t. Ampouleswere slowly heated up to 800 ◦ C over a period of1 week. The resultant was reground, pelletized and firedat 900 ◦ C for 3 days. Samples were characterized by X-raydiffraction. Patterns were fully indexed in the Space GroupFd3m, with no secondary phases observed within the limitsof the experim<strong>en</strong>tal detection. Magnetic measurem<strong>en</strong>tswere performed on specim<strong>en</strong>s cut from ceramic pellets.The ordered regime was investigated through ZFC/FC magnetizationcycles performed under low applied field (figure131). Samples were first cooled under non-magneticfield and th<strong>en</strong> warmed from 2 up to 300 K under the appliedfield of 0.01 T (ZFC mode). Once in the paramagnetic state,samples were th<strong>en</strong> cooled down to the lowest temperatureof 2 K under the same applied field (FC mode).into a stronger overall ferromagnetism [Barahona et al., J.Alloys Comp. 480, 291 (2009)].Figure 132: Magnetization at giv<strong>en</strong> temperatures for theMn 1−x Cd x Cr 2 S 4 solid solution.In order to obtain a better knowledge concerning spins reori<strong>en</strong>tation,magnetization measurem<strong>en</strong>ts were performedat fixed temperatures in fields up to 20 T (figure 132). Datashow a progressive loss of the antiferromagnetic interactionsbetwe<strong>en</strong> A and B sublattices, favouring the parallelalignm<strong>en</strong>t of mom<strong>en</strong>ts pointing into the same direction, thatis, the ferromagnetism of the Cr 3+ network. To be noticedthat the threshold field for the mom<strong>en</strong>ts realignm<strong>en</strong>tis 5 times smaller (H C ∼ 6 − 8 T) than the one reported forpure MnCr 2 S 4 . However, for all samples, magnetizationsdo not attain full saturation of free spins at 20 T (see figure133).Figure 131: ZFC/FC magnetization for Mn 1−x Cd x Cr 2 S 4 solidsolution (ZFC : op<strong>en</strong> symbols ; FC : filled symbols).In the par<strong>en</strong>t compound MnCr 2 S 4 , the Cr 3+ and Mn 2+networks are ferromagnetic but point in opposite direction,creating a ferrimagnetic state, while in the solid solution(Mn 1−x Cd x )Cr 2 S 4 , the antiferromagnetic interactionbetwe<strong>en</strong> the Mn and Cr networks is progressively lost wh<strong>en</strong>the cont<strong>en</strong>t of non-magnetic cadmium increases, resultingFigure 133: Normalized magnetization at 4 Kfor Mn 1−x Cd x Cr 2 S 4 . The normalization was done with respectto effective magnetic mom<strong>en</strong>t calculated from high temperaturedata of figure 131 fitted to Curie-Weiss law (not shown).A. B. AntunesP. Barahona (Instituto de Ci<strong>en</strong>cias Básicas, Universidad Católica del Maule, Talca, Chile), A. Galdamez, V. Manriquez(Departam<strong>en</strong>to de Química, Facultad de Ci<strong>en</strong>cias, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile), C. M. Campos, O. Peña(Sci<strong>en</strong>ces Chimiques de R<strong>en</strong>nes, Université de R<strong>en</strong>nes 1, R<strong>en</strong>nes, France)92
- Page 1 and 2:
LABORATOIRE NATIONAL DES CHAMPS MAG
- Page 4 and 5:
TABLE OF CONTENTSPreface 1Carbon Al
- Page 6 and 7:
Coexistence of closed orbit and qua
- Page 8:
2009PrefaceDear Reader,You have bef
- Page 12 and 13:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESInvestigation
- Page 14 and 15:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESPropagative L
- Page 16 and 17:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESEdge fingerpr
- Page 18 and 19:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESObservation o
- Page 20 and 21:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESImproving gra
- Page 22 and 23:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESHow perfect c
- Page 24 and 25:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESTuning the el
- Page 26 and 27:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESElectric fiel
- Page 28 and 29:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESMagnetotransp
- Page 30 and 31:
2009 CARBON ALLOTROPESGraphite from
- Page 32:
2009Two-Dimensional Electron Gas25
- Page 35 and 36:
TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Di
- Page 37 and 38:
TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Sp
- Page 39 and 40:
TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Cr
- Page 41 and 42:
TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Re
- Page 43 and 44:
TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009In
- Page 45 and 46:
TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Ho
- Page 47 and 48: TWO-DIMENSIONAL ELECTRON GAS 2009Te
- Page 50 and 51: 2009 SEMICONDUCTORS AND NANOSTRUCTU
- Page 52 and 53: 2009 SEMICONDUCTORS AND NANOSTRUCTU
- Page 54 and 55: 2009 SEMICONDUCTORS AND NANOSTRUCTU
- Page 56 and 57: 2009 SEMICONDUCTORS AND NANOSTRUCTU
- Page 58 and 59: 2009 SEMICONDUCTORS AND NANOSTRUCTU
- Page 60: 2009Metals, Superconductors and Str
- Page 63 and 64: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Anom
- Page 65 and 66: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Magn
- Page 67 and 68: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS ... 2009Coe
- Page 69 and 70: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS ... 2009Fie
- Page 71 and 72: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009High
- Page 73 and 74: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Angu
- Page 75 and 76: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Magn
- Page 77 and 78: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Meta
- Page 79 and 80: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 2009Temp
- Page 81 and 82: METALS, SUPERCONDUCTORS... 200974
- Page 84 and 85: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSY b 3+ → Er
- Page 86 and 87: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSMagnetotranspo
- Page 88 and 89: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSHigh field tor
- Page 90 and 91: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSNuclear magnet
- Page 92 and 93: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSStructural ana
- Page 94 and 95: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSEnhancement ma
- Page 96 and 97: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSInvestigation
- Page 100 and 101: 2009 MAGNETIC SYSTEMSMagnetic prope
- Page 102: 2009Biology, Chemistry and Soft Mat
- Page 105 and 106: BIOLOGY, CHEMISTRY AND SOFT MATTER
- Page 108 and 109: 2009 APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITYMagne
- Page 110 and 111: 2009 APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITYPhtha
- Page 112: 2009Magneto-Science105
- Page 115 and 116: MAGNETO-SCIENCE 2009Study of the in
- Page 117 and 118: MAGNETO-SCIENCE 2009Magnetohydrodyn
- Page 119 and 120: MAGNETO-SCIENCE 2009112
- Page 122 and 123: 2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 124 and 125: 2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 126 and 127: 2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 128 and 129: 2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 130 and 131: 2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 132 and 133: 2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 134 and 135: 2009 MAGNET DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUM
- Page 136 and 137: 2009 PROPOSALSProposals for Magnet
- Page 138 and 139: 2009 PROPOSALSSpin-Jahn-Teller effe
- Page 140 and 141: 2009 PROPOSALSQuantum Oscillations
- Page 142 and 143: 2009 PROPOSALSThermoelectric tensor
- Page 144 and 145: 2009 PROPOSALSDr. EscoffierCyclotro
- Page 146 and 147: 2009 PROPOSALSHigh field magnetotra
- Page 148 and 149:
2009 THESESPhD Theses 20091. Nanot
- Page 150 and 151:
2009 PUBLICATIONS[21] O. Drachenko,
- Page 152 and 153:
2009 PUBLICATIONS[75] S. Nowak, T.
- Page 154 and 155:
Contributors of the LNCMI to the Pr
- Page 156 and 157:
Institut Jean Lamour, Nancy : 68Ins
- Page 158 and 159:
Lawrence Berkeley National Laborato