Electronic Material Properties - und Geowissenschaften ...
Electronic Material Properties - und Geowissenschaften ...
Electronic Material Properties - und Geowissenschaften ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Synthesis of oxide-polymer nanocomposites via plasma<br />
polymerization<br />
Jens Suffner (1) , Gallus Schechner (2) , Hermann Sieger (1) , Horst Hahn (1),(3)<br />
(1) Joint Research Laboratory Nanomaterials<br />
(2) SusTech GmbH<br />
(3) Institute for Nanotechnology (FZ Karlsruhe)<br />
In the last years, nanoscale materials have gained tremendous interest in science<br />
due to their unique properties, like superparamagnetism, superplasticity, and<br />
quantum confinement.<br />
Nanoscale powders are characterized by a large surface-to-volume ratio leading to<br />
specific surface areas in the range of several h<strong>und</strong>reds of square meters per gram.<br />
Therefore it is obvious, that the particle-matrix interface has a large impact on the<br />
properties of the particles. In this work [1] , the oxide nanoparticles silica and zirconia<br />
have been produced by thermal decomposition in a hot wall reactor followed by a<br />
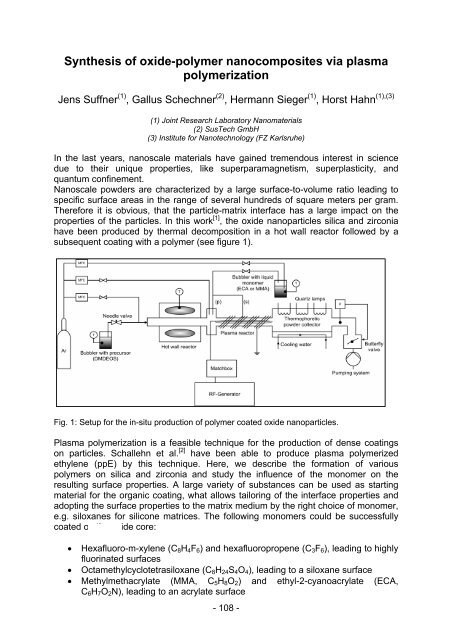
subsequent coating with a polymer (see figure 1).<br />
Fig. 1: Setup for the in-situ production of polymer coated oxide nanoparticles.<br />
Plasma polymerization is a feasible technique for the production of dense coatings<br />
on particles. Schallehn et al. [2] have been able to produce plasma polymerized<br />
ethylene (ppE) by this technique. Here, we describe the formation of various<br />
polymers on silica and zirconia and study the influence of the monomer on the<br />
resulting surface properties. A large variety of substances can be used as starting<br />
material for the organic coating, what allows tailoring of the interface properties and<br />
adopting the surface properties to the matrix medium by the right choice of monomer,<br />
e.g. siloxanes for silicone matrices. The following monomers could be successfully<br />
coated on the oxide core:<br />
• Hexafluoro-m-xylene (C8H4F6) and hexafluoropropene (C3F6), leading to highly<br />
fluorinated surfaces<br />
• Octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane (C8H24S4O4), leading to a siloxane surface<br />
• Methylmethacrylate (MMA, C5H8O2) and ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate (ECA,<br />
C6H7O2N), leading to an acrylate surface<br />
- 108 -