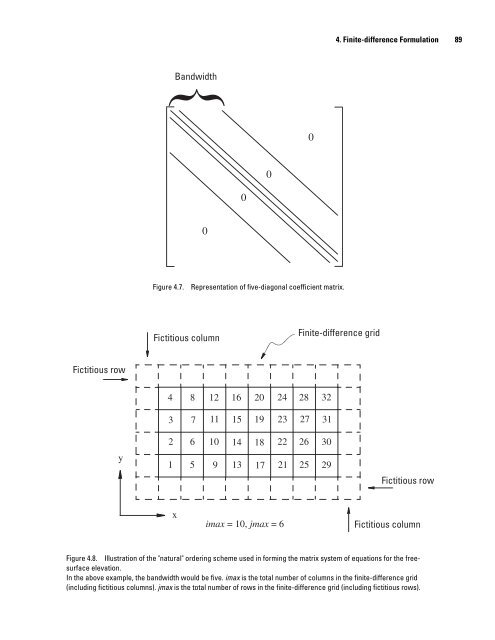
88 A <strong>Semi</strong>-<strong>Implicit</strong>, <strong>Three</strong>-<strong>Dimensional</strong> <strong>Model</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Estuarine</strong> Circulation Because the matrix A is an M-matrix, its matrix inverse A −1 has all non-negative elements (<strong>for</strong> proof see Lancaster and Tismenetsky, 1985). There<strong>for</strong>e, the matrix products ΞA −1 R and ΞA −1 G in equation 4.35 are each a single non-negative number. Rearranging equation 4.35, the following <strong>for</strong>m can be obtained: where n + 1 n + 1 n + 1 – , ζij , – 1 ri, jζi, j sxi – 1⁄ 2, j ζ – i – 1, j syi j – 1⁄ 2 sxi ± 1⁄ 2 , j syi, j± 1⁄ 2 n + 1 + – syi , j + 1⁄ ζ 2 i, j + 1 sx 1 i ⁄ 2 g Δt ⎛----- ⎞ ⎝Δx⎠ 2 n ρ 1 i ± ⁄ 2 , j, 1 ΞA 1 – = R i ± 1⁄ 2 , j g Δt ⎛----- ⎞ ⎝Δx⎠ 2 n = ri, j = 1 sxi 1⁄ 2, j qi, j ρi, j± 1 2 ⁄ , 1 ΞA 1 – R i, j± 1⁄ 2 + + + sxi – 1⁄ 2, j + syi, j + 1⁄ + sy 2 i j – 1⁄ 2 n – 1 Δt ζ i, j – ----- Δx ΞA 1 – G i + 1⁄ 2, j ΞA 1 – = ⎛ – ⎞ ⎜ G i – 1⁄ 2, j⎟ ⎝ ⎠ , , n + 1 – + , j ζi + 1, j = qi, j (4.36) , , Δt – ----- Δy ΞA 1 – G i, j + 1⁄ ΞA 2 1 – n – 1 ⎛ – ⎞ – d G ij , , ⎜ i, j– 1⁄ ⎟ 2 ⎝ ⎠ n – 1 and di, j is as defined <strong>for</strong> equation 4.34. Equation 4.36 can be written at each of the interior nodal points of the rectangular grid (excluding the fictitious row and column along each boundary) to <strong>for</strong>m N = (imax − 2) × (jmax − 2) simultaneous linear equations in the unknowns { ζi, j}. If the set of equations is written in matrix <strong>for</strong>m, the coefficient matrix is five-diagonal with a tridiagonal band along the main diagonal and two additional diagonals displaced an equal amount above and below the main diagonal (fig.4.7); the amount the outer diagonals are displaced is referred to as the matrix bandwidth and is dependent on the dimensions of the grid and the ordering of the unknowns. Here the most common “natural” ordering is used in which the numbering is done along the smallest dimension of the finite-difference grid. For example, if the smallest dimension is the y (north-south) direction, the natural ordering scheme numbers from bottom to top (south to north) on a column starting with the first (westernmost) column that is not fictitious (fig. 4.8). Other orderings such as the “ordering along the diagonals” and the “red-black” ordering also are mathematically consistent (see Young, 1971, p. 159). For problems involving irregularly shaped regions, the <strong>for</strong>m of the coefficient matrix does not change. Dry point equations are represented with a value of 1.0 on the main diagonal and zeros <strong>for</strong> the other elements of the n + 1 n equation row; the continuity equation <strong>for</strong> a dry point there<strong>for</strong>e is reduced to ζi, j = ζi, jwhere the assigned water surface elevation is artificial. Because all the dry point equations can be made identical, only one must be stored. The coefficient matrix <strong>for</strong> the system of water surface elevation equations 4.36 is both symmetric and positive definite, 41 a <strong>for</strong>tuitous circumstance. There<strong>for</strong>e, the equations can be solved efficiently by iteration using the preconditioned conjugate-gradient n + 1 n + 1 method discussed in the next section. Once the ζi, j are determined, equation 4.32 and the corresponding equation <strong>for</strong> Vi, j+ 1⁄ 2 can be solved explicitly <strong>for</strong> the new layer volumetric transports. 41 For a <strong>for</strong>mal discussion of positive definite equation systems, see Golub and Van Loan (1989, p. 139ff). In general terms, if A is symmetric with non- negative diagonal elements and diagonally dominant, A is positive definite.
Fictitious row y Bandwidth { 0 0 Figure 4.7. Representation of five-diagonal coefficient matrix. Fictitious column 4 3 2 1 x 8 7 6 5 12 11 10 9 16 15 14 13 20 19 18 17 0 24 23 22 21 imax = 10, jmax = 6 0 4. Finite-difference Formulation 89 Finite-difference grid 28 27 26 25 32 31 30 29 Fictitious row Fictitious column Figure 4.8. Illustration of the "natural" ordering scheme used in <strong>for</strong>ming the matrix system of equations <strong>for</strong> the free- surface elevation. In the above example, the bandwidth would be five. imax is the total number of columns in the finite-difference grid (including fictitious columns). jmax is the total number of rows in the finite-difference grid (including fictitious rows).
- Page 1:
In cooperation with the Interagency
- Page 4 and 5:
U.S. Department of the Interior Dir
- Page 6 and 7:
This page intentionally left blank.
- Page 8 and 9:
vi 4.2 Semi-Implicit One-Dimensiona
- Page 10 and 11:
viii Figure 5.6. Graph showing solu
- Page 12 and 13:
x Tables Table 2.1. Dimensionless n
- Page 14 and 15:
This page intentionally left blank.
- Page 16 and 17:
2 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensiona
- Page 18 and 19:
4 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensiona
- Page 20 and 21:
6 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensiona
- Page 22 and 23:
8 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensiona
- Page 24 and 25:
10 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 26 and 27:
12 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 28 and 29:
14 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 30 and 31:
16 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 32 and 33:
18 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 34 and 35:
20 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 36 and 37:
22 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 38 and 39:
24 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 40 and 41:
26 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 42 and 43:
28 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 44 and 45:
30 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 46 and 47:
32 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 48 and 49:
2.4.1.2 Dynamic Surface Condition 2
- Page 50 and 51:
36 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 52 and 53: 38 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 54 and 55: 40 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 56 and 57: 42 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 58 and 59: 44 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 60 and 61: 46 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 62 and 63: 48 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 64 and 65: 50 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 66 and 67: 52 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 68 and 69: Water surface Water surface Level p
- Page 70 and 71: h 1 h 2 h 3 h 4 h 5 h 6 z 1 ⁄ 2 z
- Page 72 and 73: 58 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 74 and 75: 60 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 76 and 77: 62 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 78 and 79: 64 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 80 and 81: 66 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 82 and 83: 68 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 84 and 85: 70 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 86 and 87: 72 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 88 and 89: 74 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 90 and 91: 76 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 92 and 93: 78 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 94 and 95: 80 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 96 and 97: 82 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 98 and 99: 84 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 100 and 101: 86 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 104 and 105: 90 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 106 and 107: 92 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 108 and 109: 94 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 110 and 111: 96 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 112 and 113: 98 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimension
- Page 114 and 115: 100 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 116 and 117: 102 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 118 and 119: 104 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 120 and 121: 106 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 122 and 123: 108 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 124 and 125: 110 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 126 and 127: 112 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 128 and 129: 114 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 130 and 131: 116 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 132 and 133: 118 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 134 and 135: 120 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 136 and 137: 122 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 138 and 139: 124 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 140 and 141: 126 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 142 and 143: 128 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 144 and 145: 130 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 146 and 147: 132 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 148 and 149: 134 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 150 and 151: 136 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 152 and 153:
138 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 154 and 155:
140 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 156 and 157:
142 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 158 and 159:
144 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 160 and 161:
146 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 162 and 163:
148 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 164 and 165:
150 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 166 and 167:
152 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 168 and 169:
154 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 170 and 171:
156 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 172 and 173:
158 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 174 and 175:
160 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 176 and 177:
162 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 178 and 179:
164 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 180 and 181:
166 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 182 and 183:
168 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 184 and 185:
170 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 186 and 187:
172 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 188 and 189:
174 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio
- Page 190:
176 A Semi-Implicit, Three-Dimensio