a la physique de l'information - Lisa - Université d'Angers
a la physique de l'information - Lisa - Université d'Angers
a la physique de l'information - Lisa - Université d'Angers
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
10<br />
log2[ number of boxes N(a) ]<br />
8<br />
7<br />
6<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
Cameraman<br />
−1<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8<br />
log2( box size a )<br />
log2[ number of boxes N(a) ]<br />
8<br />
7<br />
6<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
Einstein<br />
−1<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8<br />
log2( box size a )<br />
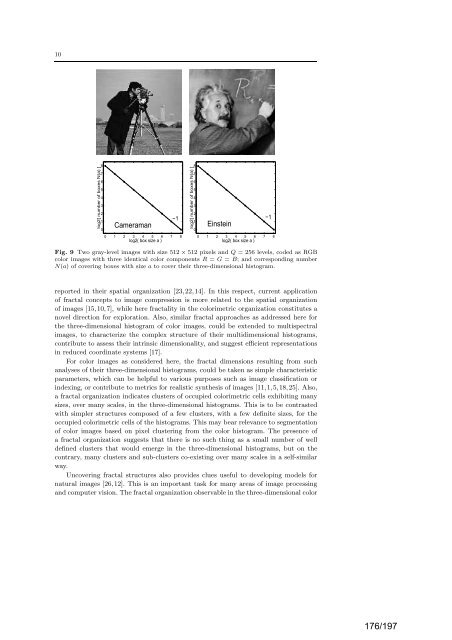
Fig. 9 Two gray-level images with size 512 × 512 pixels and Q = 256 levels, co<strong>de</strong>d as RGB<br />
color images with three i<strong>de</strong>ntical color components R = G = B; and corresponding number<br />
N(a) of covering boxes with size a to cover their three-dimensional histogram.<br />
reported in their spatial organization [23,22,14]. In this respect, current application<br />
of fractal concepts to image compression is more re<strong>la</strong>ted to the spatial organization<br />
of images [15,10,7], while here fractality in the colorimetric organization constitutes a<br />
novel direction for exploration. Also, simi<strong>la</strong>r fractal approaches as addressed here for<br />
the three-dimensional histogram of color images, could be exten<strong>de</strong>d to multispectral<br />
images, to characterize the complex structure of their multidimensional histograms,<br />
contribute to assess their intrinsic dimensionality, and suggest efficient representations<br />
in reduced coordinate systems [17].<br />
For color images as consi<strong>de</strong>red here, the fractal dimensions resulting from such<br />
analyses of their three-dimensional histograms, could be taken as simple characteristic<br />
parameters, which can be helpful to various purposes such as image c<strong>la</strong>ssification or<br />
in<strong>de</strong>xing, or contribute to metrics for realistic synthesis of images [11,1,5,18,25]. Also,<br />
a fractal organization indicates clusters of occupied colorimetric cells exhibiting many<br />
sizes, over many scales, in the three-dimensional histograms. This is to be contrasted<br />
with simpler structures composed of a few clusters, with a few <strong>de</strong>finite sizes, for the<br />
occupied colorimetric cells of the histograms. This may bear relevance to segmentation<br />
of color images based on pixel clustering from the color histogram. The presence of<br />
a fractal organization suggests that there is no such thing as a small number of well<br />
<strong>de</strong>fined clusters that would emerge in the three-dimensional histograms, but on the<br />
contrary, many clusters and sub-clusters co-existing over many scales in a self-simi<strong>la</strong>r<br />
way.<br />
Uncovering fractal structures also provi<strong>de</strong>s clues useful to <strong>de</strong>veloping mo<strong>de</strong>ls for<br />
natural images [26,12]. This is an important task for many areas of image processing<br />
and computer vision. The fractal organization observable in the three-dimensional color<br />
176/197