RESEARCHTable 3. Crude and adjusted odds ratios for enterically transmitted hepatitis E virus, Malawi*Characteristics Crude OR p value Adjusted OR (95% CI)Study, periodICAR, 1989–1995 Reference NA ReferenceSUCOMA, 1994–1999 2.80 0.03 3.54 (0.75–16.76)NVAZ, 2000–2003 1.39 0.51 1.59 (0.55–4.62)MWANZA, 2001 1.59 0.37 1.85 (0.51–6.70)METRO, 2003–2005 3.82 0.004 3.44 (1.37–8.67)PEPI, 2004–2009 1.59 0.35 1.87 (0.64–5.49)Enrollment year† 1.02 0.38 NAHIV statusHIV-negative Reference NA ReferenceHIV-positive 0.59 0.01 0.72 (0.38–1.36)Age, y† 1.01 0.56 1.00 (0.97–1.02)Age range, y15–19 Reference NA NA20–29 0.81 0.51 NA30–39 0.71 0.33 NA40–49 0.55 0.22 NA50–59 2.07 0.21 NA60–69 4.13 0.17 NASexM Reference NA 1.00F 0.83 0.36 1.40 (0.41–4.76)SettingRural Reference NA NAUrban 0.85 0.41 NARunning water in houseNo Reference NA 1.00Yes 0.61 0.06 1.40 (0.41–4.76)Electricity in houseNo Reference NA NAYes 0.82 0.40 NAEducationNone Reference NA NAAny 0.92 0.78 NAMarital statusMarried Reference NA NASingle 0.60 0.14 NAEmployment statusUnemployed Reference NA NAEmployed 1.18 0.41 NAParity† 0.90 0.61 NA*OR, odds ratio; ICAR, International Collaborations on AIDS Research; SUCOMA, a study of HIV prevalence among male workers for the SugarCompany of Malawi; NVAZ, a study of efficacy of nevirapine/zidovudinel post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV;MWANZA, a study of risk factors associated with prevalent HIV infection in the rural town of Malawi; METRO, a study in which efficacy of intravaginalmetronidazole gel in reducing bacterial vaginosis was assessed; PEPI, a study of antiretroviral postexposure prophylaxis to prevent mother-to-childtransmission of HIV; NA: not applicable.†Continuous variable.participants, and urban residents were less likely to testpositive than rural residents (OR 0.52 and 0.51, p = 0.02and 0.02, respectively). Although not statistically significant(p = 0.06), the ORs for participation in the SUCOMAstudy and having electricity in the house (an indicator ofhigher socioeconomic status) were 4.06 (95% CI 0.92–17.93) and 0.46 (95% CI 0.20–1.03), respectively. In themultivariate logistic regression analyses for the associationof HBsAg and HCV with various covariates (studyenrollment, HIV status, age, sex, whether there were multiplelifetime sexual partners, history of sexually transmitteddiseases, and history of condom use), only enrollmentin the NVAZ study (2000–2003) remained significantlyassociated with lower likelihood to test positive for HBsAg(adjusted OR 0.24, p = 0.006). No other variables werefound to be associated with HBV or HCV seroprevalence.DiscussionThis study provides preliminary estimates of HEV seroprevalencein Malawi, which has a population of ≈12 million, ismostly rural, and has a limited safe water supply and constrainedhealth care services (29). Overall, 16.5% (95% CI13.9%–19.1%) of the samples were positive for HEV IgG.In addition to examining seroprevalence of HEV in Malawi,this study has several other notable features: 1) samplesfrom 6 epidemiologic studies conducted by the same researchteam among adult men and women in urban and rural Malawiduring 1989–2008 were included, representing diverse1178 Emerging Infectious Diseases • www.cdc.gov/eid • Vol. 21, No. 7, July 2015
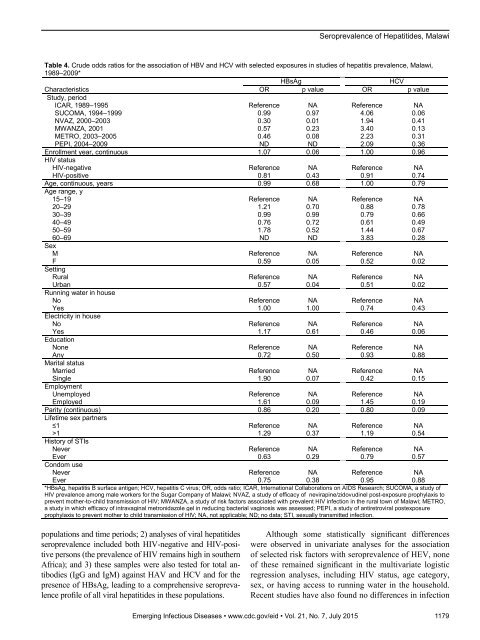
Seroprevalence of Hepatitides, MalawiTable 4. Crude odds ratios for the association of HBV and HCV with selected exposures in studies of hepatitis prevalence, Malawi,1989–2009*HBsAgHCVCharacteristicsOR p value OR p valueStudy, periodICAR, 1989–1995 Reference NA Reference NASUCOMA, 1994–1999 0.99 0.97 4.06 0.06NVAZ, 2000–2003 0.30 0.01 1.94 0.41MWANZA, 2001 0.57 0.23 3.40 0.13METRO, 2003–2005 0.46 0.08 2.23 0.31PEPI, 2004–2009 ND ND 2.09 0.36Enrollment year, continuous 1.07 0.06 1.00 0.96HIV statusHIV-negative Reference NA Reference NAHIV-positive 0.81 0.43 0.91 0.74Age, continuous, years 0.99 0.68 1.00 0.79Age range, y15–19 Reference NA Reference NA20–29 1.21 0.70 0.88 0.7830–39 0.99 0.99 0.79 0.6640–49 0.76 0.72 0.61 0.4950–59 1.78 0.52 1.44 0.6760–69 ND ND 3.83 0.28SexM Reference NA Reference NAF 0.59 0.05 0.52 0.02SettingRural Reference NA Reference NAUrban 0.57 0.04 0.51 0.02Running water in houseNo Reference NA Reference NAYes 1.00 1.00 0.74 0.43Electricity in houseNo Reference NA Reference NAYes 1.17 0.61 0.46 0.06EducationNone Reference NA Reference NAAny 0.72 0.50 0.93 0.88Marital statusMarried Reference NA Reference NASingle 1.90 0.07 0.42 0.15EmploymentUnemployed Reference NA Reference NAEmployed 1.61 0.09 1.45 0.19Parity (continuous) 0.86 0.20 0.80 0.09Lifetime sex partners≤1 Reference NA Reference NA>1 1.29 0.37 1.19 0.54History of STIsNever Reference NA Reference NAEver 0.63 0.29 0.79 0.57Condom useNever Reference NA Reference NAEver 0.75 0.38 0.95 0.88*HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen; HCV, hepatitis C virus; OR, odds ratio; ICAR, International Collaborations on AIDS Research; SUCOMA, a study ofHIV prevalence among male workers for the Sugar Company of Malawi; NVAZ, a study of efficacy of nevirapine/zidovudinel post-exposure prophylaxis toprevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV; MWANZA, a study of risk factors associated with prevalent HIV infection in the rural town of Malawi; METRO,a study in which efficacy of intravaginal metronidazole gel in reducing bacterial vaginosis was assessed; PEPI, a study of antiretroviral postexposureprophylaxis to prevent mother to child transmission of HIV; NA, not applicable; ND; no data; STI, sexually transmitted infection.populations and time periods; 2) analyses of viral hepatitidesseroprevalence included both HIV-negative and HIV-positivepersons (the prevalence of HIV remains high in southernAfrica); and 3) these samples were also tested for total antibodies(IgG and IgM) against HAV and HCV and for thepresence of HBsAg, leading to a comprehensive seroprevalenceprofile of all viral hepatitides in these populations.Although some statistically significant differenceswere observed in univariate analyses for the associationof selected risk factors with seroprevalence of HEV, noneof these remained significant in the multivariate logisticregression analyses, including HIV status, age category,sex, or having access to running water in the household.Recent studies have also found no differences in infectionEmerging Infectious Diseases • www.cdc.gov/eid • Vol. 21, No. 7, July 2015 1179
- Page 3 and 4:
July 2015SynopsisOn the CoverMarian
- Page 5 and 6:
1240 Gastroenteritis OutbreaksCause
- Page 7 and 8:
SYNOPSISDisseminated Infections wit
- Page 9 and 10:
Disseminated Infections with Talaro
- Page 11 and 12:
Disseminated Infections with Talaro
- Page 13 and 14:
Macacine Herpesvirus 1 inLong-Taile
- Page 15 and 16:
Macacine Herpesvirus 1 in Macaques,
- Page 17 and 18:
Macacine Herpesvirus 1 in Macaques,
- Page 19:
Macacine Herpesvirus 1 in Macaques,
- Page 23:
Malaria among Young Infants, Africa
- Page 26 and 27:
RESEARCHFigure 3. Dynamics of 19-kD
- Page 28 and 29:
Transdermal Diagnosis of MalariaUsi
- Page 30 and 31:
RESEARCHFigure 2. A) Acoustic trace
- Page 32 and 33:
RESEARCHof malaria-infected mosquit
- Page 34 and 35: Lack of Transmission amongClose Con
- Page 36 and 37: RESEARCH(IFA) and microneutralizati
- Page 38 and 39: RESEARCHoropharyngeal, and serum sa
- Page 40 and 41: RESEARCH6. Assiri A, McGeer A, Perl
- Page 42 and 43: RESEARCHadvanced genomic sequencing
- Page 44 and 45: RESEARCHTable 2. Next-generation se
- Page 46 and 47: RESEARCHTable 3. Mutation analysis
- Page 48 and 49: RESEARCHReferences1. Baize S, Panne
- Page 50 and 51: Parechovirus Genotype 3 Outbreakamo
- Page 52 and 53: RESEARCHFigure 1. Venn diagramshowi
- Page 54 and 55: RESEARCHTable 2. HPeV testing of sp
- Page 56 and 57: RESEARCHFigure 5. Distribution of h
- Page 58 and 59: RESEARCHReferences1. Selvarangan R,
- Page 60 and 61: RESEARCHthe left lobe was sampled b
- Page 62 and 63: RESEARCHTable 2. Middle East respir
- Page 64 and 65: RESEARCHseroprevalence in domestic
- Page 66 and 67: RESEARCHmeasure their current surve
- Page 68 and 69: RESEARCHTable 2. States with labora
- Page 70 and 71: RESEARCHFigure 2. Comparison of sur
- Page 72 and 73: RESEARCH9. Centers for Disease Cont
- Page 74 and 75: RESEARCHthe analyses. Cases in pers
- Page 76 and 77: RESEARCHTable 3. Sampling results (
- Page 78 and 79: RESEARCHpresence of Legionella spp.
- Page 80 and 81: Seroprevalence for Hepatitis Eand O
- Page 82 and 83: RESEARCHTable 1. Description of stu
- Page 86 and 87: RESEARCHrates by gender or HIV stat
- Page 88 and 89: RESEARCH25. Taha TE, Kumwenda N, Ka
- Page 90 and 91: POLICY REVIEWDutch Consensus Guidel
- Page 92 and 93: POLICY REVIEWTable 3. Comparison of
- Page 94 and 95: POLICY REVIEW6. Botelho-Nevers E, F
- Page 96 and 97: DISPATCHESFigure 1. Phylogenetic tr
- Page 98 and 99: DISPATCHESSevere Pediatric Adenovir
- Page 100 and 101: DISPATCHESTable 1. Demographics and
- Page 102 and 103: DISPATCHES13. Kim YJ, Hong JY, Lee
- Page 104 and 105: DISPATCHESTable. Alignment of resid
- Page 106 and 107: DISPATCHESFigure 2. Interaction of
- Page 108 and 109: DISPATCHESSchmallenberg Virus Recur
- Page 110 and 111: DISPATCHESFigure 2. Detection of Sc
- Page 112 and 113: DISPATCHESFigure 1. Histopathologic
- Page 114: DISPATCHESFigure 2. Detection of fo
- Page 117 and 118: Influenza Virus Strains in the Amer
- Page 119 and 120: Novel Arenavirus Isolates from Nama
- Page 121 and 122: Novel Arenaviruses, Southern Africa
- Page 123 and 124: Readability of Ebola Informationon
- Page 125 and 126: Readability of Ebola Information on
- Page 127 and 128: Patients under investigation for ME
- Page 129 and 130: Patients under investigation for ME
- Page 131 and 132: Wildlife Reservoir for Hepatitis E
- Page 133 and 134: Asymptomatic Malaria and Other Infe
- Page 135 and 136:
Asymptomatic Malaria in Children fr
- Page 137 and 138:
Bufavirus in Wild Shrews and Nonhum
- Page 139 and 140:
Bufavirus in Wild Shrews and Nonhum
- Page 141 and 142:
Range Expansion for Rat Lungworm in
- Page 143 and 144:
Slow Clearance of Plasmodium falcip
- Page 145 and 146:
Slow Clearance of Plasmodium falcip
- Page 147 and 148:
Gastroenteritis Caused by Norovirus
- Page 149 and 150:
Ebola Virus Stability on Surfaces a
- Page 151 and 152:
Ebola Virus Stability on Surfaces a
- Page 153 and 154:
Outbreak of Ciprofloxacin-Resistant
- Page 155 and 156:
Outbreak of S. sonnei, South KoreaT
- Page 157 and 158:
Rapidly Expanding Range of Highly P
- Page 159 and 160:
Cluster of Ebola Virus Disease, Bon
- Page 161 and 162:
Cluster of Ebola Virus Disease, Lib
- Page 163 and 164:
ANOTHER DIMENSIONThe Past Is Never
- Page 165 and 166:
Measles Epidemic, Boston, Massachus
- Page 167 and 168:
LETTERSInfluenza A(H5N6)Virus Reass
- Page 169 and 170:
LETTERSsystem (8 kb-span paired-end
- Page 171 and 172:
LETTERS3. Van Hong N, Amambua-Ngwa
- Page 173 and 174:
LETTERSTable. Prevalence of Bartone
- Page 175 and 176:
LETTERSavian influenza A(H5N1) viru
- Page 177 and 178:
LETTERSprovinces and a total of 200
- Page 179 and 180:
LETTERS7. Manian FA. Bloodstream in
- Page 181 and 182:
LETTERSforward projections. N Engl
- Page 183 and 184:
LETTERS3. Guindon S, Gascuel OA. Si
- Page 185 and 186:
BOOKS AND MEDIAin the port cities o
- Page 187 and 188:
ABOUT THE COVERNorth was not intere
- Page 189 and 190:
Earning CME CreditTo obtain credit,
- Page 191:
Emerging Infectious Diseases is a p