Gazprom-AR2014
Gazprom-AR2014
Gazprom-AR2014
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
48<br />
Trends and Developments on Oil and Gas Markets<br />
In the challenging environment, <strong>Gazprom</strong> kept its financial stability and ability to run largescale<br />
projects.<br />
Falling oil prices<br />
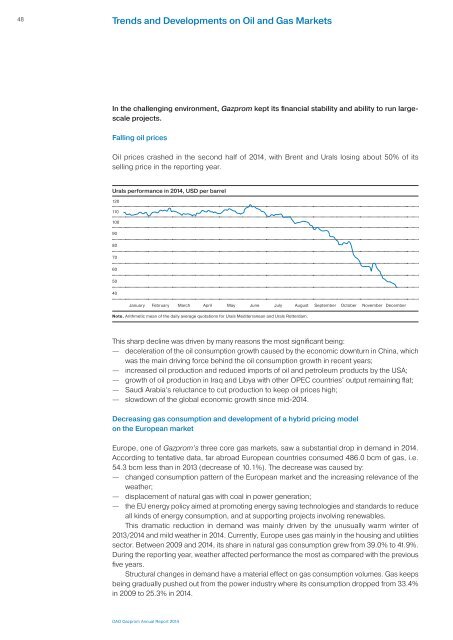
Oil prices crashed in the second half of 2014, with Brent and Urals losing about 50% of its<br />
selling price in the reporting year.<br />
Urals performance in 2014, USD per barrel<br />
120<br />
110<br />
100<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
January February March April May June July August September October November December<br />
Note. Arithmetic mean of the daily average quotations for Urals Mediterranean and Urals Rotterdam.<br />
This sharp decline was driven by many reasons the most significant being:<br />
— deceleration of the oil consumption growth caused by the economic downturn in China, which<br />
was the main driving force behind the oil consumption growth in recent years;<br />
— increased oil production and reduced imports of oil and petroleum products by the USA;<br />
— growth of oil production in Iraq and Libya with other OPEC countries’ output remaining flat;<br />
— Saudi Arabia’s reluctance to cut production to keep oil prices high;<br />
— slowdown of the global economic growth since mid-2014.<br />
Decreasing gas consumption and development of a hybrid pricing model<br />
on the European market<br />
Europe, one of <strong>Gazprom</strong>’s three core gas markets, saw a substantial drop in demand in 2014.<br />
According to tentative data, far abroad European countries consumed 486.0 bcm of gas, i.e.<br />
54.3 bcm less than in 2013 (decrease of 10.1%). The decrease was caused by:<br />
— changed consumption pattern of the European market and the increasing relevance of the<br />
weather;<br />
— displacement of natural gas with coal in power generation;<br />
— the EU energy policy aimed at promoting energy saving technologies and standards to reduce<br />
all kinds of energy consumption, and at supporting projects involving renewables.<br />
This dramatic reduction in demand was mainly driven by the unusually warm winter of<br />
2013/2014 and mild weather in 2014. Currently, Europe uses gas mainly in the housing and utilities<br />
sector. Between 2009 and 2014, its share in natural gas consumption grew from 39.0% to 41.9%.<br />
During the reporting year, weather affected performance the most as compared with the previous<br />
five years.<br />
Structural changes in demand have a material effect on gas consumption volumes. Gas keeps<br />
being gradually pushed out from the power industry where its consumption dropped from 33.4%<br />
in 2009 to 25.3% in 2014.<br />
OAO <strong>Gazprom</strong> Annual Report 2014