MAINTAINABILITY DESIGN TECHNIQUES METRIC - AcqNotes.com
MAINTAINABILITY DESIGN TECHNIQUES METRIC - AcqNotes.com
MAINTAINABILITY DESIGN TECHNIQUES METRIC - AcqNotes.com
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
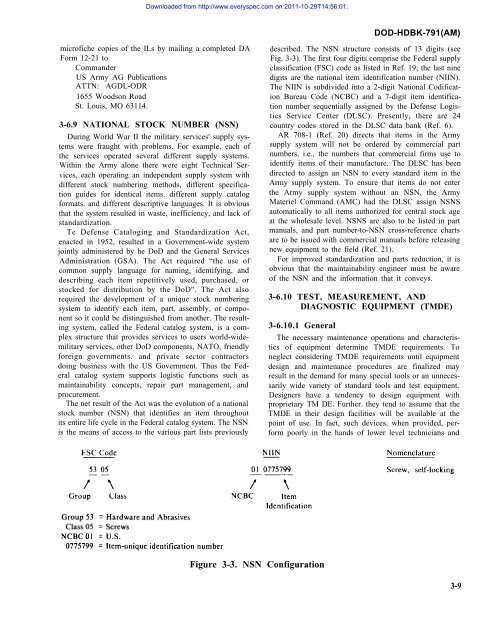
Downloaded from http://www.everyspec.<strong>com</strong> on 2011-10-29T14:56:01.DOD-HDBK-791(AM)microfiche copies of the ILs by mailing a <strong>com</strong>pleted DAForm 12-21 toCommanderUS Army AG PublicationsATTN: AGDL-ODR1655 Woodson RoadSt. Louis, MO 63114.3-6.9 NATIONAL STOCK NUMBER (NSN)During World War II the military services' supply systemswere fraught with problems. For example, each ofthe services operated several different supply systems.Within the Army alone there were eight Technical Services,each operating an independent supply system withdifferent stock numbering methods, different specificationguides for identical items. different supply catalogformats. and different descriptive languages. It is obviousthat the system resulted in waste, inefficiency, and lack ofstandardization.Te Defense Cataloging and Standardization Act,enacted in 1952, resulted in a Government-wide systemjointly administered by he DoD and the General ServicesAdministration (GSA). The Act required “the use of<strong>com</strong>mon supply language for naming, identifying, anddescribing each item repetitively used, purchased, orstocked for distribution by the DoD". The Act alsorequired the development of a unique stock numberingsystem to identify each item, part, assembly, or <strong>com</strong>ponentso it could be distinguished from another. The resultingsystem, called the Federal catalog system, is a <strong>com</strong>plexstructure that provides services to users world-widemilitaryservices, other DoD <strong>com</strong>ponents, NATO, friendlyforeign governments. and private sector contractorsdoing business with the US Government. Thus the Federalcatalog system supports logistic functions such asmaintainability concepts, repair part management, andprocurement.The net result of the Act was the evolution of a nationalstock number (NSN) that identifies an item throughoutits entire life cycle in the Federal catalog system. The NSNis the means of access to the various part lists previouslydescribed. The NSN structure consists of 13 digits (seeFig. 3-3). The first four digits <strong>com</strong>prise the Federal supplyclassification (FSC) code as listed in Ref. 19; the last ninedigits are the national item identification number (NIIN).The NIIN is subdivided into a 2-digit National CodificationBureau Code (NCBC) and a 7-digit item identificationnumber sequentially assigned by the Defense LogisticsService Center (DLSC). Presently, there are 24country codes stored in the DLSC data bank (Ref. 6).AR 708-1 (Ref. 20) directs that items in the Armysupply system will not be ordered by <strong>com</strong>mercial partnumbers, i.e., the numbers that <strong>com</strong>mercial firms use toidentify items of their manufacture. The DLSC has beendirected to assign an NSN to every standard item in theArmy supply system. To ensure that items do not enterthe Army supply system without an NSN, the ArmyMateriel Command (AMC) had the DLSC assign NSNSautomatically to all items authorized for central stock ageat the wholesale level. NSNS are also to be listed in partmanuals, and part number-to-NSN cross-reference chartsare to be issued with <strong>com</strong>mercial manuals before releasingnew equipment to the field (Ref. 21).For improved standardization and parts reduction, it isobvious that the maintainability engineer must be awareof the NSN and the information that it conveys.3-6.10 TEST, MEASUREMENT, ANDDIAGNOSTIC EQUIPMENT (TMDE)3-6.10.1 GeneralThe necessary maintenance operations and characteristicsof equipment determine TMDE requirements. Toneglect considering TMDE requirements until equipmentdesign and maintenance procedures are finalized mayresult in the demand for many special tools or an unnecessarilywide variety of standard tools and test equipment.Designers have a tendency to design equipment withproprietary TM DE. Further. they tend to assume that theTMDE in their design facilities will be available at thepoint of use. In fact, such devices, when provided, performpoorly in the hands of lower level technicians andFigure 3-3. NSN Configuration3-9