Annual Meeting - SCEC.org
Annual Meeting - SCEC.org
Annual Meeting - SCEC.org
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Report | <strong>SCEC</strong> Research Accomplishments<br />
surface wave arrivals. They find an apparent migration of<br />
triggered LFEs along strike at 80 km/hr. The observation of<br />
triggered tremor on northern and southern California faults is<br />
less frequent and these tremor episodes have lower<br />
amplitudes (Figure 4).<br />
Cochran et al. are developing a neural network approach to<br />
detect tremor within continuous data. The approach uses Self<br />
Organizing Maps (SOMs) based on the work of Köhler et al<br />
[2009] to classify the time-series data into prototype vectors<br />
based on waveform characteristics including frequency<br />
content, amplitude, and polarization. These prototype vectors<br />
can then be associated with different signal types including<br />
earthquakes, tremor, and noise. The method is being applied<br />
to data collected during a temporary deployment of<br />
broadband instruments near Cholame, California.<br />
Fault Structure and Damage Zones<br />
Li et al. completed a detailed study of the on- and near-fault<br />
damage and healing at the San Andreas fault (SAF) Parkfield<br />
and the Longmen-Shan Fault (LSF) in Sichuan, both of which<br />
ruptured in the recent major earthquakes. Along the SAF,<br />
they find a waveguide that is interpreted to be a damage zone<br />
of reduced seismic velocities with a width of 100-200 m that<br />
extend to at least 7 km depth (Figure 5). The Wenchuan fault<br />
is found to have a 200-400 m wide damage zone with<br />
velocities reduced by up to 50% at shallow depths.<br />
Ma modeled the effect of heterogeneity of fault geometry on<br />
rupture dynamics in three dimensions with off-fault<br />
plasticity (Figure 6). He finds that fault roughness results in<br />
irregular rupture fronts that could result in greater highfrequency<br />
radiation. In addition, he finds that fault roughness<br />
results in more pulse-like ruptures due to rapid healing.<br />
Duan models the effect of off-fault damage and pore-pressure<br />
variations on the dynamics of parallel strike-slip faults. He<br />
finds that when effects of off-fault plastic yielding and timedependent<br />
pore pressure changes are combined, the effect of<br />
time-dependent pore-pressure dominates, while off-fault<br />
plastic yielding only exerts a second-order effect.<br />
References<br />
Aiken, C., Z. Peng, and C. Wu (2011), Dynamic triggering of<br />
microearthquakes at three geothermal regions in<br />
California, Seismological Society of America <strong>Annual</strong><br />
<strong>Meeting</strong>, Memphis, TN.<br />
Aguiar, A. C., J. R. Brown, and G. C. Beroza (2009), Nonvolcanic<br />
tremor near the Calaveras Fault Triggered by<br />
Mw~8 Teleseisms, Eos Trans. AGU, 90(54), Fall Meet.<br />
Suppl., Abstract T23E-06.<br />
Chao, K., Z. Peng, A. Fabian, and L. Ojha (2011),<br />
Comparisons of Triggered Tremor in California, Seis. Res.<br />
42 | Southern California Earthquake Center<br />
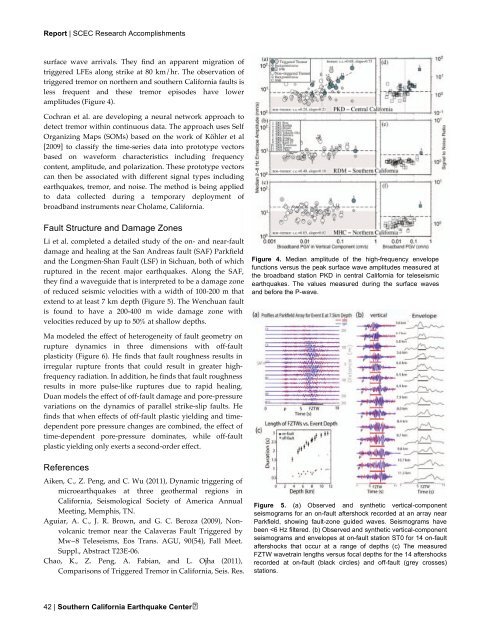
Figure 4. Median amplitude of the high-frequency envelope<br />
functions versus the peak surface wave amplitudes measured at<br />
the broadband station PKD in central California for teleseismic<br />
earthquakes. The values measured during the surface waves<br />
and before the P-wave.<br />
Figure 5. (a) Observed and synthetic vertical-component<br />
seismograms for an on-fault aftershock recorded at an array near<br />
Parkfield, showing fault-zone guided waves. Seismograms have<br />
been