Teaching Algebra with Manipulatives
Teaching Algebra with Manipulatives
Teaching Algebra with Manipulatives
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter<br />
6<br />
Quadratic Functions and Inequalities<br />
<strong>Teaching</strong> Notes and Overview<br />
Mini-Project<br />
Parabolas<br />
(p. 243 of this booklet)<br />
Use With Lesson 6-1.<br />
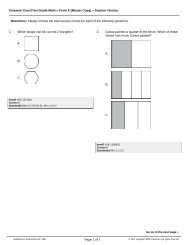
Objective Write equations for parabolas.<br />
Materials<br />
clear acetate sheet for each group<br />
Have students work in small groups to complete<br />
this Mini-Project. Give each group a clear<br />
acetate sheet. This sheet will be used to trace<br />
the parabola on the worksheet. Using 1 4 -inch<br />
grid paper, place the acetate on a coordinate<br />
plane <strong>with</strong> the vertex at the given point. Then<br />
have students align the axis <strong>with</strong> a vertical line<br />
of the grid paper. Next, they list five points that<br />
the graph contains, and write the equation for<br />
the graph. This activity shows students that<br />
parabolas <strong>with</strong> the same shape will have<br />
different equations depending on the vertex.<br />
Allow students to share and discuss their<br />
answers for Exercises 3 and 4.<br />
Some students may become interested in<br />
investigating parabolas that face downward.<br />
These students may use the same parabola that<br />
they traced on acetate paper. Encourage them<br />
to write about their findings and share their<br />
work <strong>with</strong> the other students by making a<br />
presentation.<br />
Answers<br />
1. See students’ trace of graph.<br />
2a. (2, 9), (1, 4), (0, 1), (2, 1), (3, 4), (4, 9);<br />
(x 1) 2<br />
2b. (1, 9), (0, 4), (1, 1), (3, 1), (4, 4), (5, 9);<br />
(x 2) 2<br />
2c. (0, 9), (1, 4), (2, 1), (4, 1), (5, 4), (6, 9); (x 3) 2<br />
2d. (4, 9), (3, 4), (2, 1), (0, 1), (1, 4), (2, 9);<br />
(x 1) 2<br />
2e. (3, 11), (2, 6), (1, 3), (1, 3), (2, 6), (3, 11);<br />
x 2 2<br />
2f. (3, 5), (2, 0), (1, 3), (1, 3), (2, 0),<br />
(3, 5); x 2 4<br />
2g. (0, 10), (1, 5), (2, 2), (4, 2), (5, 5), (6, 10);<br />
(x 3) 2 1<br />
2h. (2, 7), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (3, 2), (4, 7);<br />
(x 1) 2 2<br />
3. y (x h) 2 k<br />
4. y (x 2) 2 3<br />
<strong>Algebra</strong> Activity<br />
Recording Sheet<br />
Completing the Square<br />
(p. 244 of this booklet)<br />
Use With the activity on page 308 in Lesson<br />
6-4 of the Student Edition.<br />
Objective Solve quadratic equations by<br />
completing the square.<br />
Materials<br />
algebra tiles*<br />
equation mats*<br />
* available in Overhead Manipulative Resources<br />
You may need to review how to represent a<br />
quadratic equation <strong>with</strong> tiles on the equation<br />
mat. Have students follow along as you go over<br />
using the mat to complete the square for a<br />
quadratic equation. Ask students to work in<br />
pairs to complete the square for Exercises 1<br />
through 4.<br />
Answers<br />
See Teacher Wraparound Edition p. 308.<br />
<strong>Algebra</strong> Activity<br />
Completing the Square<br />
(pp. 245–246 of this booklet)<br />
Use With Lesson 6-4.<br />
Objective Solve quadratic equations by<br />
completing the square.<br />
Materials<br />
algebra tiles*<br />
classroom set of <strong>Algebra</strong> Activity worksheets<br />
transparency master of <strong>Algebra</strong> Activity<br />
grid paper*<br />
* available in Overhead Manipulative Resources<br />
© Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 241 <strong>Teaching</strong> <strong>Algebra</strong> <strong>with</strong> <strong>Manipulatives</strong><br />
<strong>Algebra</strong> 2—Chapter x 6