Detection and Expression of Biosynthetic Genes in Actinobacteria ...
Detection and Expression of Biosynthetic Genes in Actinobacteria ...
Detection and Expression of Biosynthetic Genes in Actinobacteria ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
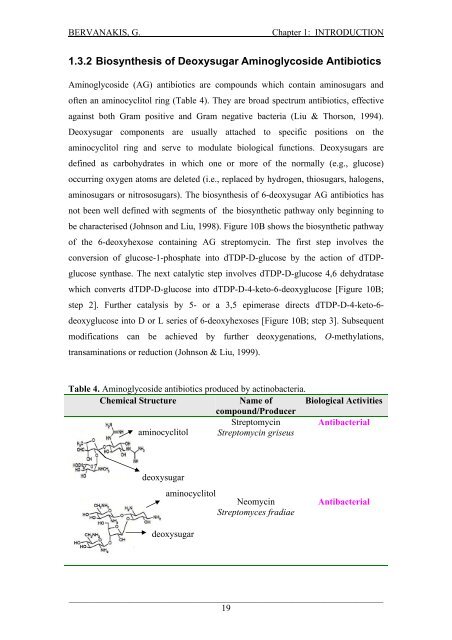
BERVANAKIS, G.Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION1.3.2 Biosynthesis <strong>of</strong> Deoxysugar Am<strong>in</strong>oglycoside AntibioticsAm<strong>in</strong>oglycoside (AG) antibiotics are compounds which conta<strong>in</strong> am<strong>in</strong>osugars <strong>and</strong><strong>of</strong>ten an am<strong>in</strong>ocyclitol r<strong>in</strong>g (Table 4). They are broad spectrum antibiotics, effectiveaga<strong>in</strong>st both Gram positive <strong>and</strong> Gram negative bacteria (Liu & Thorson, 1994).Deoxysugar components are usually attached to specific positions on theam<strong>in</strong>ocyclitol r<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> serve to modulate biological functions. Deoxysugars aredef<strong>in</strong>ed as carbohydrates <strong>in</strong> which one or more <strong>of</strong> the normally (e.g., glucose)occurr<strong>in</strong>g oxygen atoms are deleted (i.e., replaced by hydrogen, thiosugars, halogens,am<strong>in</strong>osugars or nitrososugars). The biosynthesis <strong>of</strong> 6-deoxysugar AG antibiotics hasnot been well def<strong>in</strong>ed with segments <strong>of</strong> the biosynthetic pathway only beg<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g tobe characterised (Johnson <strong>and</strong> Liu, 1998). Figure 10B shows the biosynthetic pathway<strong>of</strong> the 6-deoxyhexose conta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g AG streptomyc<strong>in</strong>. The first step <strong>in</strong>volves theconversion <strong>of</strong> glucose-1-phosphate <strong>in</strong>to dTDP-D-glucose by the action <strong>of</strong> dTDPglucosesynthase. The next catalytic step <strong>in</strong>volves dTDP-D-glucose 4,6 dehydratasewhich converts dTDP-D-glucose <strong>in</strong>to dTDP-D-4-keto-6-deoxyglucose [Figure 10B;step 2]. Further catalysis by 5- or a 3,5 epimerase directs dTDP-D-4-keto-6-deoxyglucose <strong>in</strong>to D or L series <strong>of</strong> 6-deoxyhexoses [Figure 10B; step 3]. Subsequentmodifications can be achieved by further deoxygenations, O-methylations,transam<strong>in</strong>ations or reduction (Johnson & Liu, 1999).Table 4. Am<strong>in</strong>oglycoside antibiotics produced by act<strong>in</strong>obacteria.Chemical StructureName <strong>of</strong> Biological Activitiescompound/Produceram<strong>in</strong>ocyclitolStreptomyc<strong>in</strong>Streptomyc<strong>in</strong> griseusAntibacterialdeoxysugaram<strong>in</strong>ocyclitolNeomyc<strong>in</strong>Streptomyces fradiaeAntibacterialdeoxysugar_____________________________________________________________________19