software to fit optical spectra - Quantum Materials Group
software to fit optical spectra - Quantum Materials Group
software to fit optical spectra - Quantum Materials Group
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
ε<br />
Equation 2-22<br />
N<br />
i,<br />
∧<br />
var ( ω)<br />
= ∑ Aiε<br />
( ω)<br />
i=<br />
1<br />
and consider coefficients A i as free parameters. To ensure that ε 2 ( ω)<br />
≥ 0 , we require that all<br />
A ≥ 0 . It is convenient <strong>to</strong> set them <strong>to</strong> zero at the boundaries: A A = 0 , ensuring that<br />
i<br />
ε 2 ( ω)<br />
vanishes at 1<br />
ω and N<br />
ω 8 .<br />
1 = N<br />
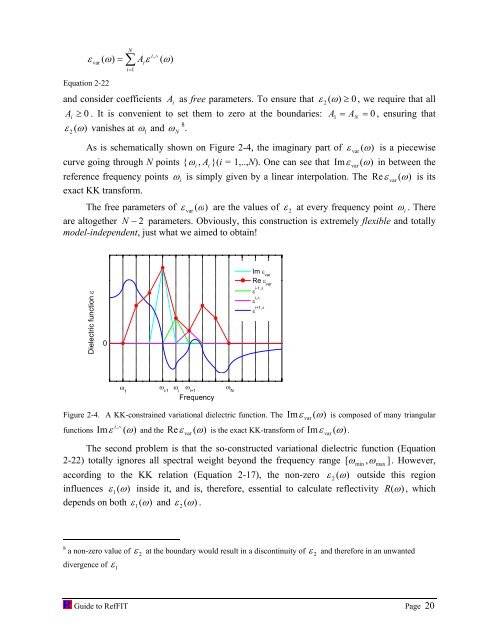
As is schematically shown on Figure 2-4, the imaginary part of ε var ( ω)<br />
is a piecewise<br />
curve going through N points { ω i , Ai<br />
}(i = 1,..,N). One can see that Imε var ( ω)<br />
in between the<br />
reference frequency points ω i is simply given by a linear interpolation. The Reε var ( ω)<br />
is its<br />
exact KK transform.<br />
The free parameters of ε var ( ω)<br />
are the values of ε 2 at every frequency point ω i . There<br />
are al<strong>to</strong>gether N − 2 parameters. Obviously, this construction is extremely flexible and <strong>to</strong>tally<br />
model-independent, just what we aimed <strong>to</strong> obtain!<br />
Dielectric function ε<br />
0<br />
ω 1<br />
ω i-1<br />
ω i<br />
ω i+1<br />
Frequency<br />
ω N<br />
Im ε var<br />
Re ε var<br />
ε i-1,Λ<br />
Figure 2-4. A KK-constrained variational dielectric function. The Imε var ( ω)<br />
is composed of many triangular<br />
functions Im ( )<br />
, ε ω<br />
∧ i<br />
and the Reε var ( ω)<br />
is the exact KK-transform of Imε var ( ω)<br />
.<br />
The second problem is that the so-constructed variational dielectric function (Equation<br />
2-22) <strong>to</strong>tally ignores all <strong>spectra</strong>l weight beyond the frequency range [ ω min , ωmax<br />
] . However,<br />
according <strong>to</strong> the KK relation (Equation 2-17), the non-zero ε 2 ( ω)<br />
outside this region<br />
influences ε 1( ω)<br />
inside it, and is, therefore, essential <strong>to</strong> calculate reflectivity R (ω)<br />
, which<br />
depends on both ε ( ) and ε ( ) .<br />
1 ω<br />
2 ω<br />
8<br />
a non-zero value of ε 2 at the boundary would result in a discontinuity of ε 2 and therefore in an unwanted<br />
divergence of ε<br />
1<br />
ε i,Λ<br />
ε i+1,Λ<br />
Guide <strong>to</strong> RefFIT Page 20